Sheet piles provide efficient temporary or permanent earth retention by interlocking steel sections, ideal for rapid installation in soft soils and waterlogged areas. Secant piles consist of overlapping reinforced concrete columns that form a continuous wall, offering superior groundwater cutoff and deeper excavation support. Choosing between sheet piles and secant piles depends on project depth, soil conditions, and structural requirements.
Table of Comparison
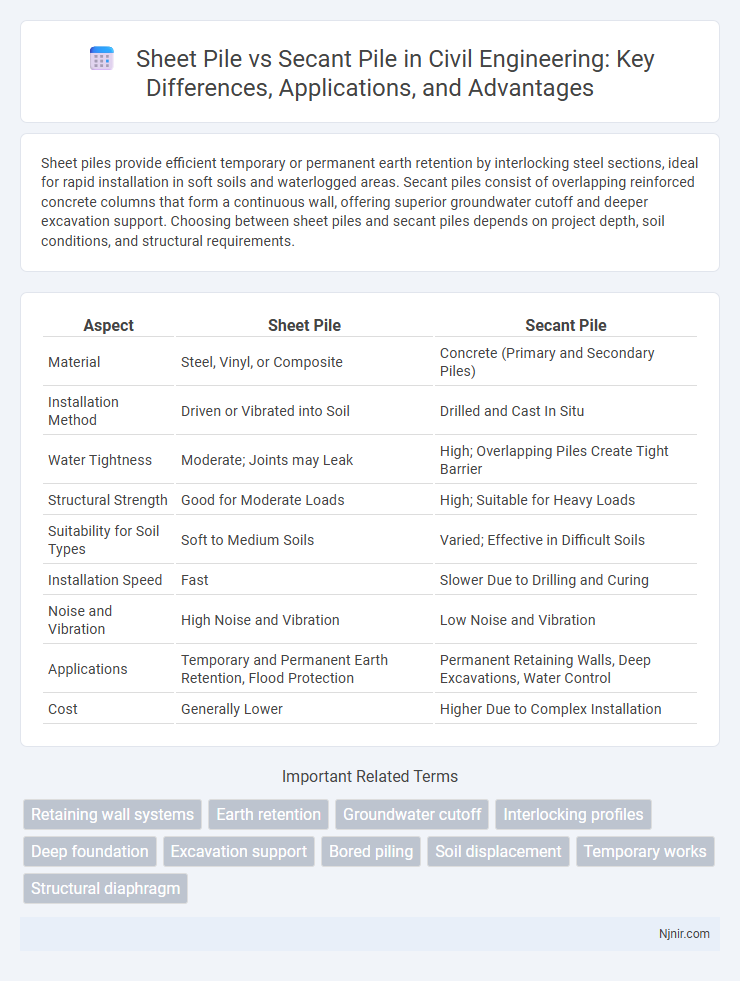
| Aspect | Sheet Pile | Secant Pile |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel, Vinyl, or Composite | Concrete (Primary and Secondary Piles) |
| Installation Method | Driven or Vibrated into Soil | Drilled and Cast In Situ |
| Water Tightness | Moderate; Joints may Leak | High; Overlapping Piles Create Tight Barrier |
| Structural Strength | Good for Moderate Loads | High; Suitable for Heavy Loads |
| Suitability for Soil Types | Soft to Medium Soils | Varied; Effective in Difficult Soils |
| Installation Speed | Fast | Slower Due to Drilling and Curing |
| Noise and Vibration | High Noise and Vibration | Low Noise and Vibration |
| Applications | Temporary and Permanent Earth Retention, Flood Protection | Permanent Retaining Walls, Deep Excavations, Water Control |
| Cost | Generally Lower | Higher Due to Complex Installation |
Introduction to Sheet Pile and Secant Pile Walls
Sheet pile walls consist of interlocking steel sheets driven into the ground to provide earth retention and excavation support primarily in soft soils and waterfront structures. Secant pile walls are constructed by drilling overlapping reinforced concrete piles, creating a continuous, rigid barrier ideal for watertight underground enclosures and deep excavations. Both techniques offer effective soil retention but differ significantly in installation methods, structural strength, and suitability for variable ground conditions.
Engineering Principles Behind Sheet Piles
Sheet piles rely on interlocking steel sections to form a continuous wall that resists lateral earth pressures through bending and shear forces. Their design is based on soil-structure interaction principles, ensuring stability against soil displacement and water seepage in excavation support or flood protection. The sections' rigidity and depth are critical factors influencing their load-bearing capacity and overall performance in various geotechnical applications.
Understanding Secant Pile Wall Systems
Secant pile wall systems consist of intersecting reinforced concrete piles formed by casting primary and secondary piles alternately to create a continuous wall that provides excellent groundwater cutoff and earth retention. These walls offer superior structural strength and impermeability compared to traditional sheet pile walls, making them ideal for deep excavation and complex soil conditions. Secant piles are often preferred in urban construction projects where limited space and stability requirements are critical.
Key Differences Between Sheet Pile and Secant Pile
Sheet piles are interlocking steel sections driven into the ground to provide earth retention and excavation support, primarily used for temporary or permanent walls in soft soils. Secant piles consist of overlapping concrete bored piles reinforced with steel, creating a continuous wall ideal for groundwater cutoff and load-bearing applications in complex soil conditions. Key differences include installation methods, material composition, structural strength, and suitability for various geotechnical challenges, with sheet piles offering faster installation and secant piles providing superior watertightness and load capacity.
Material Selection: Steel vs Concrete
Sheet piles are typically made from steel, offering high strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for temporary or permanent retaining walls in marine or soft soil conditions. Secant piles consist of interlocking reinforced concrete elements, providing excellent load-bearing capacity and watertightness for deep excavations and permanent structures. The choice between steel sheet piles and concrete secant piles depends on project requirements, environmental exposure, and structural demands, with steel favored for rapid installation and concrete preferred for durability and heavy-duty support.
Installation Methods for Sheet Pile and Secant Pile
Sheet pile installation involves driving interlocking steel sections into the ground using vibratory hammers, impact hammers, or pressing techniques for rapid and efficient wall construction. Secant pile installation requires sequential drilling and casting of overlapping concrete piles, where primary piles are poured first and secondary piles are drilled and cast between them to form a continuous, reinforced barrier. Both methods demand precise alignment and soil assessment, but sheet piles are favored for softer soils and rapid deployment, while secant piles suit complex subsurface conditions and provide superior water cutoff.
Typical Applications in Civil Engineering Projects
Sheet piles are commonly used for temporary earth retention, cofferdams, and waterfront structures due to their quick installation and cost-effectiveness in shallow to moderate depth applications. Secant piles provide robust, water-tight retaining walls ideal for deep excavations, foundation support in urban environments, and complex soil conditions requiring high structural integrity. Civil engineering projects such as basement construction, subway stations, and deep foundation walls benefit from the enhanced load-bearing capacity and groundwater control offered by secant pile systems.
Performance in Challenging Ground Conditions
Sheet piles offer rapid installation and effective temporary earth retention but may face limitations in stability and leakage control in highly permeable or mixed soil conditions. Secant piles provide superior structural integrity and water cutoff capabilities, making them ideal for complex ground conditions such as soft clays, silts, and groundwater presence. Their interlocking design enhances load-bearing capacity and minimizes soil movement, ensuring performance reliability in challenging geotechnical environments.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Sheet piles typically offer lower initial material costs and faster installation, making them cost-effective for temporary structures and projects with tight budgets or timelines. Secant piles involve higher expenses due to specialized drilling and concrete work but provide superior load-bearing capacity and water tightness, beneficial for permanent and complex foundation applications. Evaluating long-term maintenance, soil conditions, and project duration is crucial to determine the most economical solution between sheet pile and secant pile systems.
Advantages and Limitations of Each System
Sheet piles offer rapid installation, cost-effectiveness, and excellent water-tightness for temporary and permanent retaining walls, but they have limited load-bearing capacity and are less suitable for deep excavations or unstable soils. Secant piles provide superior structural strength and flexibility for complex, deep foundation projects, allowing for tailored soil reinforcement and minimal groundwater infiltration; however, they require longer installation times, higher costs, and specialized equipment. Choosing between sheet pile and secant piles depends on project depth, soil conditions, budget constraints, and long-term durability requirements.
Retaining wall systems
Sheet pile retaining walls offer rapid installation and cost-effectiveness in soft soils, while secant pile retaining walls provide superior structural strength and water-tightness for deep excavations and complex ground conditions.
Earth retention
Secant piles provide stronger, watertight earth retention ideal for deep excavations, while sheet piles offer faster installation with cost efficiency suited for temporary or shallow earth retention.
Groundwater cutoff
Sheet piles provide a temporary groundwater cutoff by interlocking steel sections to form a continuous barrier, while secant piles offer a more permanent and robust groundwater cutoff through overlapping concrete piles with enhanced structural stability.
Interlocking profiles
Sheet piles feature interlocking steel sections that create a continuous barrier for soil retention, whereas secant piles rely on overlapping reinforced concrete columns with minimal interlocking profiles to form a watertight wall.
Deep foundation
Sheet piles provide temporary earth retention with lower installation depth, while secant piles form permanent, interlocking deep foundation walls offering greater soil stabilization and load-bearing capacity.
Excavation support
Sheet piles provide temporary excavation support with quick installation and easy removal, while secant piles offer permanent, watertight excavation support suited for deep or complex soil conditions.
Bored piling
Secant piles, formed by overlapping bored concrete piles, provide superior load-bearing capacity and groundwater cutoff compared to driven sheet piles, making them ideal for deep excavations and retaining walls in saturated soils.
Soil displacement
Sheet piles cause less soil displacement due to their thin, interlocking design, whereas secant piles induce greater soil movement because of their overlapping circular cross-sections used in deep excavation support.
Temporary works
Sheet piles offer quick installation and easy removal for temporary works, while secant piles provide stronger soil retention but require longer construction time and more complex removal.
Structural diaphragm
Sheet piles provide temporary or permanent structural diaphragms with interlocking sections ideal for lateral earth retention, while secant piles form rigid structural diaphragms through overlapping concrete columns offering superior load-bearing capacity and groundwater cutoff.
Sheet pile vs Secant pile Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com