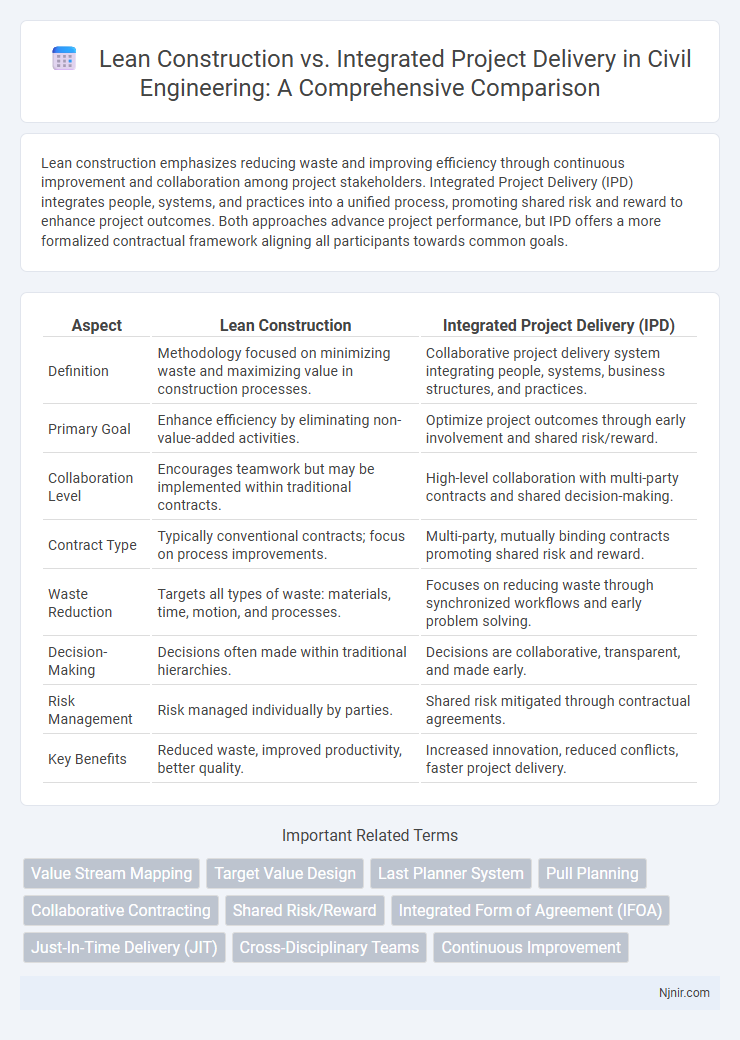
Lean construction emphasizes reducing waste and improving efficiency through continuous improvement and collaboration among project stakeholders. Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) integrates people, systems, and practices into a unified process, promoting shared risk and reward to enhance project outcomes. Both approaches advance project performance, but IPD offers a more formalized contractual framework aligning all participants towards common goals.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lean Construction | Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Methodology focused on minimizing waste and maximizing value in construction processes. | Collaborative project delivery system integrating people, systems, business structures, and practices. |
| Primary Goal | Enhance efficiency by eliminating non-value-added activities. | Optimize project outcomes through early involvement and shared risk/reward. |
| Collaboration Level | Encourages teamwork but may be implemented within traditional contracts. | High-level collaboration with multi-party contracts and shared decision-making. |
| Contract Type | Typically conventional contracts; focus on process improvements. | Multi-party, mutually binding contracts promoting shared risk and reward. |
| Waste Reduction | Targets all types of waste: materials, time, motion, and processes. | Focuses on reducing waste through synchronized workflows and early problem solving. |
| Decision-Making | Decisions often made within traditional hierarchies. | Decisions are collaborative, transparent, and made early. |
| Risk Management | Risk managed individually by parties. | Shared risk mitigated through contractual agreements. |
| Key Benefits | Reduced waste, improved productivity, better quality. | Increased innovation, reduced conflicts, faster project delivery. |
Introduction to Lean Construction and Integrated Project Delivery
Lean Construction emphasizes minimizing waste and maximizing value through continuous improvement, collaborative workflows, and efficient resource utilization. Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) fosters early involvement of key stakeholders, shared risk and reward, and transparent communication to enhance project outcomes. Both methodologies prioritize collaboration and transparency to optimize construction processes and deliver higher-quality projects on time and within budget.
Core Principles of Lean Construction
Lean construction emphasizes maximizing value and minimizing waste through continuous improvement, respect for people, and optimized workflow. Core principles include collaborative decision-making, just-in-time delivery, and reliable workflow management to enhance project efficiency. Integrated Project Delivery shares these lean principles but integrates all key stakeholders early to improve communication and reduce conflicts.
Fundamental Concepts of Integrated Project Delivery
Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) centers on early collaboration among all key stakeholders, including owners, architects, engineers, and contractors, to optimize project outcomes by sharing risks and rewards. This method emphasizes transparent communication, joint decision-making, and collective responsibility to enhance efficiency and reduce waste, contrasting with traditional Lean Construction's focus on workflow optimization and minimizing non-value-adding activities. Key fundamental concepts of IPD include mutual respect, shared financial incentives, real-time information sharing, and co-location of teams to foster a highly integrated and productive project environment.
Key Differences Between Lean Construction and IPD
Lean construction emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and value maximization through collaborative workflows, whereas Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) centers on aligning stakeholders via shared contracts and mutual risk-sharing agreements. Lean construction applies principles like Just-In-Time delivery and pull planning to optimize efficiency, while IPD integrates teams early to improve decision-making and transparency throughout the project lifecycle. The primary difference lies in Lean construction being a methodology focused on process improvement, contrasted with IPD as a contractual framework fostering integrated team collaboration.
Benefits of Lean Construction in Civil Engineering Projects
Lean Construction enhances efficiency in civil engineering projects by minimizing waste, reducing delays, and optimizing resource utilization, which leads to cost savings and improved project timelines. Its emphasis on continuous improvement and collaboration fosters better communication among stakeholders, resulting in higher quality deliverables and increased client satisfaction. Lean methodologies also support sustainable practices by promoting just-in-time delivery and reducing overproduction, contributing to environmental benefits in construction.
Advantages of IPD for Project Stakeholders
Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) offers significant advantages for project stakeholders by fostering enhanced collaboration, aligning goals through shared risks and rewards, and promoting early involvement of all key participants. This approach reduces waste, improves communication efficiency, and accelerates decision-making processes, resulting in cost savings and higher-quality outcomes. Stakeholders benefit from increased transparency and collective accountability, which minimizes disputes and ensures project objectives are met more reliably compared to traditional Lean construction methods.
Challenges and Limitations of Lean Construction
Lean construction faces challenges such as the difficulty of fully implementing collaborative workflows due to fragmented contracts and resistance to cultural change among stakeholders. Limitations include the need for extensive training, potential initial productivity slowdowns, and a heavy reliance on early and accurate information which may not always be available. The lack of standardized metrics and inconsistent adoption across projects can also hinder lean construction's effectiveness compared to integrated project delivery methods.
Obstacles in Implementing Integrated Project Delivery
Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) faces significant obstacles such as resistance to cultural change within project teams accustomed to traditional Lean Construction methods. Complex contractual frameworks and the need for early stakeholder collaboration create legal and logistical challenges that impede smooth implementation. Furthermore, IPD demands advanced technology integration and shared risk management, which can be difficult for firms lacking experience or resources.
Case Studies Comparing Lean Construction and IPD Outcomes
Case studies comparing Lean Construction and Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) highlight significant improvements in project efficiency, cost savings, and stakeholder collaboration with both approaches. Lean Construction projects consistently demonstrate reduced waste and shorter cycle times, while IPD case studies often reveal enhanced teamwork and shared risk management contributing to higher quality outcomes. Data from industry reports show Lean Construction reduces project delays by up to 25%, whereas IPD projects achieve up to 20% cost savings through early involvement of all key participants.
Future Trends in Collaborative Civil Engineering Project Delivery
Lean construction emphasizes waste reduction and continuous improvement by optimizing workflows and enhancing communication among project stakeholders. Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) fosters early collaboration through shared risk and reward, leveraging advanced BIM technologies and contractual alignment to improve project outcomes. Future trends point to increased adoption of digital tools, AI-driven decision-making, and enhanced data integration to further streamline collaborative delivery in civil engineering projects.
Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping in Lean Construction identifies and eliminates waste to optimize workflows, while Integrated Project Delivery uses it collaboratively to enhance project coordination and maximize value generation.
Target Value Design
Target Value Design in Lean Construction emphasizes continuous cost optimization by aligning project goals with stakeholder values, whereas Integrated Project Delivery enhances collaboration and risk-sharing to achieve these targets efficiently.
Last Planner System
The Last Planner System, a core component of Lean Construction, enhances workflow reliability and collaboration by enabling collaborative planning and real-time progress tracking, whereas Integrated Project Delivery integrates multidisciplinary teams to optimize project outcomes through shared risk and reward.
Pull Planning
Pull Planning in Lean construction enhances workflow efficiency by scheduling tasks based on downstream demands, whereas Integrated Project Delivery integrates multidisciplinary teams early to collaboratively optimize project timelines and resource allocation.
Collaborative Contracting
Lean construction emphasizes waste reduction and efficiency through collaborative contracting, while Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) advances this by aligning all stakeholders under a shared risk-reward contract to enhance teamwork and project outcomes.
Shared Risk/Reward
Lean Construction and Integrated Project Delivery both emphasize Shared Risk/Reward to enhance collaboration, but Integrated Project Delivery formalizes this through legally binding contracts aligning financial incentives among all stakeholders.
Integrated Form of Agreement (IFOA)
Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) utilizes the Integrated Form of Agreement (IFOA) to align stakeholders' goals, promote collaboration, and share risks and rewards, improving efficiency and reducing waste compared to traditional Lean Construction methods.
Just-In-Time Delivery (JIT)
Lean construction emphasizes Just-In-Time Delivery (JIT) to minimize waste and inventory costs, while Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) uses JIT within collaborative frameworks to enhance project efficiency and stakeholder alignment.
Cross-Disciplinary Teams
Lean construction enhances collaboration through streamlined processes in cross-disciplinary teams, while Integrated Project Delivery maximizes synergy by fostering early stakeholder involvement and shared risk among cross-disciplinary teams.
Continuous Improvement
Lean construction emphasizes continuous improvement through waste reduction and iterative feedback loops, while Integrated Project Delivery fosters continuous improvement via collaborative workflows and shared project goals.
Lean construction vs Integrated project delivery Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com