Waterstops and bentonite seals serve crucial roles in preventing water infiltration in concrete structures, but they function differently; waterstops are typically made from PVC or rubber and are embedded in concrete joints to physically block water passage. Bentonite seals utilize the swelling properties of bentonite clay to form a watertight barrier when in contact with moisture, making them ideal for sealing irregular gaps and around utilities. Choosing between the two depends on the specific application, joint movement, and environmental conditions of the construction project.
Table of Comparison
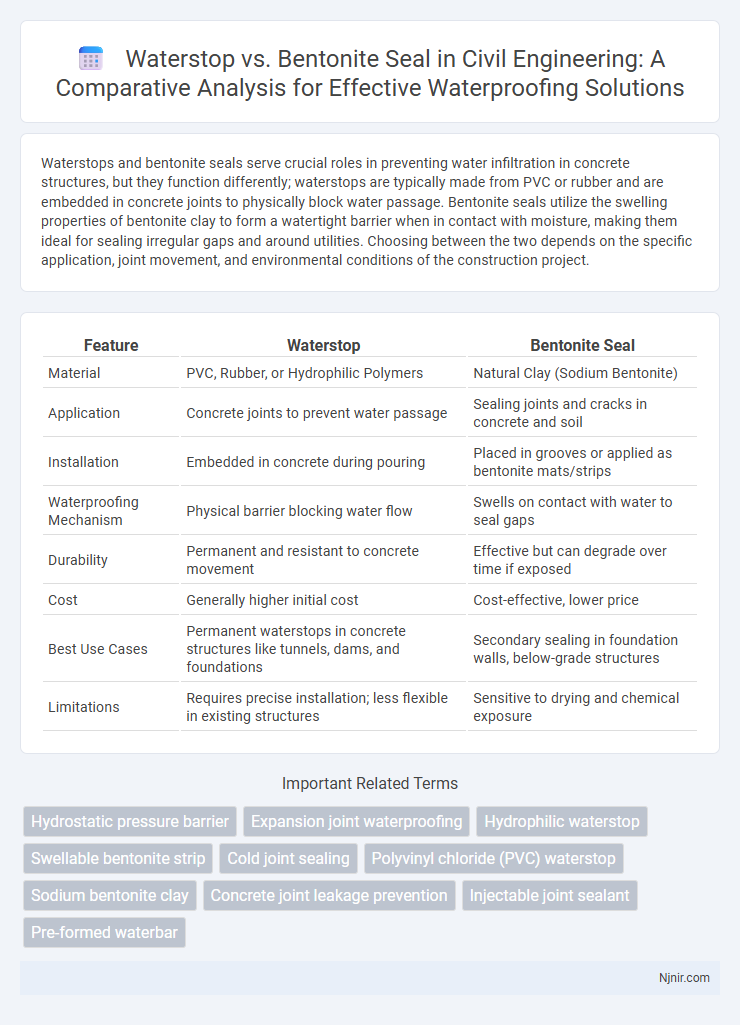
| Feature | Waterstop | Bentonite Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Material | PVC, Rubber, or Hydrophilic Polymers | Natural Clay (Sodium Bentonite) |
| Application | Concrete joints to prevent water passage | Sealing joints and cracks in concrete and soil |
| Installation | Embedded in concrete during pouring | Placed in grooves or applied as bentonite mats/strips |
| Waterproofing Mechanism | Physical barrier blocking water flow | Swells on contact with water to seal gaps |
| Durability | Permanent and resistant to concrete movement | Effective but can degrade over time if exposed |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Cost-effective, lower price |
| Best Use Cases | Permanent waterstops in concrete structures like tunnels, dams, and foundations | Secondary sealing in foundation walls, below-grade structures |
| Limitations | Requires precise installation; less flexible in existing structures | Sensitive to drying and chemical exposure |
Introduction to Waterstop and Bentonite Seal
Waterstop is a flexible waterproofing element made from materials like PVC, rubber, or metal, designed to prevent water passage through concrete joints in construction. Bentonite seal consists of natural clay with high swelling properties that expands upon contact with moisture, creating an effective barrier against water infiltration in underground structures. Both materials serve critical roles in joint waterproofing but differ significantly in composition, application methods, and performance characteristics.
Material Composition and Properties
Waterstop is typically made from PVC, rubber, or hydrophilic materials, designed to create a flexible, impermeable barrier within concrete joints, exhibiting high tensile strength and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion. Bentonite seal consists of natural clay minerals with a high swelling capacity upon contact with water, forming a dense, self-healing waterproof layer that adapts to irregular joint surfaces. The distinct material composition influences their properties: waterstops offer mechanical durability and structural integration, while bentonite seals provide superior self-sealing abilities and ease of installation in varying joint conditions.
Installation Methods and Procedures
Waterstop installation requires embedding the strip or profile into concrete joints during the pouring process, ensuring continuous overlap and proper positioning to prevent leaks. Bentonite seal installation involves placing pre-formed bentonite strips or panels into grooves or around pipe penetrations, where they swell upon contact with moisture to form a watertight barrier. Both methods demand careful surface preparation and alignment, but waterstops need precise concrete pouring coordination, while bentonite seals rely on moisture activation post-installation.
Performance in Water Containment
Waterstops provide superior performance in water containment by creating a mechanical barrier within concrete joints, effectively preventing water passage even under high hydrostatic pressure. Bentonite seals rely on swelling clay properties to form a watertight seal, which can be less reliable in dynamic or heavily moving joints. For critical waterproofing applications, especially in structural joints subjected to significant movement or pressure, waterstops offer enhanced durability and long-term watertight integrity compared to bentonite seals.
Durability and Lifespan
Waterstops made from PVC or rubber offer high durability with resistance to chemicals, UV exposure, and extreme temperatures, often lasting 30-50 years when properly installed. Bentonite sealants rely on the swelling properties of clay, providing effective sealing but with a shorter lifespan of around 10-20 years due to potential drying out or degradation over time. Choosing waterstops ensures longer-term structural integrity in concrete joints, while bentonite seals are preferable for moderate durability needs and cost efficiency.
Compatibility with Concrete Joints
Waterstops are highly compatible with concrete joints due to their ability to create a continuous barrier that prevents water passage by bonding closely with the concrete matrix. Bentonite seals rely on their swelling properties when in contact with moisture, filling gaps and ensuring watertightness, but may be less effective if not properly confined within the joint. Both materials require careful installation to maintain integrity, with waterstops offering superior chemical resistance and durability in dynamic concrete joint environments.
Resistance to Chemicals and Aggressive Environments
Waterstop made from PVC or rubber exhibits high resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and oils, making it suitable for aggressive environments such as wastewater treatment plants and chemical storage facilities. Bentonite seal swells upon contact with water to form a tight seal but can degrade in acidic or highly alkaline conditions, leading to reduced chemical resistance. Choosing waterstop provides superior durability and chemical resistance in harsh environments, whereas bentonite seals are more effective in neutral, less chemically aggressive settings.
Cost Comparison: Waterstop vs Bentonite Seal
Waterstop systems typically have higher upfront installation costs due to their durable materials like PVC or rubber, but they offer long-term reliability and minimal maintenance expenses. Bentonite seals are often less expensive initially, leveraging the natural swelling properties of bentonite clay, yet may require more frequent inspections and potential repairs over time. Evaluating total lifecycle costs reveals that waterstops provide a cost-effective solution for projects demanding enduring waterproofing performance.
Applications in Civil Engineering Projects
Waterstop materials are essential for preventing water passage in concrete joints, commonly used in water retaining structures such as dams, reservoirs, and tunnels. Bentonite seals provide swelling properties that create a watertight barrier in expansion joints, particularly effective in underground foundations, basements, and retaining walls. Civil engineering projects select waterstop or bentonite based on specific project needs for durability, joint movement accommodation, and environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Selecting between waterstop and bentonite seal depends on the specific project requirements, including joint movement, water pressure, and environmental conditions. Waterstops, typically made from PVC or rubber, excel in dynamic joints with frequent movement, providing reliable mechanical sealing against high hydrostatic pressure. Bentonite seals, composed of bentonite clay, offer self-sealing properties ideal for static or low-movement joints in applications requiring natural sealing and chemical resistance.
Hydrostatic pressure barrier
Waterstop provides a durable hydrostatic pressure barrier through flexible rubber expansion, while bentonite seal forms a self-sealing clay layer that swells upon water contact to block seepage.
Expansion joint waterproofing
Waterstop provides durable, flexible expansion joint waterproofing through physical barriers, while bentonite seal offers self-sealing properties by swelling upon water contact to fill gaps.
Hydrophilic waterstop
Hydrophilic waterstops expand upon contact with water to form a watertight seal, offering superior flexibility and self-healing properties compared to traditional bentonite seals in construction joints.
Swellable bentonite strip
Swellable bentonite strips provide superior self-sealing capabilities in waterstop applications by expanding upon contact with water to fill gaps and prevent leakage effectively.
Cold joint sealing
Waterstop offers superior cold joint sealing performance compared to bentonite seal due to its high durability, flexibility, and ability to maintain watertight integrity under varying structural movements.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) waterstop
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) waterstop offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability compared to bentonite seal, making it ideal for preventing water leakage in concrete joints of construction projects.
Sodium bentonite clay
Sodium bentonite clay offers superior swelling properties and self-sealing capabilities compared to traditional waterstops, making it highly effective for waterproofing concrete joints in construction.
Concrete joint leakage prevention
Waterstop provides durable, waterproof seals for concrete joints by physically blocking water flow, while bentonite seals prevent leakage through swelling properties that fill gaps and create a watertight barrier in concrete construction joints.
Injectable joint sealant
Injectable joint sealants using bentonite offer superior self-healing and water-swelling properties compared to rigid waterstop systems, ensuring enhanced long-term waterproofing in concrete construction joints.
Pre-formed waterbar
Pre-formed waterbar waterstops offer superior durability and consistent sealing performance compared to bentonite seals, making them ideal for concrete joint waterproofing in construction projects.
Waterstop vs Bentonite seal Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com