5S is a systematic method for workplace organization, emphasizing sorting, setting in order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining to improve efficiency and safety. Kaizen focuses on continuous incremental improvements through employee involvement and problem-solving to enhance productivity and quality. Both methodologies complement each other by creating a structured environment that supports ongoing process enhancements in industrial engineering.
Table of Comparison
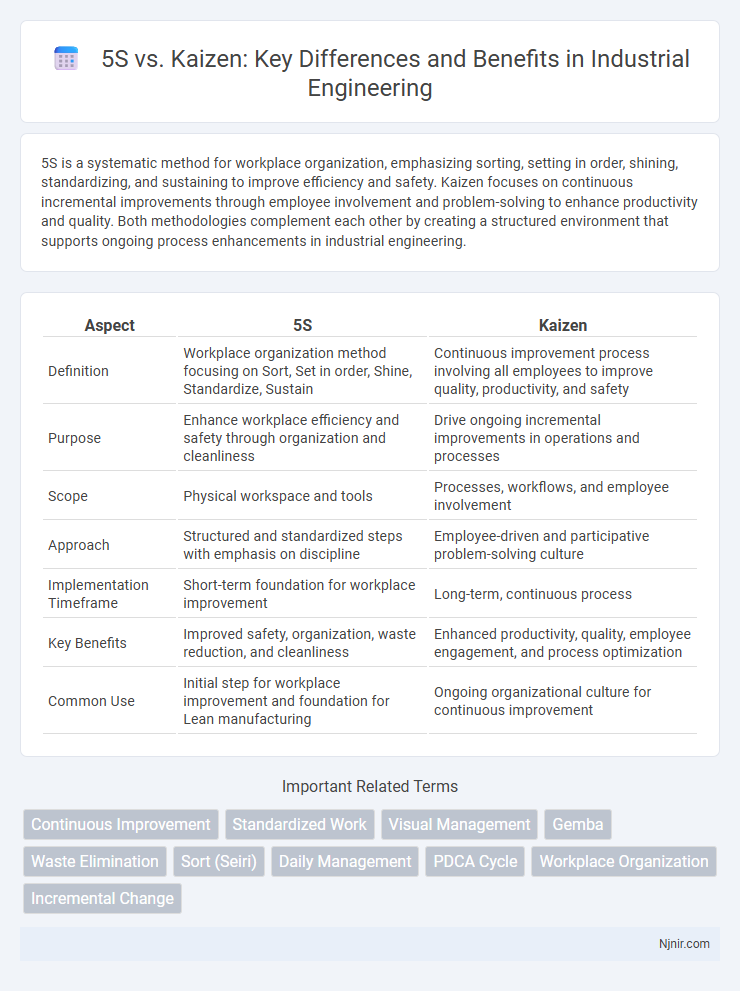
| Aspect | 5S | Kaizen |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Workplace organization method focusing on Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain | Continuous improvement process involving all employees to improve quality, productivity, and safety |
| Purpose | Enhance workplace efficiency and safety through organization and cleanliness | Drive ongoing incremental improvements in operations and processes |
| Scope | Physical workspace and tools | Processes, workflows, and employee involvement |
| Approach | Structured and standardized steps with emphasis on discipline | Employee-driven and participative problem-solving culture |
| Implementation Timeframe | Short-term foundation for workplace improvement | Long-term, continuous process |
| Key Benefits | Improved safety, organization, waste reduction, and cleanliness | Enhanced productivity, quality, employee engagement, and process optimization |
| Common Use | Initial step for workplace improvement and foundation for Lean manufacturing | Ongoing organizational culture for continuous improvement |
Introduction to 5S and Kaizen
5S is a workplace organization method originating from Japan, focusing on five principles: Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain to improve efficiency and eliminate waste. Kaizen emphasizes continuous, incremental improvements involving all employees to enhance processes, productivity, and quality over time. Both methodologies aim to optimize operational performance but differ in scope; 5S targets workplace organization while Kaizen focuses on broader process improvement and employee engagement.
Core Principles of 5S
The core principles of 5S--Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain--emphasize workplace organization and cleanliness to enhance efficiency and reduce waste. Unlike Kaizen, which focuses on continuous overall improvement through incremental changes across processes, 5S targets maintaining a structured and orderly environment as a foundation for productivity. Implementing 5S establishes a disciplined workspace that supports the broader objectives of Kaizen by creating standardized and sustainable work practices.
Fundamental Concepts of Kaizen
Kaizen centers on continuous, incremental improvements involving every employee, fostering a culture of sustained efficiency and quality enhancement. Unlike 5S, which focuses primarily on workplace organization through Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain, Kaizen emphasizes ongoing team collaboration and problem-solving to drive process innovation. Core to Kaizen is the belief that small, consistent changes lead to significant long-term benefits in productivity and operational excellence.
Key Differences Between 5S and Kaizen
5S is a workplace organization method focusing on Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain to improve efficiency and reduce waste, while Kaizen is a broader continuous improvement philosophy involving all employees to enhance processes and quality. 5S provides a foundational system for maintaining order and cleanliness, whereas Kaizen emphasizes incremental, ongoing improvements beyond just organization. The key difference lies in 5S being a structured, step-by-step approach to workplace setup, and Kaizen serving as a culture-driven mindset fostering innovation and problem-solving.
Implementation Strategies for 5S
5S implementation strategies emphasize systematic workplace organization through five key steps: Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain, promoting efficiency and safety. Successful 5S adoption requires strong leadership commitment, employee training, and continuous monitoring to ensure practices are embedded in daily routines. Integrating visual management tools and regular audits reinforces discipline and fosters a culture of continuous improvement distinct from the broader, process-focused Kaizen methodology.
Implementing Kaizen in the Workplace
Implementing Kaizen in the workplace involves continuous, incremental improvements driven by employee engagement and a culture of quality enhancement. It emphasizes small, daily changes that collectively lead to significant operational efficiencies, cost reduction, and improved team collaboration. In contrast to 5S's focus on workplace organization and standardization, Kaizen targets ongoing process optimization and waste elimination across all business functions.
Benefits of 5S in Industrial Engineering
5S enhances workplace organization by systematically sorting, setting in order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining, leading to increased efficiency and reduced waste in industrial engineering processes. Improved safety and ergonomics result from the elimination of clutter and better space utilization, minimizing the risk of accidents and improving worker comfort. By fostering discipline and continuous improvement, 5S creates a foundation that supports Kaizen initiatives and overall operational excellence.
Advantages of Kaizen for Continuous Improvement
Kaizen emphasizes ongoing, incremental improvements by involving every employee in the process, fostering a culture of continuous enhancement and higher productivity. Unlike 5S, which focuses primarily on workplace organization and standardization, Kaizen drives sustained innovation and quality enhancement across all business operations. This approach leads to reduced waste, improved efficiency, and increased employee engagement, making it a powerful strategy for long-term organizational growth.
Integrating 5S and Kaizen for Maximum Efficiency
Integrating 5S and Kaizen creates a powerful synergy that drives continuous improvement and operational efficiency by combining workplace organization with systematic problem-solving. 5S--Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain--lays the foundation for a clean, organized environment that facilitates Kaizen's ongoing incremental improvements. Companies leveraging this integration report enhanced productivity, reduced waste, and a culture of sustained quality improvements.
Choosing the Right Approach: 5S or Kaizen
Choosing between 5S and Kaizen depends on the specific goals of your organization's continuous improvement strategy. 5S focuses on workplace organization and standardization through Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain, making it ideal for creating a clean, efficient work environment. Kaizen emphasizes ongoing incremental improvements involving all employees, suited for fostering a culture of innovation and addressing complex process improvements over time.
Continuous Improvement
5S standardizes workplace organization to sustain continuous improvement, while Kaizen drives ongoing incremental changes by fostering a culture of employee involvement and process optimization.
Standardized Work
5S enhances standardized work by organizing and maintaining a clean, efficient workplace while Kaizen continuously improves standardized work processes through employee-driven incremental changes.
Visual Management
5S enhances Visual Management by organizing and standardizing workplaces for immediate visual cues, while Kaizen incorporates continuous improvement through employee-driven visual feedback systems.
Gemba
5S improves workplace organization and efficiency at the Gemba through sorting, setting in order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining, while Kaizen drives continuous incremental improvements involving all employees to optimize processes and reduce waste directly on the Gemba.
Waste Elimination
5S systematically organizes the workplace to eliminate waste by reducing clutter and improving efficiency, while Kaizen continuously drives waste elimination through incremental process improvements involving all employees.
Sort (Seiri)
Sort (Seiri) in 5S systematically eliminates unnecessary items from the workplace, enhancing efficiency and forming the foundational step for continuous improvement in Kaizen methodologies.
Daily Management
5S enhances daily management by organizing and standardizing the workplace for efficiency and safety, while Kaizen drives continuous daily improvements through employee involvement and problem-solving.
PDCA Cycle
5S emphasizes workplace organization to support the PDCA cycle, while Kaizen utilizes the PDCA cycle for continuous incremental improvements across processes.
Workplace Organization
5S enhances Workplace Organization by systematically sorting, setting in order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining, while Kaizen continuously improves processes and employee involvement beyond physical organization.
Incremental Change
5S enhances workplace efficiency through systematic organization, while Kaizen drives continuous incremental change by involving all employees in ongoing process improvements.
5S vs Kaizen Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com