Manual inspection in industrial engineering offers flexibility and human judgment skills essential for identifying subtle defects, while automated inspection ensures higher consistency, speed, and accuracy through advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms. Automated systems reduce human error and enable real-time data analysis, enhancing quality control and operational efficiency on production lines. Balancing both methods allows industries to optimize defect detection and maintain product standards effectively.
Table of Comparison
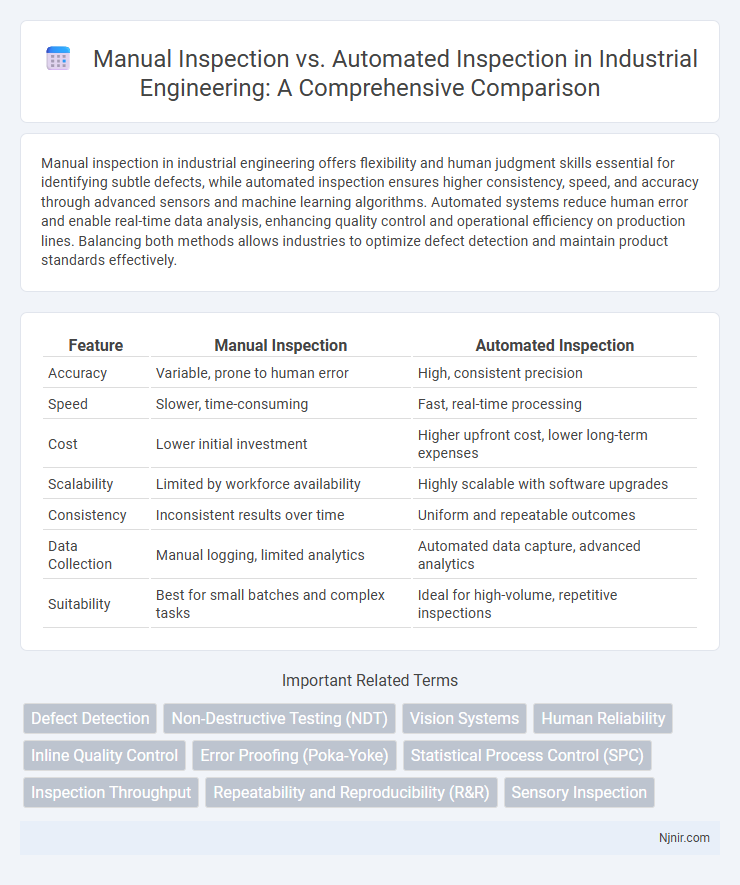
| Feature | Manual Inspection | Automated Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Variable, prone to human error | High, consistent precision |
| Speed | Slower, time-consuming | Fast, real-time processing |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher upfront cost, lower long-term expenses |
| Scalability | Limited by workforce availability | Highly scalable with software upgrades |
| Consistency | Inconsistent results over time | Uniform and repeatable outcomes |
| Data Collection | Manual logging, limited analytics | Automated data capture, advanced analytics |
| Suitability | Best for small batches and complex tasks | Ideal for high-volume, repetitive inspections |
Introduction to Manual vs Automated Inspection
Manual inspection involves human evaluators visually examining products or components to identify defects or inconsistencies, relying on experience and judgment. Automated inspection uses advanced technologies such as machine vision, sensors, and AI algorithms to perform high-speed, precise, and consistent quality assessments. The choice between manual and automated inspection depends on factors like production volume, complexity, accuracy requirements, and cost efficiency.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automated Inspection
Manual inspection relies on human observation and judgment for defect detection, often resulting in variability due to fatigue or subjectivity. Automated inspection uses advanced sensors and AI algorithms to consistently analyze products, improving accuracy and speed while reducing human error. Key differences include scalability, precision, and data integration capabilities, where automated systems excel in handling large volumes with detailed analytics.
Advantages of Manual Inspection in Industrial Engineering
Manual inspection in industrial engineering allows for nuanced judgment and adaptability when identifying complex defects that automated systems may overlook. Skilled inspectors can leverage tactile feedback and visual cues to assess product quality with high precision in irregular or custom manufacturing processes. This human expertise ensures detection of subtle anomalies, contributing to improved product reliability and reduced error rates in quality control.
Limitations of Manual Inspection Methods
Manual inspection methods often suffer from human error, inconsistency, and fatigue, which can lead to overlooked defects and reduced accuracy. These inspections typically require considerable time and labor, limiting scalability and increasing operational costs. Furthermore, manual inspections lack the precision and repeatability provided by automated systems, making them less effective for high-volume or intricate quality control processes.
Benefits of Automated Inspection Systems
Automated inspection systems significantly enhance accuracy and consistency by utilizing advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms, reducing human error and variability. These systems enable faster processing speeds, increasing production throughput while maintaining high-quality standards. Integration with data analytics allows real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
Challenges of Implementing Automated Inspection
Implementing automated inspection systems faces challenges such as high initial costs for advanced sensors and AI integration, which can strain budgets in manufacturing environments. Ensuring accuracy and reliability remains difficult due to variability in product types, surface conditions, and complex defect detection that may require human judgment. Integration with existing production lines demands significant customization and ongoing maintenance, limiting adoption speed and scalability.
Cost Comparison: Manual vs Automated Inspection
Manual inspection incurs higher labor costs due to the need for skilled inspectors working extended hours, while automated inspection systems require significant upfront investment in technology and maintenance but reduce ongoing labor expenses. Automated inspection delivers faster throughput and lower error rates, leading to cost savings from decreased rework and product recalls. Over time, automated solutions offer a favorable return on investment, especially in high-volume manufacturing environments, by minimizing operational costs compared to manual methods.
Impact on Quality Control and Productivity
Manual inspection allows for nuanced judgment and adaptability in quality control, especially for complex or irregular products, but it can introduce human error and slower processing speeds. Automated inspection employs consistent, high-speed sensors and machine vision systems that enhance accuracy, reduce defects, and significantly boost productivity through continuous, real-time monitoring. Balancing automated technology with targeted manual checks optimizes overall quality control effectiveness while maximizing throughput in manufacturing environments.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Manual inspection remains vital in industries requiring subjective evaluation or flexibility, such as aerospace and luxury automotive manufacturing, where human expertise detects subtle defects that machines may overlook. Automated inspection excels in high-throughput environments like electronics and semiconductor production, utilizing machine vision and AI algorithms to ensure consistent quality and reduce error rates by up to 90%, as demonstrated in case studies from companies like Intel and Foxconn. Hybrid models combining manual and automated inspections are increasingly adopted in pharmaceutical and food industries to balance speed, accuracy, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Future Trends in Inspection Technologies
Future trends in inspection technologies emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance accuracy and efficiency in both manual and automated inspections. Advanced sensor technologies and real-time data analytics enable predictive maintenance and defect detection with minimal human intervention. The evolution towards smart inspection systems combines robotics and IoT connectivity, paving the way for fully autonomous quality control in manufacturing industries.
Defect Detection
Automated inspection systems use advanced sensors and AI algorithms to detect defects with higher accuracy and consistency compared to manual inspection, which relies on human visual assessment prone to fatigue and subjective errors.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) leverages automated inspection for faster, more consistent defect detection in industrial materials, while manual inspection offers flexibility and nuanced judgment in complex or variable testing scenarios.
Vision Systems
Vision systems in automated inspection outperform manual inspection by providing faster, more accurate defect detection, consistent quality control, and enhanced data analysis capabilities.
Human Reliability
Manual inspection relies heavily on human reliability, which can be affected by fatigue and subjective judgment, whereas automated inspection offers consistent accuracy through machine precision and reduces human error.
Inline Quality Control
Inline quality control leverages automated inspection systems to deliver faster, more accurate defect detection and real-time process adjustments compared to traditional manual inspection methods.
Error Proofing (Poka-Yoke)
Automated inspection enhances error proofing (Poka-Yoke) by consistently detecting defects with higher accuracy and speed compared to manual inspection, reducing human error and improving quality control.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Automated inspections integrated with Statistical Process Control (SPC) enhance accuracy and real-time defect detection compared to manual inspections, enabling more consistent quality management in manufacturing processes.
Inspection Throughput
Automated inspection systems significantly increase inspection throughput by processing high volumes of items rapidly with consistent accuracy compared to slower, labor-intensive manual inspection methods.
Repeatability and Reproducibility (R&R)
Automated inspection offers higher repeatability and reproducibility (R&R) compared to manual inspection by minimizing human error and ensuring consistent measurement conditions across multiple tests.
Sensory Inspection
Manual inspection utilizes human sensory perception for detailed tactile and visual analysis, while automated inspection employs advanced sensors and imaging technologies to enhance accuracy, consistency, and speed in detecting defects.
Manual Inspection vs Automated Inspection Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com