OEE measures the percentage of planned production time that is truly productive by accounting for availability, performance, and quality losses, providing insights into equipment utilization during scheduled operating hours. TEEP expands on OEE by incorporating the loading factor to evaluate equipment effectiveness over total calendar time, including unscheduled downtime. Comparing OEE and TEEP helps industrial engineers identify opportunities to improve both operational efficiency and equipment utilization, driving overall manufacturing performance enhancements.
Table of Comparison
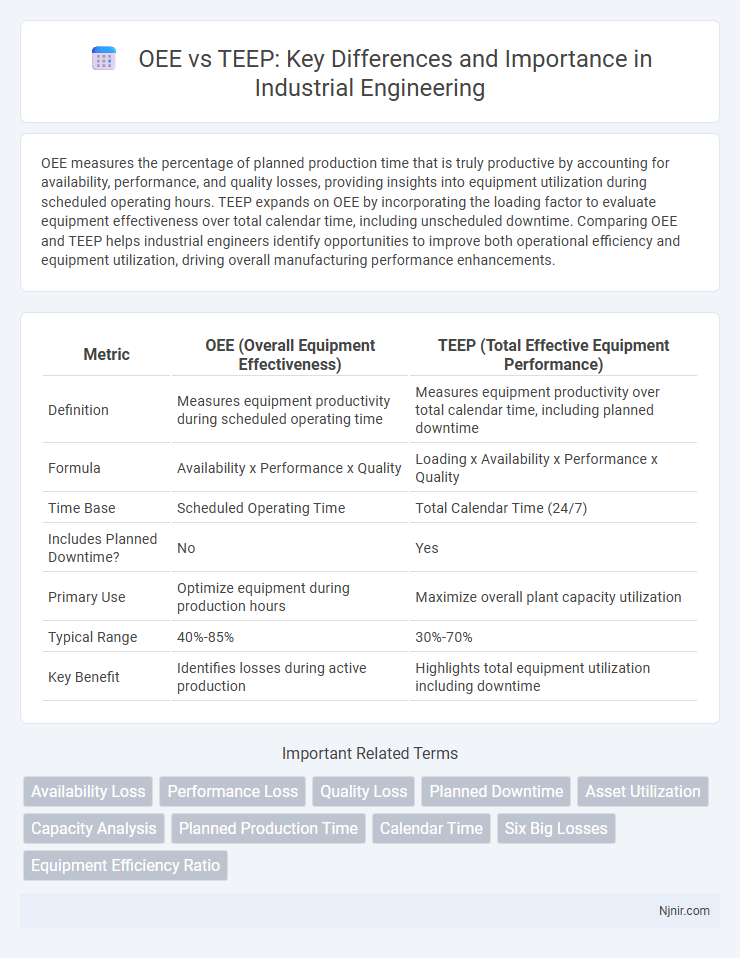
| Metric | OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) | TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures equipment productivity during scheduled operating time | Measures equipment productivity over total calendar time, including planned downtime |
| Formula | Availability x Performance x Quality | Loading x Availability x Performance x Quality |
| Time Base | Scheduled Operating Time | Total Calendar Time (24/7) |
| Includes Planned Downtime? | No | Yes |
| Primary Use | Optimize equipment during production hours | Maximize overall plant capacity utilization |
| Typical Range | 40%-85% | 30%-70% |
| Key Benefit | Identifies losses during active production | Highlights total equipment utilization including downtime |
Introduction to OEE and TEEP in Industrial Engineering
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) measures manufacturing productivity by evaluating availability, performance, and quality, providing insight into how effectively equipment is utilized during planned production time. Total Effective Equipment Performance (TEEP) extends OEE by accounting for all calendar time, including unplanned downtime, offering a comprehensive view of equipment utilization across total available time. Both metrics are essential in industrial engineering for identifying operational inefficiencies and driving continuous improvement in production processes.
Defining OEE: Components and Calculations
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) measures manufacturing productivity by combining Availability, Performance, and Quality rates into a single percentage indicating how effectively equipment is utilized during planned production time. Availability accounts for downtime losses, Performance measures speed losses relative to the ideal cycle time, and Quality reflects the proportion of good parts produced versus total parts. Calculating OEE involves multiplying these three components: OEE = Availability x Performance x Quality, providing insights into equipment efficiency during operating shifts.
Understanding TEEP: Key Metrics and Measurement
TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) measures the total productive capacity of equipment by accounting for both utilization and performance losses over all available time, including planned and unplanned downtime. Unlike OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness), which focuses on operating time, TEEP provides a holistic perspective by calculating equipment effectiveness against total calendar time. Key metrics of TEEP include availability (operating time divided by total time), performance efficiency, and quality rate, making it essential for identifying potential capacity improvements and maximizing overall equipment productivity.
Differences Between OEE and TEEP
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) measures equipment productivity based on planned production time, focusing on availability, performance, and quality during scheduled operations. TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) extends this by accounting for total calendar time, including both planned and unplanned downtime, thus providing a more comprehensive view of equipment utilization. The key difference lies in TEEP's calculation over total time, highlighting capacity improvement opportunities beyond scheduled production periods, unlike OEE which is limited to operational hours.
Use Cases: When to Apply OEE vs. TEEP
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) measures the actual production efficiency by evaluating availability, performance, and quality during scheduled production time, making it ideal for monitoring machine performance within planned shifts. TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) extends this analysis by incorporating all calendar time, including downtime and unscheduled periods, providing a comprehensive view of asset utilization across 24/7 operations. Use OEE for optimizing daily production processes and TEEP for strategic decisions on capacity and resource allocation across total operational hours.
Impact on Manufacturing Productivity
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) measures manufacturing productivity by evaluating equipment availability, performance efficiency, and quality output during scheduled production time. TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) extends this analysis by considering total calendar time, including both scheduled and unscheduled downtime, providing a broader view of equipment utilization. Using both OEE and TEEP together enables manufacturers to identify hidden production capacity and optimize asset utilization for maximum productivity improvement.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) evaluates equipment performance by measuring availability, performance, and quality losses during scheduled production time, relying on data from machine sensors, operators, and automated collection systems. TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) extends this analysis by incorporating utilization during both scheduled and unscheduled time, requiring comprehensive data on equipment availability 24/7, including downtime reasons and production status outside shifts. Advanced data collection methods for OEE and TEEP include real-time IoT monitoring, SCADA systems, and MES integration, enabling detailed analysis through time-stamped performance logs and downtime tracking for accurate root cause identification.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Metric
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) measures the productive capacity of equipment during scheduled operating time, focusing on availability, performance, and quality, making it ideal for identifying losses within planned production periods but limited by ignoring unscheduled downtime. TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) extends OEE by accounting for total calendar time, offering a comprehensive view of equipment utilization including unplanned downtime, but it may overemphasize availability at the expense of detailed performance or quality issues. OEE benefits include targeted improvement actions within operational time, while TEEP benefits lie in strategic capacity planning; however, OEE's limitation is restricted scope, and TEEP's is potential complexity in isolating specific loss factors.
Integrating OEE and TEEP for Continuous Improvement
Integrating Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and Total Effective Equipment Performance (TEEP) provides a comprehensive view of equipment productivity by combining availability, performance, and quality metrics with total calendar time utilization. Leveraging OEE identifies losses during scheduled production, while TEEP extends this by measuring equipment usage against total possible operating time, enabling targeted strategies for both production efficiency and capacity utilization improvements. This integration drives continuous improvement by pinpointing hidden downtime, scheduling inefficiencies, and quality issues for optimized manufacturing performance.
Best Practices for Optimizing Equipment Performance
Maximizing OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) and TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) requires accurate data collection on availability, performance, and quality metrics to identify bottlenecks and downtime causes. Implementing predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and continuous operator training enhances equipment reliability and throughput, thereby improving both OEE and TEEP scores. Leveraging integrated software platforms enables proactive decision-making and aligns production goals with asset utilization for optimal equipment performance.
Availability Loss
Availability loss in OEE measures equipment downtime during planned production time, while in TEEP it accounts for downtime over total calendar time, highlighting unused capacity beyond scheduled hours.
Performance Loss
Performance Loss in OEE measures the reduction in actual production speed compared to ideal speed, while TEEP Performance Loss also accounts for unplanned downtime, reflecting total production capacity utilization.
Quality Loss
OEE measures equipment performance losses including quality defects causing downtime, while TEEP extends this by accounting for all available time, highlighting that quality losses reduce overall equipment utilization and effectiveness in both metrics.
Planned Downtime
TEEP includes Planned Downtime in its calculation by measuring total equipment effectiveness over all available time, while OEE excludes Planned Downtime and evaluates performance only during scheduled operating hours.
Asset Utilization
OEE measures asset utilization by evaluating availability, performance, and quality during planned production time, while TEEP extends this by incorporating all calendar time to assess total asset utilization potential.
Capacity Analysis
OEE measures manufacturing efficiency by comparing actual production to planned production time, while TEEP assesses total equipment capacity utilization by including both planned and unplanned downtime in capacity analysis.
Planned Production Time
Planned Production Time in OEE measures scheduled operating time minus planned stops, while TEEP calculates total calendar time, highlighting differences in equipment utilization efficiency.
Calendar Time
TEEP measures equipment effectiveness based on total calendar time including planned and unplanned downtime, while OEE evaluates performance only during planned production time excluding planned downtimes.
Six Big Losses
OEE measures equipment effectiveness by accounting for Availability, Performance, and Quality losses, while TEEP extends this by including time utilization to address Six Big Losses--equipment failure, setup and adjustment, idling and minor stoppages, reduced speed, process defects, and reduced yield--providing a comprehensive view of production efficiency.
Equipment Efficiency Ratio
The Equipment Efficiency Ratio in OEE measures the ratio of actual operating time to planned production time, whereas in TEEP it accounts for total calendar time, providing a more comprehensive evaluation of equipment utilization.
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) vs TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com