Balancing supply chain resilience and supply chain efficiency requires strategic integration of risk management and process optimization to maintain operational continuity under disruptions. Enhancing resilience involves investing in flexible sourcing, inventory buffers, and robust communication networks, which can sometimes increase costs and reduce efficiency. Optimizing this trade-off ensures supply chains remain responsive and cost-effective, supporting sustainable industrial performance.
Table of Comparison
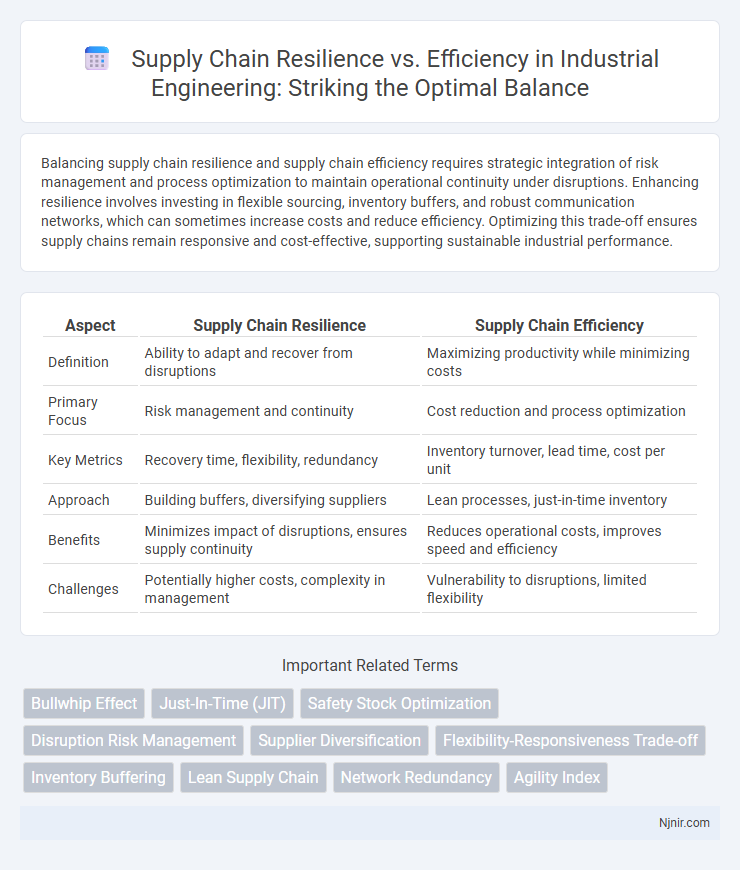
| Aspect | Supply Chain Resilience | Supply Chain Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adapt and recover from disruptions | Maximizing productivity while minimizing costs |
| Primary Focus | Risk management and continuity | Cost reduction and process optimization |
| Key Metrics | Recovery time, flexibility, redundancy | Inventory turnover, lead time, cost per unit |
| Approach | Building buffers, diversifying suppliers | Lean processes, just-in-time inventory |
| Benefits | Minimizes impact of disruptions, ensures supply continuity | Reduces operational costs, improves speed and efficiency |
| Challenges | Potentially higher costs, complexity in management | Vulnerability to disruptions, limited flexibility |
Defining Supply Chain Resilience and Efficiency
Supply chain resilience is the ability of a supply chain to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and recover from disruptions while maintaining continuous operations. Supply chain efficiency focuses on optimizing resource utilization, minimizing costs, and streamlining processes to maximize productivity and profitability. Balancing resilience and efficiency is essential for sustainable supply chain performance in dynamic market environments.
Key Differences: Resilience vs Efficiency
Supply chain resilience prioritizes the ability to quickly adapt and recover from disruptions, emphasizing flexibility, redundancy, and risk management. In contrast, supply chain efficiency focuses on minimizing costs and maximizing productivity through lean operations, just-in-time inventory, and streamlined processes. While resilience ensures continuity under uncertainty, efficiency aims for optimal resource utilization during stable conditions.
The Role of Risk Management in Supply Chains
Risk management plays a crucial role in balancing supply chain resilience and efficiency by identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential disruptions that can impact operations. Resilient supply chains incorporate risk management strategies such as diversification of suppliers, inventory buffering, and contingency planning to ensure continuity during crises, while efficient supply chains focus on minimizing costs and waste to enhance throughput. Effective risk management enables organizations to maintain optimal supply chain performance by preparing for uncertainties without sacrificing operational efficiency.
Measuring Supply Chain Performance: Metrics and KPIs
Measuring supply chain performance requires balancing supply chain resilience and efficiency through specific metrics and KPIs. Key indicators for resilience include supply chain disruption frequency, recovery time, and inventory buffer levels, while efficiency is assessed with order fulfillment rates, cycle time, and cost per unit delivered. Using a combined approach of these metrics helps organizations optimize both agility and cost-effectiveness in their supply chain operations.
Real-World Case Studies: Resilience Wins and Efficiency Losses
Real-world case studies reveal that supply chain resilience outperforms efficiency during disruptions such as the COVID-19 pandemic and the 2021 Suez Canal blockage, where companies with diversified suppliers and flexible logistics avoided severe delays. Firms prioritizing supply chain efficiency through just-in-time delivery experienced significant inventory shortages and lost revenue while resilient models ensured steady operations despite shocks. Data from global manufacturing and retail sectors confirm that investment in resilience safeguards continuity and mitigates risk more effectively than efficiency-focused strategies alone.
The Impact of Global Disruptions on Supply Chains
Global disruptions such as pandemics, geopolitical tensions, and natural disasters significantly challenge supply chain resilience by exposing vulnerabilities in sourcing, production, and distribution networks. Supply chain efficiency, often optimized through lean inventory and just-in-time delivery, may be compromised under these conditions, leading to delays, shortages, and increased costs. Enhancing resilience involves building flexible, diversified, and adaptive systems that can absorb shocks and maintain continuity while balancing the trade-offs with efficiency.
Balancing Cost Control with Flexibility
Supply chain resilience and supply chain efficiency often require balancing cost control with operational flexibility to ensure both stability and responsiveness. Investing in resilience through diversified suppliers and safety stock increases costs but reduces risks of disruption, while efficiency emphasizes lean inventory and streamlined logistics to minimize expenses. Achieving an optimal balance involves leveraging data analytics and risk management frameworks to align supply chain agility with cost-effective practices.
Digital Transformation in Supply Chain Resilience
Digital transformation enhances supply chain resilience by integrating real-time data analytics, IoT sensors, and AI-driven risk management tools to anticipate disruptions and enable swift adaptive responses. While supply chain efficiency focuses on cost reduction and streamlined processes, resilience prioritizes agility and continuity under uncertainty, supported by technologies such as blockchain for transparency and cloud computing for scalable collaboration. Emphasizing digital innovation strengthens predictive capabilities and operational flexibility, balancing resilience with ongoing efficiency improvements.
Strategies to Enhance Both Resilience and Efficiency
Implementing advanced analytics and real-time data integration enhances supply chain resilience by enabling rapid response to disruptions while optimizing efficiency through predictive demand forecasting. Diversifying suppliers and adopting flexible manufacturing processes reduce dependency risks and support efficient resource allocation. Investing in technology such as automation and blockchain improves transparency and coordination, fostering both robust risk management and streamlined operations.
Future Trends: Building Adaptable Supply Chains
Future trends emphasize building adaptable supply chains that balance resilience and efficiency by integrating advanced technologies like AI and IoT for real-time data analytics and predictive insights. Companies invest in diversified sourcing, flexible manufacturing processes, and dynamic inventory management to mitigate disruptions while maintaining lean operations. Enhanced collaboration across supply chain partners leverages digital platforms to improve responsiveness and agility in an increasingly volatile global market.
Bullwhip Effect
Minimizing the Bullwhip Effect enhances supply chain resilience by stabilizing demand signals, which often requires sacrificing some supply chain efficiency to maintain buffer stocks and flexibility.
Just-In-Time (JIT)
Just-In-Time (JIT) prioritizes supply chain efficiency by minimizing inventory costs but reduces supply chain resilience due to heightened vulnerability to disruptions.
Safety Stock Optimization
Optimizing safety stock balances supply chain resilience by mitigating disruptions and supply chain efficiency by minimizing inventory costs.
Disruption Risk Management
Supply chain resilience prioritizes disruption risk management by enhancing adaptability and recovery capabilities, whereas supply chain efficiency focuses on cost reduction and streamlined operations often at the expense of flexibility.
Supplier Diversification
Supplier diversification enhances supply chain resilience by reducing dependency risks while potentially impacting supply chain efficiency due to increased complexity and coordination efforts.
Flexibility-Responsiveness Trade-off
Supply chain resilience prioritizes flexibility and responsiveness to rapidly adapt to disruptions, whereas supply chain efficiency emphasizes streamlined processes that may reduce adaptive capacity.
Inventory Buffering
Inventory buffering enhances supply chain resilience by absorbing demand and supply shocks while potentially reducing supply chain efficiency due to increased carrying costs and capital tied up in stock.
Lean Supply Chain
Lean supply chain strategies prioritize efficiency by minimizing waste and inventory, but enhancing supply chain resilience requires balancing lean principles with flexibility to withstand disruptions.
Network Redundancy
Network redundancy enhances supply chain resilience by providing alternative pathways and resources, while supply chain efficiency often minimizes redundancy to reduce costs and streamline operations.
Agility Index
The Agility Index quantifies supply chain resilience by measuring responsiveness and adaptability, contrasting with traditional efficiency metrics that prioritize cost reduction and process optimization.
Supply Chain Resilience vs Supply Chain Efficiency Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com