MES (Manufacturing Execution System) specializes in real-time shop floor management, tracking production processes, machine performance, and labor efficiency to optimize manufacturing operations. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) integrates broader business functions such as finance, supply chain, and human resources, providing a comprehensive overview for enterprise-wide resource management. While ERP manages overall business workflows, MES delivers granular control and visibility on the plant floor, enabling faster decision-making and improved production agility.
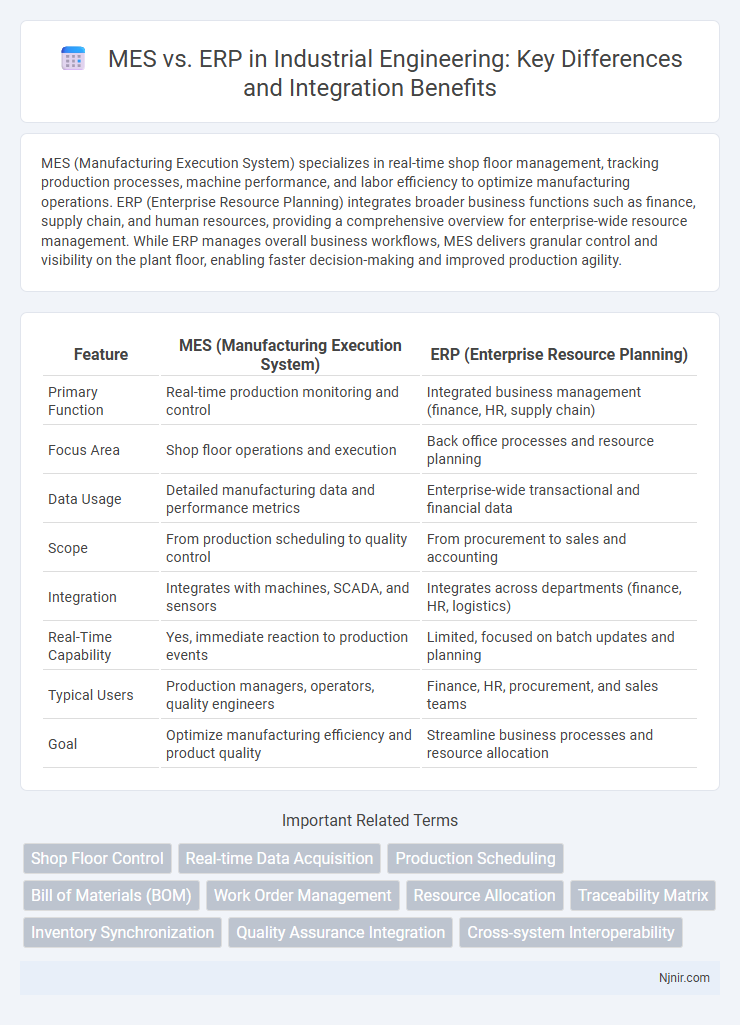
Table of Comparison
| Feature | MES (Manufacturing Execution System) | ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Real-time production monitoring and control | Integrated business management (finance, HR, supply chain) |
| Focus Area | Shop floor operations and execution | Back office processes and resource planning |
| Data Usage | Detailed manufacturing data and performance metrics | Enterprise-wide transactional and financial data |
| Scope | From production scheduling to quality control | From procurement to sales and accounting |
| Integration | Integrates with machines, SCADA, and sensors | Integrates across departments (finance, HR, logistics) |
| Real-Time Capability | Yes, immediate reaction to production events | Limited, focused on batch updates and planning |
| Typical Users | Production managers, operators, quality engineers | Finance, HR, procurement, and sales teams |
| Goal | Optimize manufacturing efficiency and product quality | Streamline business processes and resource allocation |
Introduction to MES and ERP
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) manage real-time production processes on the shop floor, enabling detailed tracking, scheduling, and quality control of manufacturing operations. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate core business functions, such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and inventory management, to provide a unified organizational overview. MES focuses on operational execution and production efficiency, while ERP emphasizes strategic resource planning and business process management.
Core Functions of MES in Industrial Engineering
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) core functions in industrial engineering include real-time monitoring of production processes, tracking work-in-progress, and ensuring quality control on the shop floor. MES provides detailed data on machine performance, operator activities, and material usage to optimize manufacturing efficiency and reduce downtime. Unlike ERP, which focuses on enterprise-wide resource planning and integration, MES specializes in execution-level control and process transparency within the manufacturing environment.
Key Capabilities of ERP Systems
ERP systems excel in integrating core business processes such as finance, human resources, procurement, and supply chain management, offering centralized data and real-time reporting. These systems facilitate resource planning, budgeting, order processing, and compliance management, enabling organizations to streamline operations and improve decision-making across departments. Unlike MES, which focuses on shop floor execution and production control, ERP systems provide a comprehensive framework for overall enterprise resource optimization and strategic management.
Differences between MES and ERP Architectures
MES architecture centers on real-time shop floor data collection, process control, and execution, featuring modules such as production scheduling, quality management, and machine monitoring designed for immediate operational responsiveness. ERP architecture integrates core business processes like finance, supply chain, and human resources through centralized databases, optimizing enterprise-wide resource planning and decision-making over longer time horizons. MES systems prioritize direct production environment interactions with deterministic timing, whereas ERP systems deliver high-level strategic planning and transactional functions across various departments.
Integration of MES and ERP: Bridging the Gap
Integrating MES and ERP systems creates a seamless flow of real-time production data with enterprise-level business processes, enabling better decision-making and operational efficiency. MES captures detailed shop floor information such as machine performance and work-in-progress status, while ERP manages broader functions like inventory, procurement, and finance. Bridging the gap between MES and ERP enhances visibility across manufacturing operations and supply chain management, driving improved resource allocation and reduced production costs.
Role of MES in Production Optimization
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) plays a critical role in production optimization by providing real-time monitoring, execution, and control of manufacturing processes on the shop floor, ensuring higher efficiency and product quality. Unlike ERP systems, which focus on enterprise-wide resource planning and management, MES focuses specifically on production operations, offering detailed data on work-in-progress, machine performance, and operator activity. This granular visibility allows manufacturers to quickly identify bottlenecks, reduce downtime, and improve throughput, directly enhancing overall production performance.
How ERP Streamlines Business Operations
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) streamlines business operations by integrating core functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, and procurement into a unified system, enabling seamless data flow and real-time visibility. This centralization reduces manual processes, minimizes errors, and enhances decision-making across departments. Unlike MES, which focuses on shop floor production control, ERP drives overall organizational efficiency by aligning business processes with strategic goals.
MES vs ERP: Data Management and Traceability
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) provides real-time data management and detailed traceability on the shop floor, enabling precise tracking of production processes, equipment status, and product genealogy. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) handles broader organizational data, consolidating finance, supply chain, and inventory information but lacks granular visibility into manufacturing operations. MES ensures comprehensive traceability by capturing batch-level data and quality metrics, critical for compliance and process optimization, which ERP systems typically aggregate at a higher level without real-time execution details.
Selecting the Right System for Industrial Applications
Selecting the right system for industrial applications requires understanding the distinct functions of MES and ERP: MES focuses on real-time production monitoring, process control, and shop floor execution, while ERP manages broader business processes including finance, supply chain, and resource planning. Industrial operations benefit from integrating MES for enhanced visibility into manufacturing workflows and ERP for strategic planning and resource optimization. Choosing between MES and ERP depends on specific operational priorities, with MES driving production efficiency and ERP supporting enterprise-wide management.
Future Trends in MES and ERP for Industrial Engineering
Future trends in MES and ERP for industrial engineering emphasize increased integration with IoT and AI technologies to enhance real-time data analytics and predictive maintenance. MES platforms are evolving to support edge computing for faster decision-making on the shop floor, while ERP systems are incorporating advanced automation and cloud-based solutions to streamline supply chain and resource management. The convergence of MES and ERP through digital twins and Industry 4.0 standards will drive smarter, more agile manufacturing environments.
Shop Floor Control
MES provides real-time Shop Floor Control by directly managing production processes and equipment, whereas ERP offers broader business resource planning with limited real-time shop floor visibility.
Real-time Data Acquisition
MES provides real-time data acquisition on the shop floor for immediate process control, whereas ERP systems primarily handle aggregated enterprise-level data with less emphasis on instant operational insights.
Production Scheduling
MES provides real-time production scheduling and execution control on the shop floor, while ERP offers high-level production planning and resource allocation across the enterprise.
Bill of Materials (BOM)
MES manages real-time production data and execution activities affecting the Bill of Materials (BOM), while ERP provides centralized BOM structure, inventory control, and procurement planning.
Work Order Management
MES offers real-time work order tracking and shop floor control while ERP provides high-level work order scheduling and resource planning across the enterprise.
Resource Allocation
MES optimizes real-time resource allocation on the production floor by tracking equipment and labor usage, while ERP manages overall enterprise-level resource planning including inventory, procurement, and workforce scheduling.
Traceability Matrix
A Traceability Matrix in MES directly links real-time production activities to quality requirements, while ERP integrates broader business data but offers less detailed manufacturing traceability.
Inventory Synchronization
MES ensures real-time inventory synchronization on the shop floor by capturing precise production data, whereas ERP integrates this data for broader enterprise-level inventory management and planning.
Quality Assurance Integration
MES integrates real-time shop floor quality control with production processes, while ERP provides broader quality assurance management across enterprise-level data and compliance standards.
Cross-system Interoperability
MES enhances cross-system interoperability by providing real-time production data integration with ERP systems, enabling seamless synchronization between shop floor operations and enterprise-level planning.
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) vs ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com