Green logistics prioritizes sustainability by reducing carbon emissions, optimizing resource use, and minimizing waste throughout the supply chain. Standard logistics often emphasizes cost efficiency and speed, sometimes at the expense of environmental impact. Incorporating eco-friendly practices in green logistics leads to long-term operational savings and enhances corporate social responsibility in industrial engineering.
Table of Comparison
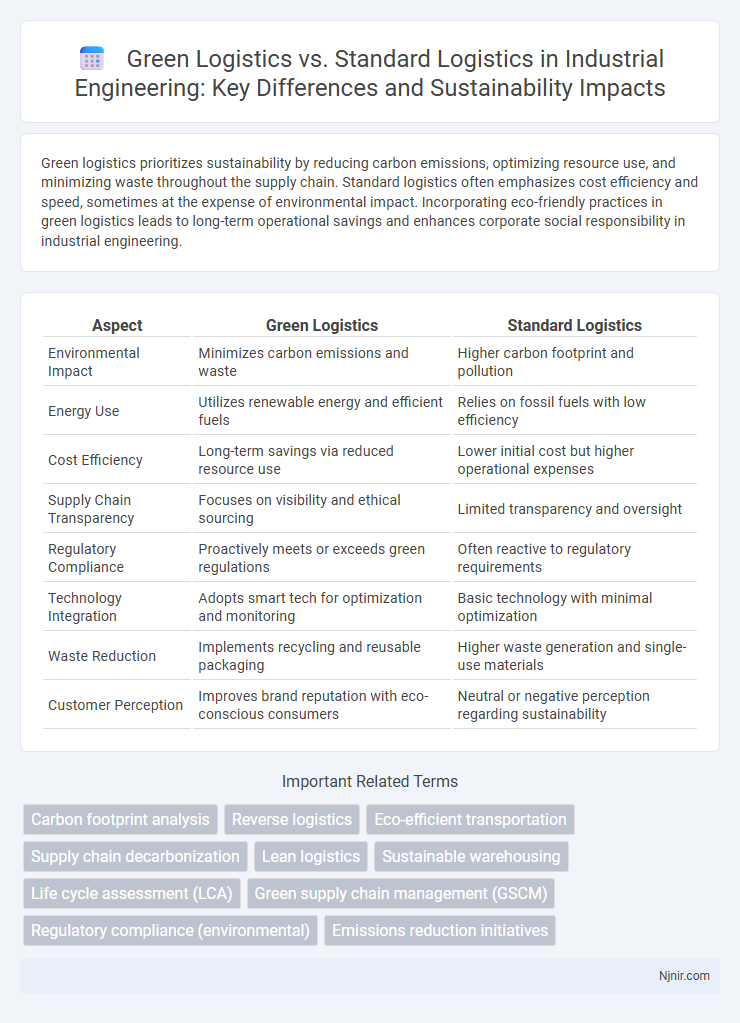
| Aspect | Green Logistics | Standard Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Minimizes carbon emissions and waste | Higher carbon footprint and pollution |
| Energy Use | Utilizes renewable energy and efficient fuels | Relies on fossil fuels with low efficiency |
| Cost Efficiency | Long-term savings via reduced resource use | Lower initial cost but higher operational expenses |
| Supply Chain Transparency | Focuses on visibility and ethical sourcing | Limited transparency and oversight |
| Regulatory Compliance | Proactively meets or exceeds green regulations | Often reactive to regulatory requirements |
| Technology Integration | Adopts smart tech for optimization and monitoring | Basic technology with minimal optimization |
| Waste Reduction | Implements recycling and reusable packaging | Higher waste generation and single-use materials |
| Customer Perception | Improves brand reputation with eco-conscious consumers | Neutral or negative perception regarding sustainability |
Introduction to Logistics: Green vs Standard
Green logistics integrates sustainable practices such as reducing carbon emissions, optimizing fuel consumption, and using eco-friendly packaging to minimize environmental impact, whereas standard logistics primarily focuses on cost efficiency and operational speed without prioritizing environmental concerns. Key differences include the use of electric or hybrid vehicles in green logistics compared to conventional diesel trucks in standard logistics, and the adoption of reverse logistics for recycling in green logistics. Businesses adopting green logistics benefit from enhanced brand reputation and compliance with environmental regulations, contrasting with the traditional emphasis on reducing transportation and warehousing costs.
Core Principles of Green Logistics
Green logistics prioritizes reducing environmental impact through sustainable transportation, efficient resource utilization, and waste minimization, contrasting with standard logistics' focus on cost and speed. Core principles include optimizing route planning to lower carbon emissions, employing eco-friendly packaging materials, and implementing reverse logistics for product reuse and recycling. These strategies collectively enhance supply chain sustainability while maintaining operational efficiency.
Key Features of Standard Logistics
Standard logistics emphasizes cost efficiency, reliability, and speed in the transportation and warehousing of goods, prioritizing streamlined supply chain processes without necessarily focusing on environmental impact. Key features include optimized route planning, just-in-time inventory management, and high utilization of transportation modes such as trucks, ships, and planes to minimize delivery times. Technologies like warehouse management systems (WMS), transportation management systems (TMS), and real-time tracking enhance operational efficiency and customer service in standard logistics.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green logistics significantly reduces carbon emissions and energy consumption by optimizing transportation routes and utilizing eco-friendly vehicles, unlike standard logistics, which often relies on conventional fossil-fuel-powered trucks and planes. It incorporates sustainable practices such as reverse logistics, waste minimization, and the use of renewable energy sources, leading to lower pollution levels and resource conservation. Studies show green logistics can cut greenhouse gas emissions by up to 30%, making it a vital strategy for companies aiming to meet environmental regulations and improve corporate sustainability.
Cost Analysis: Green vs Standard Logistics
Green logistics often incurs higher upfront costs due to investments in eco-friendly technologies, sustainable transportation modes, and energy-efficient infrastructure. Standard logistics typically has lower initial expenses but may face increasing long-term costs related to fuel consumption, regulatory penalties, and environmental impact mitigation. Cost analysis reveals that while green logistics demands greater capital expenditure, it offers potential savings through reduced fuel usage, lower carbon taxes, and improved brand value over time.
Technology Integration in Both Approaches
Green logistics leverages advanced technologies like IoT sensors, AI-driven route optimization, and electric vehicle fleets to minimize environmental impact and improve energy efficiency. Standard logistics primarily relies on traditional software systems for inventory management and transportation but often lacks integration with sustainable technologies. The contrast highlights how technology integration in green logistics fosters reduced carbon emissions and resource conservation, whereas standard logistics focuses more on operational efficiency without emphasizing ecological sustainability.
Regulatory and Compliance Differences
Green logistics requires adherence to stricter environmental regulations such as the EU Emission Trading System (ETS) and the IMO's sulfur cap for marine fuels, targeting reduction in carbon emissions and pollution. Standard logistics primarily follows general transportation, safety, and customs regulations without mandatory environmental impact constraints. Compliance in green logistics involves ongoing monitoring and reporting of sustainability metrics, often supported by certifications like ISO 14001, whereas standard logistics focuses more on operational efficiency and legal transportation standards.
Supply Chain Efficiency and Sustainability
Green logistics integrates eco-friendly practices such as optimized route planning and energy-efficient transportation to reduce carbon emissions and improve supply chain efficiency. Standard logistics typically prioritize cost and speed, often neglecting environmental impact, which can lead to higher resource consumption and waste. Embracing green logistics enhances sustainability by minimizing the ecological footprint while maintaining or even boosting overall supply chain performance and resilience.
Challenges in Implementing Green Logistics
Implementing green logistics faces challenges such as high initial investment costs in eco-friendly technologies, difficulty in integrating sustainable practices within existing supply chain frameworks, and regulatory complexities across different regions. Companies often struggle with balancing cost-efficiency and environmental impact while ensuring compliance with evolving environmental standards. Limited availability of green infrastructure and lack of widespread stakeholder awareness further complicate the transition from standard logistics to greener alternatives.
Future Trends in Industrial Logistics
Green logistics prioritizes sustainability by integrating eco-friendly practices such as reducing carbon emissions, optimizing energy consumption, and utilizing renewable resources, paving the way for future trends like electric transportation and circular supply chains. Standard logistics primarily focuses on cost-efficiency, speed, and volume management, often relying on traditional fuel-based transportation and fixed supply routes, which are gradually becoming less competitive as environmental regulations tighten. The industrial logistics sector is increasingly shifting toward green logistics innovations including smart warehousing, real-time data analytics for minimizing waste, and automated electric fleets to meet evolving regulatory demands and consumer expectations for environmental responsibility.
Carbon footprint analysis
Green logistics reduces carbon footprints by optimizing transportation routes and utilizing eco-friendly vehicles, whereas standard logistics typically results in higher emissions due to inefficient processes and reliance on fossil fuels.
Reverse logistics
Green logistics emphasizes sustainable reverse logistics practices by minimizing environmental impact through efficient waste reduction and recycling, unlike standard logistics which primarily focuses on cost and speed.
Eco-efficient transportation
Green logistics prioritizes eco-efficient transportation by minimizing carbon emissions and optimizing fuel consumption compared to standard logistics, which often lack sustainability measures.
Supply chain decarbonization
Green logistics reduces carbon emissions by integrating sustainable practices such as electric transportation and energy-efficient warehousing, significantly advancing supply chain decarbonization compared to standard logistics.
Lean logistics
Lean logistics in green logistics reduces waste and energy consumption, optimizing resource efficiency compared to standard logistics processes.
Sustainable warehousing
Green logistics emphasizes sustainable warehousing by implementing energy-efficient technologies, waste reduction strategies, and eco-friendly materials to minimize environmental impact compared to standard logistics practices.
Life cycle assessment (LCA)
Green logistics reduces environmental impact by integrating Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) to evaluate and minimize carbon emissions, energy use, and waste across all stages, unlike standard logistics which often neglects comprehensive environmental evaluation.
Green supply chain management (GSCM)
Green logistics in Green Supply Chain Management (GSCM) prioritizes eco-friendly practices such as carbon footprint reduction, waste minimization, and sustainable resource use, contrasting with standard logistics' conventional focus on cost and efficiency.
Regulatory compliance (environmental)
Green logistics ensures strict adherence to environmental regulations by minimizing carbon emissions and waste, whereas standard logistics often prioritizes cost and speed with less emphasis on regulatory environmental compliance.
Emissions reduction initiatives
Green logistics implements advanced emissions reduction initiatives such as electric vehicle fleets, route optimization, and renewable energy-powered warehouses, significantly lowering carbon footprints compared to standard logistics practices.
Green logistics vs Standard logistics Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com