Cloud manufacturing offers scalable resources, real-time data access, and improved collaboration across geographically dispersed teams, enhancing operational efficiency. On-premise manufacturing provides greater control over proprietary data and infrastructure but requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Choosing between cloud and on-premise depends on factors such as cost, security requirements, and flexibility needs.
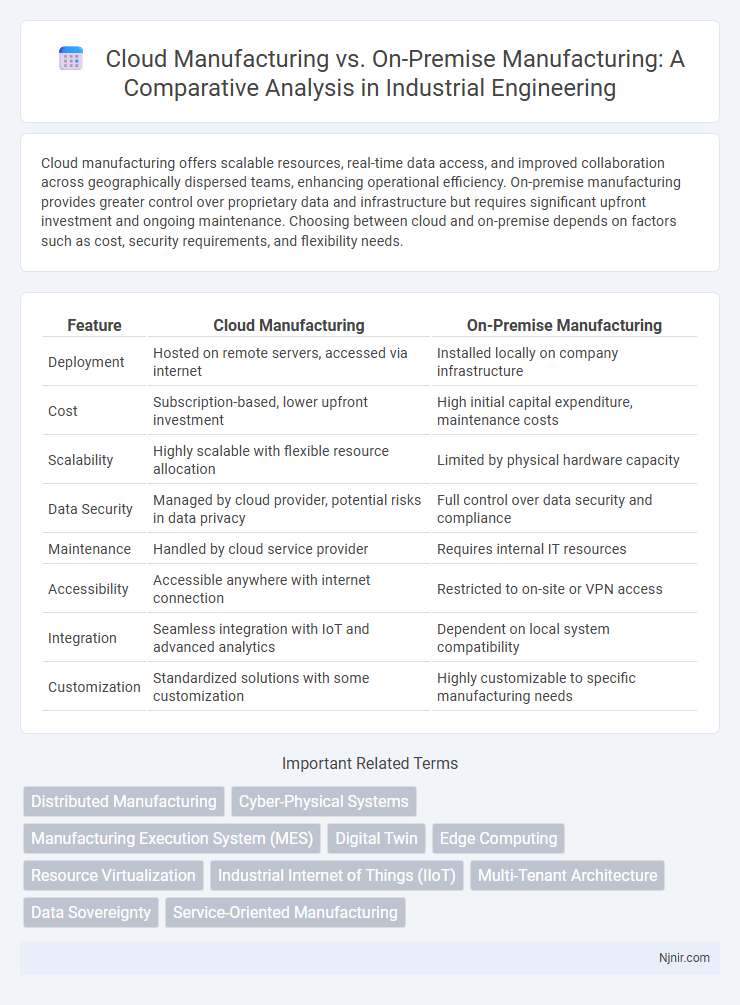
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cloud Manufacturing | On-Premise Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Hosted on remote servers, accessed via internet | Installed locally on company infrastructure |
| Cost | Subscription-based, lower upfront investment | High initial capital expenditure, maintenance costs |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with flexible resource allocation | Limited by physical hardware capacity |
| Data Security | Managed by cloud provider, potential risks in data privacy | Full control over data security and compliance |
| Maintenance | Handled by cloud service provider | Requires internal IT resources |
| Accessibility | Accessible anywhere with internet connection | Restricted to on-site or VPN access |
| Integration | Seamless integration with IoT and advanced analytics | Dependent on local system compatibility |
| Customization | Standardized solutions with some customization | Highly customizable to specific manufacturing needs |
Overview of Cloud Manufacturing and On-Premise Manufacturing
Cloud manufacturing leverages internet-connected platforms to provide scalable, flexible resources and real-time data access, enabling remote monitoring and collaboration across global supply chains. On-premise manufacturing relies on local infrastructure and physical equipment, offering greater control and security at the cost of limited scalability and higher capital expenditure. The cloud model integrates IoT, big data, and AI technologies for enhanced production efficiency, whereas on-premise systems depend on traditional automation and localized data processing.
Key Differences between Cloud and On-Premise Manufacturing
Cloud manufacturing leverages internet-based platforms to provide scalable, flexible access to manufacturing resources and data, enhancing collaboration and real-time monitoring across global locations. On-premise manufacturing relies on localized, in-house infrastructure offering more direct control, data security, and customization tailored to specific operational needs. Key differences include deployment speed, with cloud solutions enabling rapid scalability, and cost structure, where cloud reduces upfront capital expenses compared to the higher initial investment required for on-premise systems.
Scalability and Flexibility in Manufacturing Systems
Cloud manufacturing offers superior scalability by enabling manufacturers to rapidly allocate computing resources and production capacity on-demand, adapting to fluctuating market demands without significant upfront investment. Flexibility is enhanced through cloud-based platforms that support real-time data integration, remote monitoring, and seamless collaboration across global supply chains. In contrast, on-premise manufacturing systems often face limitations in scaling due to fixed infrastructure and require substantial time and capital to adjust production capabilities or implement technology upgrades.
Cost Analysis: Cloud vs. On-Premise Manufacturing Solutions
Cloud manufacturing solutions offer lower upfront capital expenditure by eliminating the need for expensive hardware and infrastructure investments typical in on-premise setups. Operational costs in cloud models are often more predictable and scalable, as businesses pay based on usage, while on-premise solutions incur ongoing expenses like maintenance, power, and dedicated IT staff. Long-term cost analysis frequently favors cloud manufacturing due to reduced downtime, faster deployment, and the ability to quickly adapt resource allocation according to demand fluctuations.
Security Considerations in Cloud and On-Premise Environments
Cloud manufacturing offers scalable security with advanced encryption, continuous monitoring, and centralized access controls, but relies heavily on third-party providers for data protection and compliance. On-premise manufacturing provides direct control over security infrastructure, enabling tailored safeguards and physical access restrictions while often facing higher costs and complexity in maintaining up-to-date defenses. Evaluating risk tolerance and regulatory requirements is critical in choosing between the flexible security model of cloud environments and the controlled, isolated security of on-premise setups.
Integration with Industrial IoT and Smart Devices
Cloud manufacturing offers seamless integration with Industrial IoT and smart devices through centralized data platforms, enabling real-time analytics and remote monitoring. On-premise manufacturing often faces challenges in scaling IoT integrations due to limited infrastructure and higher maintenance costs for smart device connectivity. The cloud's ability to aggregate and process large volumes of sensor data enhances predictive maintenance and operational efficiency compared to traditional on-site systems.
Data Accessibility and Real-Time Monitoring
Cloud manufacturing offers superior data accessibility by enabling real-time monitoring and remote management through internet connectivity, facilitating instant updates and seamless collaboration across multiple locations. On-premise manufacturing typically restricts data access to local networks, limiting the ability to perform real-time monitoring remotely and often requiring physical presence for system updates or troubleshooting. Enhanced cloud-based platforms integrate IoT sensors and advanced analytics, providing comprehensive visibility into production processes, which significantly improves decision-making and operational efficiency compared to traditional on-premise setups.
Implementation Challenges and Migration Strategies
Cloud manufacturing faces implementation challenges such as data security concerns, integration complexity with legacy systems, and dependency on reliable internet connectivity. Migration strategies emphasize phased adoption, comprehensive data backup, and hybrid cloud models to ensure seamless transition and minimize operational disruptions. On-premise manufacturing requires extensive upfront infrastructure investment and manual updates, making gradual migration to cloud-based solutions critical for maintaining production continuity.
Maintenance, Upgrades, and Support Comparison
Cloud manufacturing offers seamless maintenance through automated updates and remote diagnostics, significantly reducing downtime compared to on-premise setups that require manual intervention and on-site technician visits. Upgrades in cloud systems are implemented centrally, ensuring immediate access to the latest features and security patches, whereas on-premise manufacturing faces delayed upgrade cycles due to hardware dependencies and complex installations. Support for cloud manufacturing includes 24/7 vendor assistance and real-time monitoring, while on-premise support often involves limited hours and slower response times due to localized resource constraints.
Future Trends in Cloud and On-Premise Manufacturing
Cloud manufacturing leverages IoT, AI, and big data analytics to enable real-time collaboration, scalability, and cost-efficiency, driving its adoption in smart factories and Industry 4.0. On-premise manufacturing continues to evolve with advanced automation, edge computing, and enhanced cybersecurity to maintain control over sensitive data and ensure low-latency operations. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach combining cloud flexibility and on-premise reliability for optimized production workflows and innovation acceleration.
Distributed Manufacturing
Cloud manufacturing enables scalable, real-time collaboration and resource sharing across distributed manufacturing networks, while on-premise manufacturing limits production to localized facilities with higher upfront costs and reduced flexibility.
Cyber-Physical Systems
Cloud manufacturing enhances Cyber-Physical Systems by enabling real-time data integration, scalability, and remote monitoring, unlike on-premise manufacturing which relies on localized CPS networks with limited flexibility and higher maintenance costs.
Manufacturing Execution System (MES)
Cloud-based Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) offer scalable, real-time data access and remote monitoring, enhancing flexibility and reducing IT infrastructure costs compared to traditional on-premise MES solutions that require substantial upfront investment and maintenance.
Digital Twin
Cloud manufacturing leverages digital twin technology for real-time, scalable, and remote monitoring, while on-premise manufacturing employs digital twins primarily for localized, detailed simulation and predictive maintenance.
Edge Computing
Edge computing in cloud manufacturing enhances real-time data processing and scalability, outperforming on-premise manufacturing systems limited by localized resources and slower decision-making.
Resource Virtualization
Cloud manufacturing leverages resource virtualization to optimize scalability and remote access, whereas on-premise manufacturing relies on physical resource allocation, limiting flexibility and real-time resource sharing.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
Cloud manufacturing leverages Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) for real-time data analytics, remote monitoring, and scalable resource allocation, whereas on-premise manufacturing relies on localized IIoT infrastructure with limited scalability and higher maintenance costs.
Multi-Tenant Architecture
Cloud manufacturing utilizes a multi-tenant architecture enabling scalable resource sharing and real-time collaboration, whereas on-premise manufacturing relies on isolated, single-tenant systems with limited flexibility and higher maintenance costs.
Data Sovereignty
Cloud manufacturing offers scalable resources but raises complex data sovereignty issues due to cross-border data storage, whereas on-premise manufacturing ensures complete control and compliance by keeping data within local jurisdictions.
Service-Oriented Manufacturing
Cloud manufacturing leverages Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) to provide scalable, flexible, and real-time access to manufacturing resources and services, whereas On-premise manufacturing relies on localized, fixed infrastructure limiting adaptability and remote collaboration.
Cloud manufacturing vs On-premise manufacturing Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com