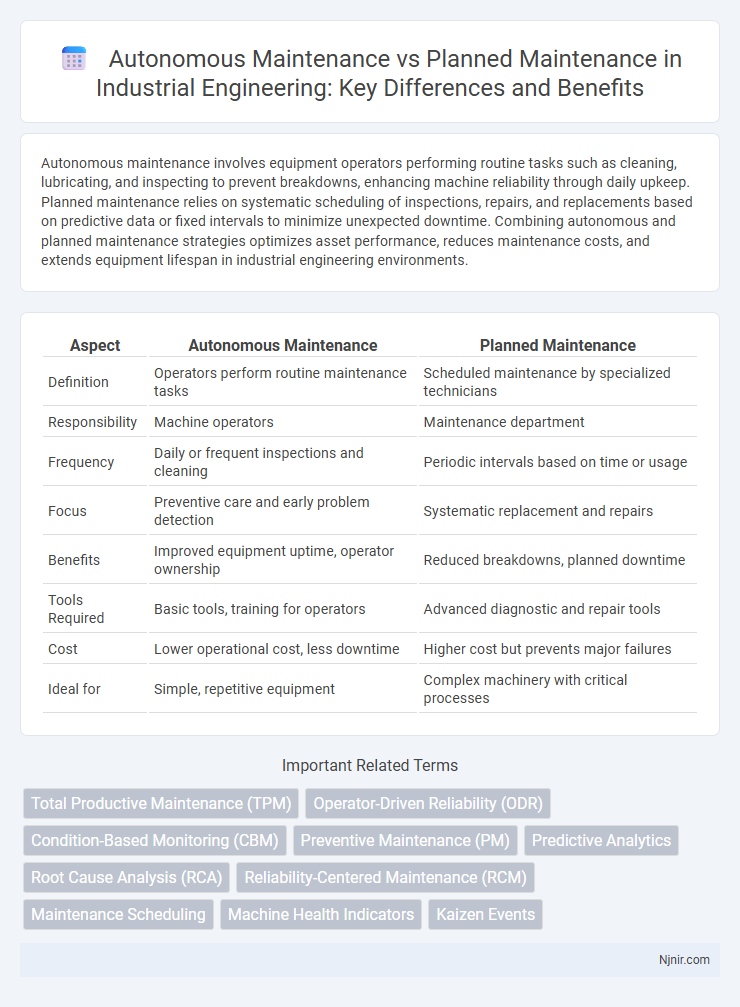
Autonomous maintenance involves equipment operators performing routine tasks such as cleaning, lubricating, and inspecting to prevent breakdowns, enhancing machine reliability through daily upkeep. Planned maintenance relies on systematic scheduling of inspections, repairs, and replacements based on predictive data or fixed intervals to minimize unexpected downtime. Combining autonomous and planned maintenance strategies optimizes asset performance, reduces maintenance costs, and extends equipment lifespan in industrial engineering environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Autonomous Maintenance | Planned Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Operators perform routine maintenance tasks | Scheduled maintenance by specialized technicians |
| Responsibility | Machine operators | Maintenance department |
| Frequency | Daily or frequent inspections and cleaning | Periodic intervals based on time or usage |
| Focus | Preventive care and early problem detection | Systematic replacement and repairs |
| Benefits | Improved equipment uptime, operator ownership | Reduced breakdowns, planned downtime |
| Tools Required | Basic tools, training for operators | Advanced diagnostic and repair tools |
| Cost | Lower operational cost, less downtime | Higher cost but prevents major failures |
| Ideal for | Simple, repetitive equipment | Complex machinery with critical processes |
Defining Autonomous Maintenance in Industrial Engineering
Autonomous maintenance in industrial engineering empowers operators to take ownership of routine equipment care, including cleaning, lubrication, and basic inspections, to prevent breakdowns and optimize machine performance. This approach contrasts with planned maintenance, which involves scheduled, specialized interventions performed by maintenance professionals. Implementing autonomous maintenance enhances equipment reliability, reduces downtime, and fosters continuous improvement in manufacturing processes.
Understanding Planned Maintenance Strategies
Planned maintenance strategies encompass preventive, predictive, and condition-based techniques designed to schedule maintenance activities in advance, reducing unexpected equipment failures and downtime. Understanding these strategies involves analyzing asset criticality, failure patterns, and maintenance costs to optimize resource allocation and extend equipment lifespan. Implementing a robust planned maintenance program improves operational efficiency by systematically addressing wear and tear before breakdowns occur.
Key Differences between Autonomous and Planned Maintenance
Autonomous maintenance empowers operators to perform routine upkeep tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection without waiting for specialized technicians, enhancing equipment reliability and detecting issues early. Planned maintenance follows a scheduled approach based on time or usage intervals, involving professional technicians conducting preventive tasks to minimize unexpected breakdowns. The key difference lies in autonomy and responsibility: autonomous maintenance decentralizes daily maintenance to operators, while planned maintenance relies on expert intervention according to a predefined schedule.
Benefits of Autonomous Maintenance for Manufacturers
Autonomous maintenance empowers manufacturers by enabling operators to perform routine equipment inspections, cleaning, and minor repairs, which reduces downtime and enhances machine reliability. This proactive approach fosters greater operator engagement, leading to early detection of potential issues and decreased dependence on specialized maintenance teams. The result is improved overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), cost savings from reduced breakdowns, and extended machinery lifespan.
Advantages of Planned Maintenance in Industrial Settings
Planned maintenance in industrial settings increases equipment reliability by scheduling regular inspections and repairs, minimizing unexpected breakdowns and costly downtime. It optimizes resource allocation through pre-arranged labor and parts availability, reducing emergency maintenance expenses. Enhanced safety protocols are enforced systematically, lowering the risk of accidents and extending machinery lifespan.
Impact on Equipment Reliability and Performance
Autonomous maintenance empowers operators to perform routine inspections and basic upkeep, leading to early detection of potential issues and reducing unexpected equipment failures, thereby enhancing equipment reliability and consistent performance. Planned maintenance involves scheduled interventions based on time or usage metrics, ensuring systematic component replacements and servicing, which extends asset lifespan and prevents breakdowns through proactive care. Combining both strategies often yields optimal equipment reliability by balancing operator vigilance with expert maintenance precision, minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency.
Workforce Involvement in Maintenance Approaches
Autonomous maintenance empowers operators to take an active role in routine upkeep by performing tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and minor repairs, which fosters a deeper understanding of equipment and reduces downtime. Planned maintenance, on the other hand, relies on trained maintenance professionals executing scheduled inspections and repairs, ensuring systematic upkeep and technical expertise. Workforce involvement in autonomous maintenance improves equipment reliability through operator accountability, whereas planned maintenance emphasizes specialized skills and preventive strategies.
Cost Implications: Autonomous vs. Planned Maintenance
Autonomous maintenance reduces labor costs by empowering operators to perform routine tasks, minimizing the need for specialized technician intervention and lowering downtime expenses. Planned maintenance involves scheduled inspections and repairs by trained maintenance personnel, often incurring higher labor and parts costs but reducing the risk of unexpected failures. Cost implications vary as autonomous maintenance can decrease immediate operational expenses, while planned maintenance may offer long-term cost savings by preventing major equipment breakdowns.
Integrating Both Maintenance Systems for Optimal Results
Integrating autonomous maintenance, where operators perform routine upkeep, with planned maintenance schedules enhances equipment reliability and reduces downtime. Combining real-time machine condition monitoring from autonomous maintenance with data-driven interventions in planned maintenance ensures early fault detection and optimized resource allocation. This synergy maximizes operational efficiency by balancing proactive operator involvement and systematic, expert-driven maintenance.
Future Trends in Maintenance Techniques in Industrial Engineering
Autonomous maintenance leverages operator-driven routine inspections and upkeep, enhancing equipment reliability through real-time condition monitoring and predictive analytics integration. Planned maintenance relies on scheduled interventions based on historical data and machine learning algorithms, optimizing maintenance windows to minimize downtime. Future trends emphasize hybrid frameworks combining AI-driven predictive insights with operator autonomy, advancing Industry 4.0 standards for smarter, adaptive maintenance strategies in industrial engineering.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Autonomous maintenance empowers operators to perform routine upkeep and early defect detection, enhancing Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) by reducing downtime, while planned maintenance schedules expert interventions to address complex repairs and preventive tasks.
Operator-Driven Reliability (ODR)
Operator-Driven Reliability (ODR) enhances Autonomous Maintenance by empowering operators to perform routine inspections and minor repairs, reducing downtime compared to Scheduled Planned Maintenance.
Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM)
Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM) enhances autonomous maintenance by enabling real-time asset health assessment, reducing unplanned downtime compared to traditional planned maintenance schedules.
Preventive Maintenance (PM)
Autonomous maintenance empowers operators to perform routine Preventive Maintenance (PM) tasks, improving equipment reliability and reducing downtime, while Planned Maintenance relies on scheduled interventions by specialized technicians to systematically prevent equipment failure.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics enhances autonomous maintenance by enabling real-time equipment condition monitoring and early fault detection, whereas planned maintenance relies on scheduled interventions without continuous data-driven insights.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Autonomous maintenance empowers operators to perform daily root cause analysis (RCA) for immediate issue resolution, while planned maintenance relies on scheduled RCA by specialists to prevent long-term equipment failures.
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM)
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) emphasizes integrating Autonomous Maintenance and Planned Maintenance to enhance equipment reliability by empowering operators with proactive upkeep tasks while scheduling expert interventions based on critical failure analysis.
Maintenance Scheduling
Autonomous maintenance empowers operators to perform routine upkeep, reducing scheduled downtime and enhancing flexibility, while planned maintenance relies on predefined schedules and professional technicians to ensure optimal equipment reliability and prevent unexpected failures.
Machine Health Indicators
Autonomous maintenance improves machine health indicators by enabling operators to perform regular inspections and basic upkeep, while planned maintenance relies on scheduled interventions based on predictive data to optimize machine performance and prevent breakdowns.
Kaizen Events
Kaizen Events in autonomous maintenance empower operators to identify and resolve equipment issues proactively, while planned maintenance relies on scheduled interventions to prevent breakdowns.
Autonomous maintenance vs Planned maintenance Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com