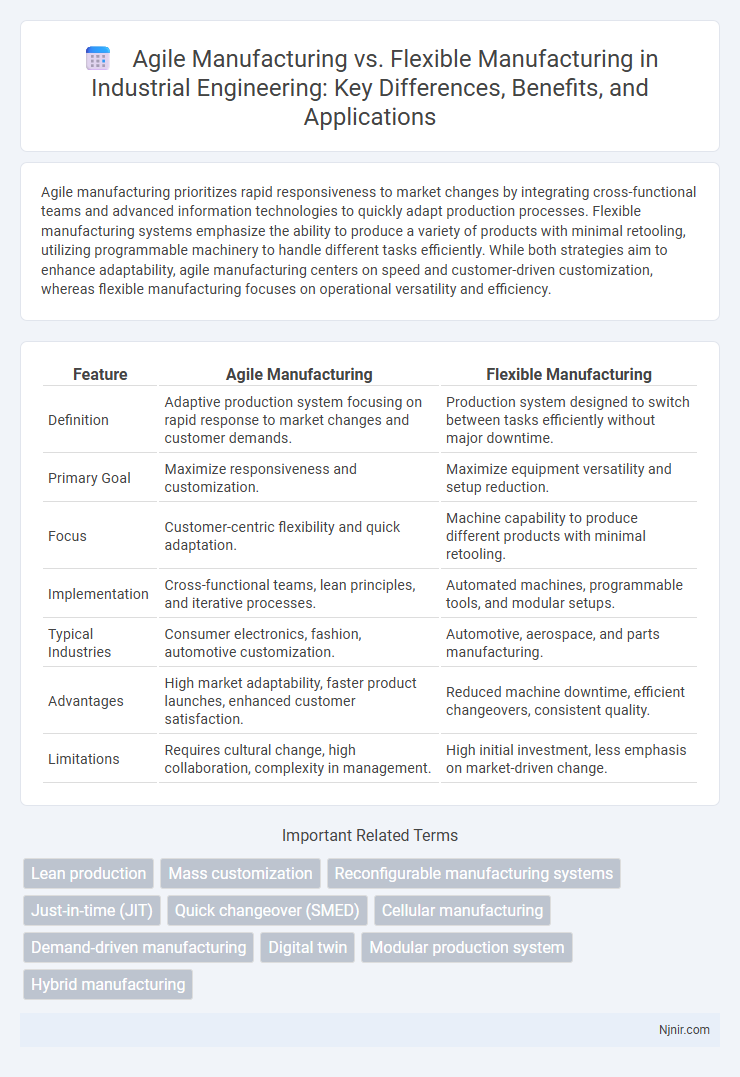
Agile manufacturing prioritizes rapid responsiveness to market changes by integrating cross-functional teams and advanced information technologies to quickly adapt production processes. Flexible manufacturing systems emphasize the ability to produce a variety of products with minimal retooling, utilizing programmable machinery to handle different tasks efficiently. While both strategies aim to enhance adaptability, agile manufacturing centers on speed and customer-driven customization, whereas flexible manufacturing focuses on operational versatility and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Agile Manufacturing | Flexible Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adaptive production system focusing on rapid response to market changes and customer demands. | Production system designed to switch between tasks efficiently without major downtime. |
| Primary Goal | Maximize responsiveness and customization. | Maximize equipment versatility and setup reduction. |
| Focus | Customer-centric flexibility and quick adaptation. | Machine capability to produce different products with minimal retooling. |
| Implementation | Cross-functional teams, lean principles, and iterative processes. | Automated machines, programmable tools, and modular setups. |
| Typical Industries | Consumer electronics, fashion, automotive customization. | Automotive, aerospace, and parts manufacturing. |
| Advantages | High market adaptability, faster product launches, enhanced customer satisfaction. | Reduced machine downtime, efficient changeovers, consistent quality. |
| Limitations | Requires cultural change, high collaboration, complexity in management. | High initial investment, less emphasis on market-driven change. |
Introduction to Agile and Flexible Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing emphasizes rapid response to changing market demands by integrating advanced technologies and collaborative processes to enhance product customization and speed. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) focus on the ability to adapt machinery and workflows to produce different products with minimal downtime, improving efficiency in varied production runs. Both approaches prioritize adaptability but differ in scope; agile manufacturing addresses overall business responsiveness while flexible manufacturing concentrates on technical versatility within production operations.
Core Principles of Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing emphasizes rapid response to customer needs and market changes through principles such as collaboration, modularity, and adaptability, enabling companies to quickly reconfigure processes and products. It prioritizes cross-functional teams, information sharing, and continuous improvement to enhance innovation and reduce lead times. Unlike flexible manufacturing, which focuses mainly on equipment versatility to handle various products, agile manufacturing integrates organizational and technological agility for a holistic, customer-driven approach.
Fundamentals of Flexible Manufacturing Systems
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) prioritize adaptability by integrating automated machinery, computer-controlled processes, and robotics to accommodate varying product types and volumes with minimal downtime. Unlike Agile Manufacturing, which emphasizes rapid response and customer-driven customization, FMS focuses on efficiency through the reconfiguration of manufacturing cells and tooling to handle different tasks without extensive manual intervention. Core components of FMS include automated material handling, real-time monitoring, and programmable logic controllers that collectively enhance production flexibility and operational cost-effectiveness.
Key Differences: Agile vs Flexible Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing emphasizes rapid responsiveness to customer demands and market changes by integrating cross-functional teams and adaptive processes, while flexible manufacturing focuses on the efficient reconfiguration of equipment and production lines to handle varying product types with minimal downtime. Agile systems prioritize speed and collaboration to quickly develop and deliver customized products, whereas flexible manufacturing prioritizes operational versatility and cost-effectiveness through automated tooling and modular machinery. Key differences include agility's emphasis on market-driven adaptability versus flexibility's focus on technical adaptability and production efficiency.
Benefits of Agile Manufacturing in Industry
Agile manufacturing enhances industry responsiveness by enabling rapid adaptation to changing market demands and customer preferences, resulting in reduced lead times and increased product customization. This approach drives cost efficiency through minimized inventory levels and quicker production cycles, boosting overall operational agility. Companies leveraging agile manufacturing often experience improved competitive advantage by fostering innovation and accelerating product development processes.
Advantages of Flexible Manufacturing Approaches
Flexible manufacturing offers significant advantages by enabling rapid adaptation to product variations and fluctuations in demand, reducing downtime and increasing production efficiency. It supports customized production without extensive retooling, which lowers costs and improves response times in dynamic markets. Enhanced scalability and integration with advanced technologies make flexible manufacturing ideal for industries requiring agility and precision.
Technology Enablers for Agile and Flexible Manufacturing
Technology enablers for agile manufacturing include advanced robotics, IoT sensors, and real-time data analytics platforms that facilitate rapid reconfiguration and adaptive decision-making. Flexible manufacturing relies on CNC machines, modular automation, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to efficiently produce varied product mixes with minimal downtime. Both systems leverage digital twin technology and cloud-based manufacturing execution systems (MES) to optimize production responsiveness and customization.
Challenges in Implementing Agile vs Flexible Systems
Implementing Agile manufacturing systems faces challenges such as rapidly adapting to changing customer demands and integrating cross-functional teams while maintaining efficient workflows. Flexible manufacturing systems confront difficulties in managing complex machinery setups and ensuring seamless reconfiguration for various product types. Both approaches require significant investment in advanced technology and skilled labor to overcome operational complexity and maintain production consistency.
Case Studies: Real-World Industry Applications
Agile manufacturing is demonstrated by companies like Boeing, which employs rapid reconfiguration of production lines to meet fluctuating demand for aircraft customization. Flexible manufacturing is exemplified by Toyota's production system, allowing seamless switching between different vehicle models without significant downtime. Case studies reveal that agile systems prioritize responsiveness and customer-driven adaptation, while flexible systems focus on equipment versatility and efficient changeover.
Future Trends in Manufacturing Flexibility and Agility
Future trends in manufacturing flexibility and agility emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, IoT, and digital twins to enhance real-time responsiveness and customization. Agile manufacturing prioritizes rapid adaptation to market changes through modular production systems and collaborative networks, while flexible manufacturing focuses on versatile equipment capable of handling diverse product variations efficiently. The convergence of these approaches drives the evolution of smart factories, enabling seamless transitions between product lines and accelerating innovation cycles.
Lean production
Agile manufacturing emphasizes rapid responsiveness to market changes through customer-driven adaptability, while flexible manufacturing prioritizes equipment versatility and efficiency, both integral to Lean production by minimizing waste and maximizing value.
Mass customization
Agile manufacturing excels in delivering mass customization through rapid responsiveness and adaptability to customer demands, while flexible manufacturing emphasizes versatile machinery and processes to efficiently produce varied product types at scale.
Reconfigurable manufacturing systems
Reconfigurable manufacturing systems (RMS) enhance agile manufacturing by enabling rapid adaptability to product changes, contrasting with flexible manufacturing's emphasis on broad process versatility across multiple product types.
Just-in-time (JIT)
Agile manufacturing enhances Just-in-Time (JIT) efficiency by rapidly adapting to market changes, while flexible manufacturing supports JIT through versatile production systems capable of handling variable product types and volumes.
Quick changeover (SMED)
Agile manufacturing leverages Quick Changeover (SMED) techniques to rapidly switch production lines and meet dynamic customer demands, while flexible manufacturing employs SMED primarily to enhance machine versatility and reduce downtime across varied product types.
Cellular manufacturing
Cellular manufacturing enhances Agile manufacturing by organizing workstations into self-contained cells to optimize flexibility and efficiency, contrasting with Flexible manufacturing systems that rely on programmable machines for broader product variations.
Demand-driven manufacturing
Agile manufacturing rapidly responds to fluctuating customer demands through flexible processes and workforce, while flexible manufacturing emphasizes adaptable machinery and equipment to efficiently handle varied product types in demand-driven production environments.
Digital twin
Digital twin technology enhances Agile manufacturing by providing real-time virtual simulations for rapid adaptation, while in Flexible manufacturing it supports equipment reconfiguration through detailed digital replicas.
Modular production system
Agile manufacturing excels in rapid market response through modular production systems designed for quick reconfiguration, whereas flexible manufacturing prioritizes efficient adaptation to varying product types using modular machinery for seamless production changes.
Hybrid manufacturing
Hybrid manufacturing combines Agile manufacturing's adaptability and Flexible manufacturing's versatility to optimize production responsiveness and efficiency.
Agile manufacturing vs Flexible manufacturing Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com