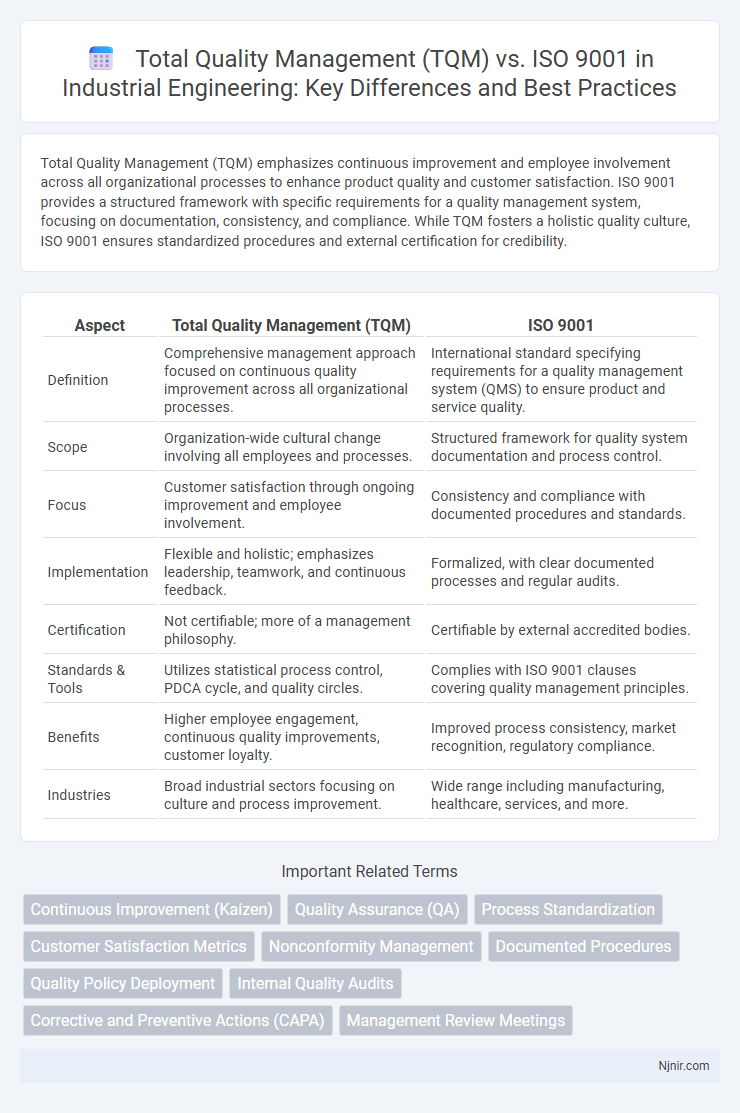
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement across all organizational processes to enhance product quality and customer satisfaction. ISO 9001 provides a structured framework with specific requirements for a quality management system, focusing on documentation, consistency, and compliance. While TQM fosters a holistic quality culture, ISO 9001 ensures standardized procedures and external certification for credibility.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Total Quality Management (TQM) | ISO 9001 |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive management approach focused on continuous quality improvement across all organizational processes. | International standard specifying requirements for a quality management system (QMS) to ensure product and service quality. |
| Scope | Organization-wide cultural change involving all employees and processes. | Structured framework for quality system documentation and process control. |
| Focus | Customer satisfaction through ongoing improvement and employee involvement. | Consistency and compliance with documented procedures and standards. |
| Implementation | Flexible and holistic; emphasizes leadership, teamwork, and continuous feedback. | Formalized, with clear documented processes and regular audits. |
| Certification | Not certifiable; more of a management philosophy. | Certifiable by external accredited bodies. |
| Standards & Tools | Utilizes statistical process control, PDCA cycle, and quality circles. | Complies with ISO 9001 clauses covering quality management principles. |
| Benefits | Higher employee engagement, continuous quality improvements, customer loyalty. | Improved process consistency, market recognition, regulatory compliance. |
| Industries | Broad industrial sectors focusing on culture and process improvement. | Wide range including manufacturing, healthcare, services, and more. |
Overview of Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a comprehensive organizational approach focused on continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and employee involvement across all processes. It emphasizes proactive quality control through systematic efforts to integrate quality principles into the culture and operations of the company. Unlike ISO 9001, which is a standardized certification framework, TQM operates as a holistic management philosophy without a formal certification process.
Introduction to ISO 9001 Standards
ISO 9001 is an internationally recognized standard that specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS) to enhance customer satisfaction and ensure consistent product quality. Unlike Total Quality Management (TQM), which emphasizes continuous organization-wide improvement and employee involvement, ISO 9001 provides a formalized framework that organizations can be certified against to demonstrate compliance. The ISO 9001 standard focuses on process approach, risk-based thinking, and leadership commitment to achieve effective quality management and continual improvement.
Core Principles of TQM
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement, customer focus, employee involvement, and process-centered approaches as its core principles, fostering a culture of quality at every organizational level. ISO 9001, a standardized quality management system, provides specific requirements for consistent quality processes but does not inherently encompass the broad cultural and philosophical aspects integral to TQM. Implementing TQM principles ensures an ongoing commitment to quality that extends beyond the compliance framework of ISO 9001 certification.
Key Requirements of ISO 9001
ISO 9001 emphasizes defining a quality management system with a strong focus on customer satisfaction, process approach, and continuous improvement, requiring documented procedures, risk-based thinking, and leadership commitment. Key requirements include establishing a quality policy, setting measurable quality objectives, conducting internal audits, and managing nonconformities effectively to ensure product and service consistency. TQM shares similar goals but is broader in philosophy, while ISO 9001 provides a standardized framework with specific documentation and certification criteria.
TQM vs ISO 9001: Main Differences
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes a holistic, continuous improvement culture involving all employees, whereas ISO 9001 provides a standardized framework for quality management systems with specific requirements. TQM focuses on long-term organizational change and customer satisfaction through employee participation, while ISO 9001 certification ensures consistent processes and compliance with internationally recognized quality standards. The main differences lie in TQM's broader cultural approach versus ISO 9001's prescriptive, audit-based methodology.
Implementation Processes Compared
Total Quality Management (TQM) implementation focuses on continuous organizational improvement through employee involvement, cultural change, and customer satisfaction, embedding quality in every process. ISO 9001 implementation centers on establishing a documented quality management system (QMS) with standardized procedures, risk management, and compliance with specific requirements validated through audits. Both approaches emphasize process control and quality enhancement, but ISO 9001 demands formal certification, while TQM promotes a more holistic, flexible culture of quality improvement.
Benefits of TQM in Industrial Engineering
Total Quality Management (TQM) in industrial engineering enhances process efficiency by promoting continuous improvement and worker involvement, leading to reduced waste and higher product quality. TQM fosters a culture of quality across all organizational levels, improving customer satisfaction and operational performance beyond compliance standards. Unlike ISO 9001, which provides a formalized quality management framework, TQM offers a holistic approach that integrates quality into daily workflows for sustained competitiveness.
Advantages of ISO 9001 Certification
ISO 9001 certification offers standardized framework for quality management that is recognized internationally, enhancing credibility and customer confidence. It facilitates consistent process control, documentation, and continuous improvement, leading to higher operational efficiency and reduced defects. Compared to Total Quality Management (TQM), ISO 9001 provides clear requirements and external auditing, making it easier for organizations to demonstrate compliance and achieve competitive advantage in global markets.
Challenges in Adopting TQM and ISO 9001
Organizations face significant challenges in adopting Total Quality Management (TQM) and ISO 9001, including cultural resistance to change and the extensive training requirements necessary for effective implementation. TQM demands a continuous commitment to quality improvement across all organizational levels, which can be difficult to sustain in environments lacking leadership support or employee engagement. In contrast, ISO 9001 focuses on standardized processes and documentation, but ensuring compliance can be resource-intensive and may encounter difficulties in aligning rigid requirements with dynamic business practices.
Choosing Between TQM and ISO 9001 for Industrial Organizations
Industrial organizations evaluating quality frameworks often compare Total Quality Management (TQM) and ISO 9001 to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. TQM emphasizes a holistic approach involving continuous improvement and employee involvement across all organizational levels, fostering a culture of quality. ISO 9001 provides a standardized, certifiable quality management system focusing on documented processes and compliance, which can streamline audits and improve customer trust in regulated industries.
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement through Kaizen as a core philosophy, while ISO 9001 provides a structured framework that incorporates continuous improvement requirements to enhance quality management systems.
Quality Assurance (QA)
Total Quality Management (TQM) provides a comprehensive, organization-wide approach to Quality Assurance emphasizing continuous improvement and employee involvement, while ISO 9001 establishes a standardized, certification-based Quality Management System focusing on consistent process documentation and compliance.
Process Standardization
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous process improvement and employee involvement for quality enhancement, while ISO 9001 provides a formalized, standardized framework for process documentation and consistency across organizational operations.
Customer Satisfaction Metrics
Customer satisfaction metrics in Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasize continuous improvement and employee involvement to enhance customer experience, while ISO 9001 standardizes processes and documentation to consistently meet customer requirements and regulatory standards.
Nonconformity Management
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement in nonconformity management, while ISO 9001 provides a structured framework and standardized processes for identifying, documenting, and correcting nonconformities to ensure consistent quality compliance.
Documented Procedures
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction through broad organizational culture changes, whereas ISO 9001 requires specific documented procedures to ensure consistent quality management system implementation and compliance.
Quality Policy Deployment
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement in Quality Policy Deployment, whereas ISO 9001 provides a structured framework with documented procedures to ensure consistent quality management and policy implementation.
Internal Quality Audits
Internal quality audits in Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasize continuous process improvement and employee involvement, while ISO 9001 audits prioritize standardized compliance with documented quality management system requirements.
Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasizes a continuous improvement culture involving corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) across all organizational processes, while ISO 9001 specifically mandates documented CAPA procedures to systematically identify, address, and prevent nonconformities within a quality management system.
Management Review Meetings
Management review meetings in Total Quality Management (TQM) emphasize continuous improvement and stakeholder involvement, whereas ISO 9001 mandates structured periodic reviews focused on assessing the Quality Management System's effectiveness and compliance.
Total Quality Management (TQM) vs ISO 9001 Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com