Human Factors Engineering emphasizes designing systems and processes that optimize human well-being and overall system performance by integrating psychological, cognitive, and physical considerations. Ergonomics primarily concentrates on the interaction between humans and their physical environment, focusing on improving comfort, posture, and reducing strain or injury risk. Both disciplines overlap but Human Factors Engineering adopts a broader approach by addressing system design, user interaction, and safety in complex industrial operations.
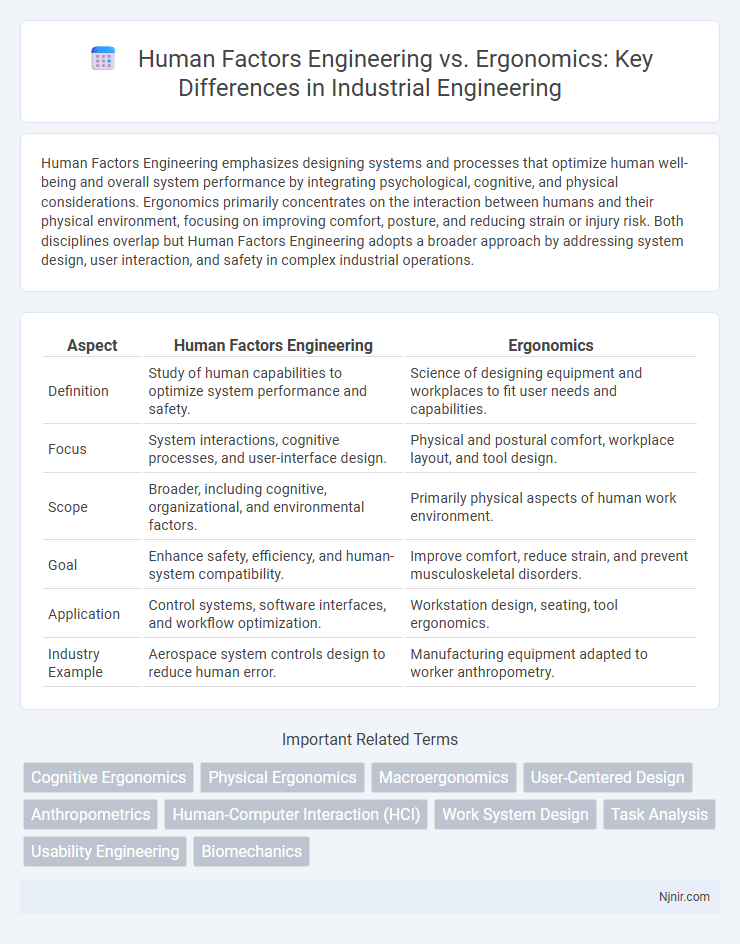
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Human Factors Engineering | Ergonomics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of human capabilities to optimize system performance and safety. | Science of designing equipment and workplaces to fit user needs and capabilities. |
| Focus | System interactions, cognitive processes, and user-interface design. | Physical and postural comfort, workplace layout, and tool design. |
| Scope | Broader, including cognitive, organizational, and environmental factors. | Primarily physical aspects of human work environment. |
| Goal | Enhance safety, efficiency, and human-system compatibility. | Improve comfort, reduce strain, and prevent musculoskeletal disorders. |
| Application | Control systems, software interfaces, and workflow optimization. | Workstation design, seating, tool ergonomics. |
| Industry Example | Aerospace system controls design to reduce human error. | Manufacturing equipment adapted to worker anthropometry. |
Introduction to Human Factors Engineering and Ergonomics
Human Factors Engineering focuses on designing systems, products, and environments optimized for human use, emphasizing cognitive, physical, and organizational interactions. Ergonomics primarily addresses the physical aspects of human interaction with tools and environments, aiming to improve comfort, safety, and performance. Both disciplines integrate human-centered principles to enhance usability and efficiency, but Human Factors Engineering incorporates broader psychological and systemic considerations.
Defining Human Factors Engineering
Human Factors Engineering is the scientific discipline focused on designing systems, products, and environments that optimize human well-being and overall system performance by understanding human capabilities and limitations. It integrates knowledge from psychology, engineering, and design to enhance safety, efficiency, and usability in complex systems such as aviation, healthcare, and manufacturing. Unlike ergonomics, which primarily emphasizes physical comfort and workplace design, Human Factors Engineering encompasses cognitive, organizational, and environmental considerations to improve human-system interaction comprehensively.
Understanding Ergonomics in Industry
Human Factors Engineering and Ergonomics both aim to improve safety, efficiency, and comfort in industrial settings by optimizing the interaction between workers and machines. Ergonomics specifically focuses on designing tools, workstations, and processes that fit human physical capabilities and limitations to prevent workplace injuries and enhance productivity. Industries implementing ergonomic principles see reduced repetitive strain injuries, increased worker satisfaction, and higher operational performance.
Key Principles of Human Factors Engineering
Human Factors Engineering emphasizes designing systems and products based on human capabilities and limitations to optimize performance, safety, and user experience. Key principles include understanding human cognition, applying anthropometric data, and enhancing usability through intuitive interfaces and error reduction strategies. Ergonomics overlaps by focusing on physical interactions between humans and their environments but Human Factors Engineering integrates broader psychological and organizational factors for comprehensive system design.
Core Concepts of Ergonomics
Ergonomics centers on optimizing the interaction between humans and their work environments by studying physical, cognitive, and organizational factors to enhance comfort, safety, and productivity. Core concepts include anthropometry, which involves designing tools and workspaces to fit human body dimensions, and cognitive ergonomics, focusing on mental processes such as perception, memory, and decision-making. Unlike Human Factors Engineering, which integrates system design with human capabilities and limitations, ergonomics specifically targets improving human well-being and system performance through tailored environmental adjustments.
Similarities Between Human Factors Engineering and Ergonomics
Human Factors Engineering and Ergonomics both aim to improve human interaction with systems, products, and environments by optimizing comfort, safety, and performance. They share a focus on analyzing human capabilities and limitations to design tools, workspaces, and processes that reduce errors and enhance efficiency. Both disciplines integrate principles from psychology, physiology, and engineering to create user-centered solutions that promote well-being and productivity.
Major Differences: Human Factors Engineering vs Ergonomics
Human Factors Engineering primarily focuses on designing systems and technology to improve human interaction, emphasizing safety, efficiency, and usability in complex environments. Ergonomics centers on optimizing physical workspaces and tools to enhance comfort, reduce strain, and prevent musculoskeletal disorders. While overlapping, Human Factors Engineering addresses cognitive and system-level considerations, whereas Ergonomics concentrates more on physical and biomechanical aspects.
Applications in Industrial Engineering
Human Factors Engineering and Ergonomics both enhance industrial engineering by optimizing human-machine interactions, improving safety, productivity, and worker comfort. Human Factors Engineering focuses on designing systems and processes tailored to human capabilities and limitations, while Ergonomics centers on workstation design, physical task optimization, and reducing musculoskeletal disorders. Applications include layout planning, control system design, and operator interface development to minimize errors and increase operational efficiency in manufacturing and assembly lines.
Impact on Workplace Safety and Productivity
Human Factors Engineering focuses on designing systems and processes to optimize human well-being and overall system performance, directly reducing workplace errors and accidents. Ergonomics emphasizes the physical interaction between workers and their environment, thereby minimizing musculoskeletal disorders and enhancing comfort, which leads to increased productivity. Both disciplines synergistically improve occupational safety standards and operational efficiency by tailoring tasks, tools, and environments to human capabilities and limitations.
Future Trends in Human Factors and Ergonomics
Future trends in Human Factors Engineering and Ergonomics emphasize integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance adaptive system designs and user experience. Advances in wearable technology and biometric sensors facilitate real-time data collection, enabling personalized ergonomic interventions and predictive analytics. Emphasis on virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications drives more immersive training environments and human-centered product development.
Cognitive Ergonomics
Human Factors Engineering and Ergonomics overlap in optimizing human-system interaction, with Cognitive Ergonomics specifically focusing on enhancing mental processes such as perception, memory, and decision-making to improve safety and performance.
Physical Ergonomics
Physical ergonomics, a subdivision of human factors engineering, specifically studies the interaction between humans and physical environments to optimize comfort, safety, and performance in workplaces.
Macroergonomics
Macroergonomics examines the systemic interaction between organizational structures and human factors engineering to optimize workplace design and improve overall safety and productivity.
User-Centered Design
Human Factors Engineering and Ergonomics both optimize User-Centered Design by integrating cognitive, physical, and environmental considerations to enhance usability, safety, and performance in product and system development.
Anthropometrics
Human Factors Engineering and Ergonomics both utilize anthropometrics to optimize product and system designs for human physical dimensions, but Human Factors Engineering emphasizes cognitive and systemic interactions while Ergonomics primarily addresses physical comfort and efficiency.
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)
Human Factors Engineering enhances Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) by optimizing system design for user performance and safety, while Ergonomics focuses on adapting physical and cognitive environments to improve comfort and efficiency in HCI contexts.
Work System Design
Human Factors Engineering and Ergonomics both optimize work system design by integrating human capabilities and limitations to enhance safety, efficiency, and usability in occupational environments.
Task Analysis
Task analysis in Human Factors Engineering systematically examines user interactions to enhance system design, while Ergonomics primarily applies these analyses to optimize physical workplace comfort and safety.
Usability Engineering
Usability Engineering within Human Factors Engineering emphasizes optimizing user-system interaction by applying ergonomic principles to enhance efficiency, safety, and user satisfaction.
Biomechanics
Human Factors Engineering emphasizes optimizing system performance and safety by integrating biomechanics principles to enhance human-machine interaction, while Ergonomics focuses on designing work environments and tools that align with biomechanical capabilities to prevent musculoskeletal disorders.
Human Factors Engineering vs Ergonomics Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com