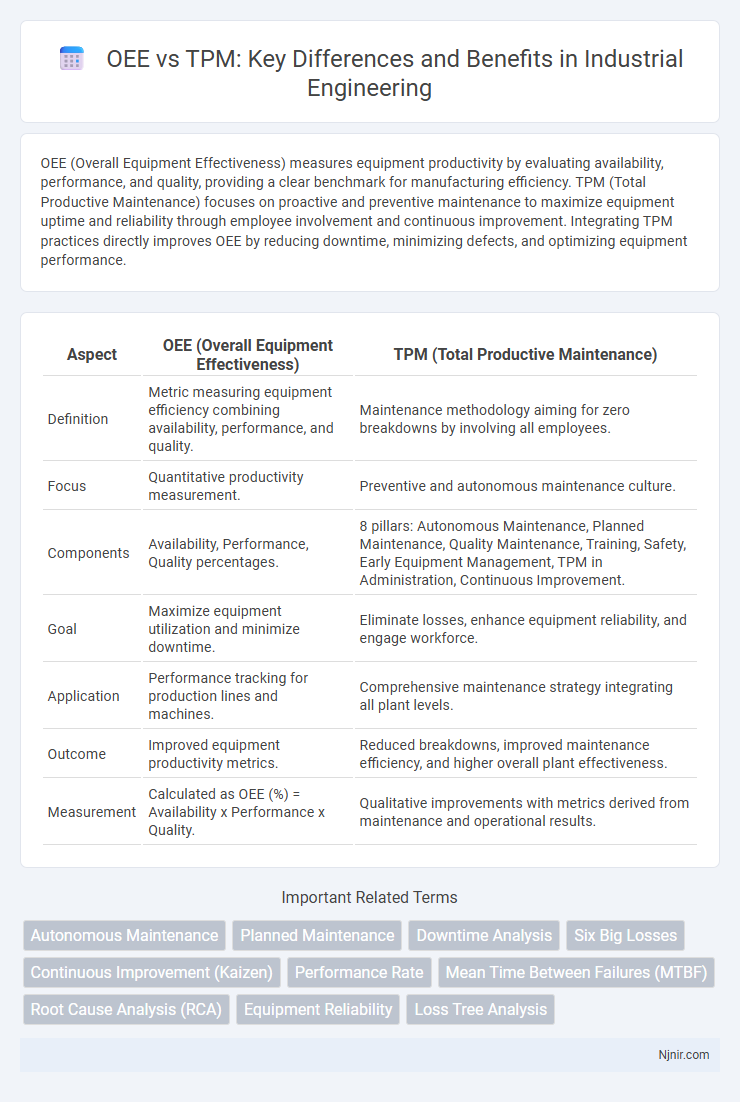
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) measures equipment productivity by evaluating availability, performance, and quality, providing a clear benchmark for manufacturing efficiency. TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) focuses on proactive and preventive maintenance to maximize equipment uptime and reliability through employee involvement and continuous improvement. Integrating TPM practices directly improves OEE by reducing downtime, minimizing defects, and optimizing equipment performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) | TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Metric measuring equipment efficiency combining availability, performance, and quality. | Maintenance methodology aiming for zero breakdowns by involving all employees. |
| Focus | Quantitative productivity measurement. | Preventive and autonomous maintenance culture. |
| Components | Availability, Performance, Quality percentages. | 8 pillars: Autonomous Maintenance, Planned Maintenance, Quality Maintenance, Training, Safety, Early Equipment Management, TPM in Administration, Continuous Improvement. |
| Goal | Maximize equipment utilization and minimize downtime. | Eliminate losses, enhance equipment reliability, and engage workforce. |
| Application | Performance tracking for production lines and machines. | Comprehensive maintenance strategy integrating all plant levels. |
| Outcome | Improved equipment productivity metrics. | Reduced breakdowns, improved maintenance efficiency, and higher overall plant effectiveness. |
| Measurement | Calculated as OEE (%) = Availability x Performance x Quality. | Qualitative improvements with metrics derived from maintenance and operational results. |
Introduction to OEE and TPM
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) measures manufacturing productivity by evaluating equipment availability, performance efficiency, and quality output, providing a comprehensive indicator of production effectiveness. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive and preventive maintenance to maximize equipment uptime and performance through operator involvement and continuous improvement. Both concepts aim to enhance operational efficiency, with OEE quantifying performance while TPM focuses on maintaining and improving the physical condition of equipment.
Core Principles of OEE
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) measures manufacturing productivity by evaluating availability, performance, and quality to identify equipment downtime, speed losses, and defects. TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) focuses on maximizing equipment efficiency through proactive maintenance, involving all employees in continuous improvement activities to prevent breakdowns and reduce downtime. The core principles of OEE emphasize real-time data analysis to optimize equipment utilization, enhance process reliability, and improve product quality.
Fundamental Concepts of TPM
The Fundamental Concepts of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasize proactive and preventive maintenance to maximize equipment efficiency and eliminate breakdowns, downtime, and defects. Unlike Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), which primarily measures equipment performance through availability, performance, and quality metrics, TPM focuses on engaging all employees in maintaining equipment, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. TPM's core pillars include autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, and focused improvement, aiming to achieve zero unplanned downtime and enhance overall productivity.
Key Differences Between OEE and TPM
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) measures manufacturing productivity by evaluating availability, performance, and quality, providing a quantitative metric of equipment efficiency. TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) is a comprehensive maintenance strategy focused on proactive and preventive maintenance to maximize equipment uptime and involve all employees in maintenance activities. The key difference lies in OEE being a performance metric, while TPM is a holistic approach to maintenance aimed at improving that metric through systematic equipment care and operator engagement.
Measuring Equipment Performance: OEE Metrics
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) quantifies equipment performance by combining availability, performance efficiency, and quality rate into a single metric, providing a comprehensive view of production effectiveness. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive maintenance strategies to prevent downtime and improve equipment reliability before measurement. OEE metrics enable precise identification of production losses and bottlenecks, making it essential for tracking improvements driven by TPM initiatives.
TPM Pillars in Practice
TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) emphasizes proactive maintenance strategies through pillars such as Autonomous Maintenance, Planned Maintenance, Quality Maintenance, Focused Improvement, Early Equipment Management, Training and Education, Safety, Health, and Environment, and TPM in Administration. These pillars drive continuous improvement by empowering operators to maintain equipment, reducing unplanned downtime and enhancing machine reliability. While OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) quantifies equipment productivity by measuring availability, performance, and quality, TPM provides the structured approach necessary to improve these OEE components systematically.
How OEE Supports TPM Initiatives
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) quantifies equipment performance by measuring availability, performance, and quality, providing essential data that drives TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) initiatives aimed at maximizing equipment uptime and productivity. By identifying losses related to breakdowns, slow cycles, and defects, OEE highlights specific areas for TPM activities such as autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, and continuous improvement. Leveraging OEE metrics enables TPM teams to prioritize maintenance efforts, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall production efficiency.
Implementation Challenges of OEE vs TPM
Implementation challenges of OEE often include accurate data collection and real-time monitoring complexity, which require advanced sensors and integration with existing systems. TPM implementation faces obstacles such as workforce involvement and sustained cultural change, demanding continuous training and employee engagement to maintain equipment reliability. Both methodologies require significant initial investment and management commitment, but TPM emphasizes proactive maintenance culture whereas OEE focuses on measurement and analysis for productivity improvement.
Case Studies: OEE and TPM in Industry
Case studies in manufacturing reveal OEE as a critical metric for quantifying equipment productivity by measuring availability, performance, and quality rates. TPM implementation focuses on proactive maintenance and operator involvement, significantly reducing downtime and improving machine reliability. Combining OEE analysis with TPM strategies has led industries to achieve up to 20% increases in operational efficiency and a 30% reduction in unexpected equipment failures.
Future Trends in Equipment Optimization
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) continues to evolve with advanced data analytics and AI integration, enabling real-time performance monitoring and predictive maintenance for maximizing machine uptime. TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) shifts towards incorporating IoT sensors and automated workflows, fostering proactive maintenance strategies that reduce unplanned downtime and extend equipment lifespan. Future trends highlight the convergence of OEE and TPM through digital twins and machine learning, driving smarter, fully automated equipment optimization in manufacturing environments.
Autonomous Maintenance
Autonomous Maintenance, a core pillar of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), empowers operators to perform routine equipment care, directly enhancing Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) by reducing downtime and improving machine reliability.
Planned Maintenance
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) measures manufacturing productivity by integrating availability, performance, and quality metrics, while Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes planned maintenance schedules to proactively prevent equipment downtime and enhance OEE scores.
Downtime Analysis
OEE's downtime analysis quantifies equipment unavailability and performance losses, while TPM emphasizes proactive downtime elimination through operator-led maintenance and root cause problem-solving.
Six Big Losses
OEE quantifies manufacturing productivity by measuring Availability, Performance, and Quality to identify Six Big Losses, while TPM focuses on proactive maintenance strategies to minimize these losses through operator involvement and continuous improvement.
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) measures manufacturing productivity by evaluating availability, performance, and quality, while TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) drives Continuous Improvement (Kaizen) through proactive equipment maintenance and employee involvement to maximize OEE and minimize downtime.
Performance Rate
OEE's Performance Rate metric quantifies actual production speed against ideal cycle time, while TPM emphasizes continuous equipment maintenance to sustain optimal performance and minimize downtime.
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is a critical metric in both OEE and TPM frameworks, where OEE quantifies overall equipment performance including availability impacted by MTBF, while TPM emphasizes proactive maintenance strategies to maximize MTBF and minimize downtime.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in OEE focuses on identifying factors reducing equipment availability, performance, and quality, while TPM integrates RCA within proactive maintenance to eliminate downtime and improve equipment reliability.
Equipment Reliability
OEE measures equipment reliability by quantifying availability, performance, and quality loss, while TPM focuses on maximizing equipment reliability through proactive maintenance and operator involvement.
Loss Tree Analysis
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) uses Loss Tree Analysis to quantify equipment availability, performance, and quality losses, whereas TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) applies Loss Tree Analysis to identify root causes of equipment downtime and productivity losses for proactive maintenance strategies.
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) vs TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com