Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and advanced analytics to predict equipment failures before they occur, optimizing maintenance schedules and reducing downtime. Preventive maintenance relies on scheduled inspections and routine servicing to prevent breakdowns, often leading to unnecessary maintenance tasks and higher costs. Combining predictive maintenance with preventive strategies enhances asset reliability and operational efficiency in industrial engineering.
Table of Comparison
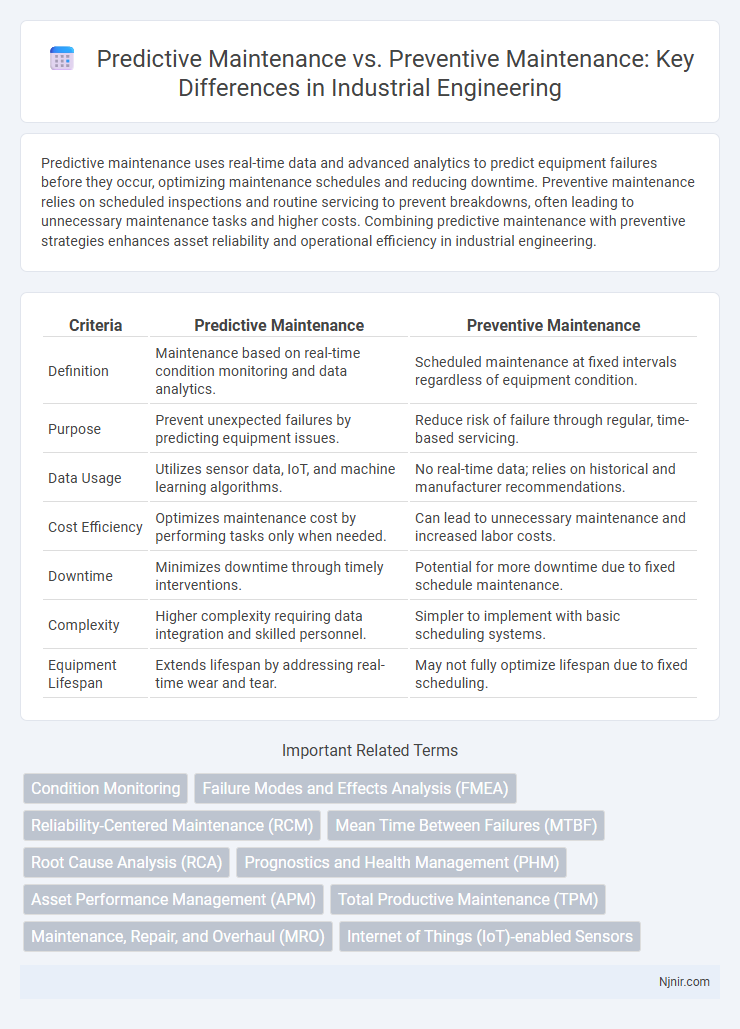
| Criteria | Predictive Maintenance | Preventive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance based on real-time condition monitoring and data analytics. | Scheduled maintenance at fixed intervals regardless of equipment condition. |
| Purpose | Prevent unexpected failures by predicting equipment issues. | Reduce risk of failure through regular, time-based servicing. |
| Data Usage | Utilizes sensor data, IoT, and machine learning algorithms. | No real-time data; relies on historical and manufacturer recommendations. |
| Cost Efficiency | Optimizes maintenance cost by performing tasks only when needed. | Can lead to unnecessary maintenance and increased labor costs. |
| Downtime | Minimizes downtime through timely interventions. | Potential for more downtime due to fixed schedule maintenance. |
| Complexity | Higher complexity requiring data integration and skilled personnel. | Simpler to implement with basic scheduling systems. |
| Equipment Lifespan | Extends lifespan by addressing real-time wear and tear. | May not fully optimize lifespan due to fixed scheduling. |
Understanding Predictive Maintenance in Industrial Engineering
Predictive maintenance in industrial engineering utilizes real-time data analytics, machine learning algorithms, and IoT sensors to monitor equipment health and predict failures before they occur, optimizing maintenance schedules and reducing unplanned downtime. Unlike preventive maintenance, which relies on fixed time intervals for routine service, predictive maintenance focuses on actual equipment condition, enabling more precise resource allocation and cost efficiency. This condition-based approach enhances asset longevity, increases operational reliability, and supports data-driven decision-making in industrial environments.
Key Principles of Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance relies on scheduled inspections, routine servicing, and replacement of parts based on time or usage intervals to prevent equipment failures. It emphasizes maintaining equipment condition through regular activities such as lubrication, adjustments, cleaning, and part replacements before breakdowns occur. Key principles include adherence to maintenance schedules, detailed record-keeping, and standardized procedures to ensure consistent performance and extend asset lifespan.
Data Analytics in Predictive Maintenance Strategies
Predictive maintenance leverages advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms to analyze real-time sensor data and historical performance metrics, enabling precise prediction of equipment failures before they occur. In contrast to preventive maintenance, which relies on scheduled inspections and replacement intervals, predictive strategies optimize maintenance timing by continuously monitoring asset conditions, reducing downtime and minimizing unnecessary servicing. The integration of IoT devices and big data analytics in predictive maintenance enhances decision-making accuracy, operational efficiency, and cost savings across industries.
Scheduling and Planning in Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance relies on a fixed schedule based on time or usage intervals, ensuring equipment is serviced regularly to prevent unexpected failures. Scheduling in preventive maintenance involves detailed planning of routine tasks such as inspections, lubrication, and part replacements before failures occur. This approach minimizes downtime by maintaining consistent operational conditions and preemptively addressing wear and tear.
Cost Implications: Predictive vs. Preventive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and condition monitoring to perform maintenance only when necessary, minimizing unnecessary labor and parts costs, which often results in lower overall expenses compared to preventive maintenance. Preventive maintenance follows a fixed schedule regardless of equipment condition, leading to more frequent replacements and higher labor costs due to potentially unneeded interventions. Studies indicate that predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by 10-40% and lower downtime by up to 50%, optimizing budget allocation and enhancing operational efficiency.
Impact on Equipment Lifespan and Reliability
Predictive maintenance utilizes real-time data and condition monitoring to address equipment issues precisely when needed, significantly extending equipment lifespan and enhancing reliability by preventing unexpected failures. Preventive maintenance relies on scheduled inspections and part replacements regardless of equipment condition, often resulting in unnecessary downtime or premature component changes that may not optimize durability. By minimizing over-maintenance and reducing unplanned outages, predictive maintenance delivers superior equipment availability and longevity compared to traditional preventive strategies.
Sensor Technologies in Predictive Maintenance Systems
Sensor technologies in predictive maintenance systems enable real-time monitoring of equipment conditions by collecting data on vibration, temperature, pressure, and humidity, which helps in identifying potential failures before they occur. Advanced sensors such as accelerometers, ultrasonic sensors, and infrared thermometers provide precise and continuous measurements, enhancing the accuracy of predictive analytics. Unlike preventive maintenance that follows fixed schedules, predictive maintenance relies on sensor-driven data analytics to optimize maintenance intervals, reduce downtime, and increase machinery lifespan.
Implementing Preventive Maintenance Programs
Implementing preventive maintenance programs involves scheduling regular inspections and servicing to avoid equipment failures before they occur, leveraging historical data and manufacturer recommendations. These programs reduce unplanned downtime and extend asset lifespan by addressing wear and tear proactively. Integrating computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) enhances tracking and ensures timely execution of maintenance tasks.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Predictive maintenance faces challenges including the requirement for advanced sensor technology and sophisticated data analytics, which can lead to high implementation costs and complexity in accurately forecasting equipment failures. Preventive maintenance limitations include the risk of unnecessary maintenance actions, leading to increased downtime and higher operational costs due to fixed schedules that do not account for actual machine condition. Both approaches struggle with integrating legacy systems and ensuring reliable data quality, impacting the effectiveness of maintenance strategies.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Strategy for Industrial Operations
Predictive maintenance utilizes real-time data and machine learning algorithms to monitor equipment health and predict failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs in industrial operations. Preventive maintenance follows a scheduled approach based on time or usage intervals, offering reliability but potentially leading to unnecessary part replacements. Choosing the right maintenance strategy depends on factors such as equipment criticality, available data infrastructure, operational budget, and the goal of maximizing asset lifespan while minimizing unplanned outages.
Condition Monitoring
Condition monitoring in predictive maintenance leverages real-time sensor data and analytics to detect equipment anomalies, optimizing maintenance schedules and reducing downtime compared to the time-based tasks in preventive maintenance.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data from Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to anticipate equipment failures, while preventive maintenance relies on scheduled interventions based on historical FMEA risk assessments.
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM)
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) prioritizes predictive maintenance techniques over traditional preventive maintenance by utilizing real-time data and condition monitoring to optimize asset reliability and reduce unplanned downtime.
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
Predictive maintenance extends Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) more effectively than preventive maintenance by using real-time data to address equipment issues before failure occurs.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and Root Cause Analysis (RCA) to identify potential equipment failures before they occur, whereas preventive maintenance relies on scheduled inspections without necessarily addressing the underlying causes.
Prognostics and Health Management (PHM)
Predictive maintenance leverages Prognostics and Health Management (PHM) technologies to analyze real-time data and predict equipment failures, whereas preventive maintenance relies on scheduled inspections and routine servicing regardless of actual equipment condition.
Asset Performance Management (APM)
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and analytics to optimize Asset Performance Management (APM) by forecasting equipment failures, whereas preventive maintenance relies on scheduled inspections and replacements to maintain asset reliability.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) integrates predictive maintenance techniques using real-time data analytics to enhance equipment reliability and reduce downtime, surpassing traditional preventive maintenance schedules based solely on fixed intervals.
Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO)
Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and analytics to optimize Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) schedules by forecasting equipment failures, whereas preventive maintenance relies on fixed intervals regardless of actual equipment condition.
Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled Sensors
IoT-enabled sensors enhance predictive maintenance by continuously monitoring equipment conditions and predicting failures, whereas preventive maintenance relies on scheduled inspections without real-time data.
Predictive maintenance vs Preventive maintenance Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com