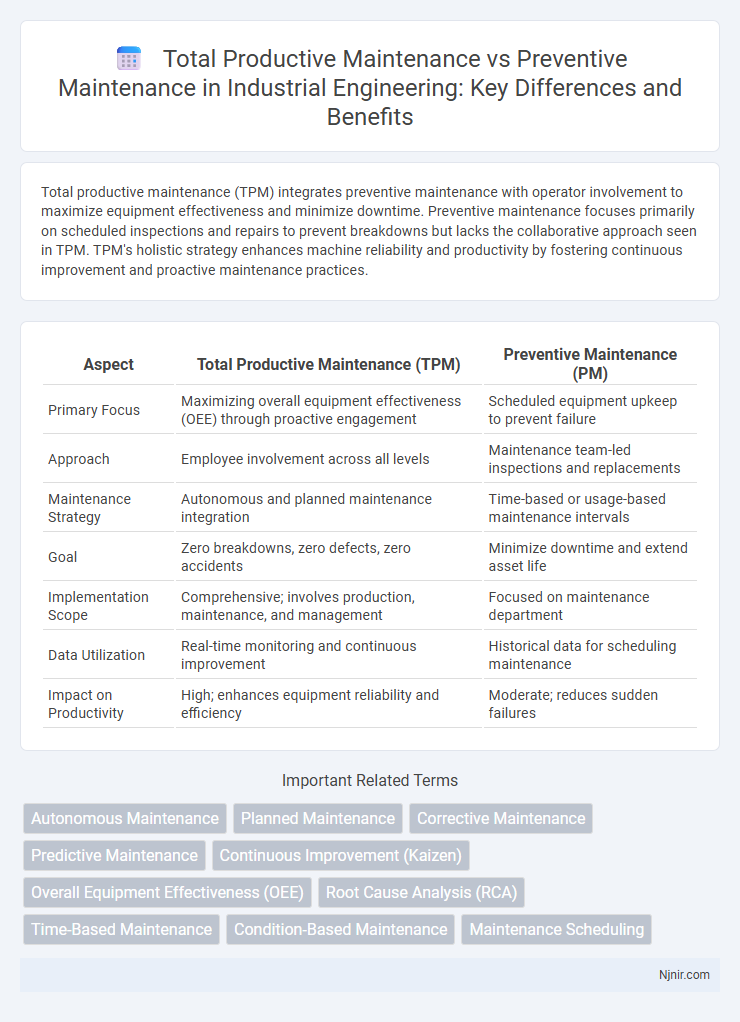
Total productive maintenance (TPM) integrates preventive maintenance with operator involvement to maximize equipment effectiveness and minimize downtime. Preventive maintenance focuses primarily on scheduled inspections and repairs to prevent breakdowns but lacks the collaborative approach seen in TPM. TPM's holistic strategy enhances machine reliability and productivity by fostering continuous improvement and proactive maintenance practices.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) | Preventive Maintenance (PM) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Maximizing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) through proactive engagement | Scheduled equipment upkeep to prevent failure |
| Approach | Employee involvement across all levels | Maintenance team-led inspections and replacements |
| Maintenance Strategy | Autonomous and planned maintenance integration | Time-based or usage-based maintenance intervals |
| Goal | Zero breakdowns, zero defects, zero accidents | Minimize downtime and extend asset life |
| Implementation Scope | Comprehensive; involves production, maintenance, and management | Focused on maintenance department |
| Data Utilization | Real-time monitoring and continuous improvement | Historical data for scheduling maintenance |
| Impact on Productivity | High; enhances equipment reliability and efficiency | Moderate; reduces sudden failures |
Understanding Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a comprehensive approach that involves all employees in proactive maintenance activities to maximize equipment effectiveness and minimize downtime. Unlike Preventive Maintenance, which schedules repairs based on time intervals, TPM emphasizes autonomous maintenance by operators and continuous improvement to prevent breakdowns and optimize productivity. TPM integrates techniques like 5S and root cause analysis to enhance equipment reliability and foster a culture of shared responsibility.
Defining Preventive Maintenance in Industrial Engineering
Preventive maintenance in industrial engineering involves routine inspections and scheduled servicing to reduce equipment breakdowns and extend machinery lifespan. It focuses on detecting potential failures before they occur through systematic tasks like lubrication, adjustments, and parts replacement. Total productive maintenance (TPM) expands on this by incorporating operator involvement and continuous improvement to maximize overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Key Objectives: TPM vs Preventive Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) aims to maximize equipment effectiveness by involving all employees in proactive maintenance activities to prevent breakdowns, improve safety, and enhance productivity. Preventive Maintenance focuses on scheduled inspections and servicing to reduce equipment failures and extend asset lifespan. TPM emphasizes a holistic approach integrating continuous improvement and operator involvement, while Preventive Maintenance centers on routine, time-based upkeep tasks.
Core Principles of Total Productive Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes autonomous maintenance, continuous improvement, and cross-functional team involvement to maximize equipment effectiveness and minimize downtime. Unlike preventive maintenance, which schedules service based on time intervals or usage, TPM integrates operators in routine maintenance tasks, fostering ownership and early detection of abnormalities. Core principles include improving equipment reliability, enhancing workforce skills, and promoting proactive problem-solving to achieve zero defects and stoppages.
Preventive Maintenance: Essential Practices
Preventive maintenance focuses on scheduled inspections, lubrication, and part replacements to reduce equipment failures and increase uptime. Key practices include detailed maintenance checklists, regular equipment monitoring, and timely intervention based on manufacturer guidelines. This approach minimizes unexpected breakdowns and extends machinery lifespan by addressing wear and tear before critical issues arise.
Comparing Implementation Strategies
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) implementation emphasizes employee involvement and cross-functional teams to enhance equipment effectiveness, integrating autonomous maintenance and continuous improvement activities. Preventive Maintenance (PM) relies on scheduled inspections and part replacements based on time or usage intervals, often managed by maintenance specialists with less operator engagement. TPM strategies focus on fostering a proactive maintenance culture, while PM typically follows a reactive, calendar-driven approach to reduce unexpected failures.
Equipment Reliability: TPM vs Preventive Approaches
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) enhances equipment reliability by involving all employees in proactive and predictive maintenance tasks, ensuring continuous monitoring and immediate response to potential issues. Preventive maintenance schedules regular inspections and replacements based on set intervals, which can reduce unexpected failures but may not address real-time equipment conditions. TPM's holistic approach to equipment care leads to higher overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and reduced downtime compared to traditional preventive maintenance strategies.
Cost Implications and ROI Analysis
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) drives higher ROI by integrating proactive equipment care with operator involvement, reducing downtime and repair costs more effectively than traditional Preventive Maintenance (PM). TPM's comprehensive approach extends asset life and boosts productivity, resulting in significant cost savings despite higher initial implementation expenses. In contrast, PM primarily focuses on scheduled inspections and replacements, often leading to increased maintenance costs and unscheduled failures that negatively impact overall ROI.
Impact on Workforce Involvement and Training
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) drives workforce involvement by integrating operators directly into maintenance tasks, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and shared responsibility, which significantly enhances skill development and cross-functional training. Preventive Maintenance primarily relies on specialized maintenance teams, limiting broader employee engagement and focusing training on technical maintenance procedures rather than collaborative problem-solving. TPM's holistic approach boosts employee empowerment and operational effectiveness, while Preventive Maintenance maintains equipment reliability through scheduled interventions with less emphasis on workforce integration.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Strategy for Industrial Operations
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive engagement of all employees in maintaining equipment to maximize overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and minimize downtime, while Preventive Maintenance (PM) focuses on scheduled inspections and servicing to prevent unexpected breakdowns. Choosing the right maintenance strategy depends on factors such as equipment criticality, production complexity, resource availability, and desired operational efficiency. Integrating TPM can foster a culture of continuous improvement and autonomy, whereas PM suits environments prioritizing predictable maintenance cycles and cost control.
Autonomous Maintenance
Autonomous maintenance empowers operators to perform routine preventive maintenance tasks, enhancing equipment reliability and fostering total productive maintenance by reducing downtime and increasing overall equipment effectiveness.
Planned Maintenance
Planned maintenance in total productive maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive equipment care involving operator participation and continuous improvement, whereas preventive maintenance primarily relies on scheduled inspections and repairs conducted by maintenance personnel.
Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance addresses equipment failures after they occur, contrasting with total productive maintenance's focus on proactive employee involvement and preventive maintenance's routine scheduling to avoid breakdowns.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive Maintenance uses real-time data and advanced analytics to anticipate equipment failures, enhancing Total Productive Maintenance by reducing downtime more effectively than traditional Preventive Maintenance schedules.
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Total productive maintenance integrates continuous improvement (Kaizen) principles to enhance equipment reliability and efficiency beyond the routine scheduling of preventive maintenance.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) improves Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) by involving all employees in proactive equipment care and continuous improvement, whereas Preventive Maintenance (PM) focuses on scheduled inspections and repairs to reduce downtime.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) incorporates Root Cause Analysis (RCA) to identify and eliminate underlying equipment issues, enhancing overall efficiency, while Preventive Maintenance (PM) primarily focuses on scheduled inspections and minor repairs to prevent failures without deeply addressing root causes.
Time-Based Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) enhances Time-Based Maintenance by integrating operator involvement to reduce downtime, whereas Preventive Maintenance strictly schedules routine checks based on time intervals to prevent equipment failure.
Condition-Based Maintenance
Condition-Based Maintenance enhances Total Productive Maintenance by using real-time equipment data to perform maintenance only when necessary, improving efficiency over traditional time-based Preventive Maintenance.
Maintenance Scheduling
Total productive maintenance maximizes equipment uptime by integrating operator involvement and proactive scheduling, while preventive maintenance relies on fixed time-based schedules to reduce breakdowns.
total productive maintenance vs preventive maintenance Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com