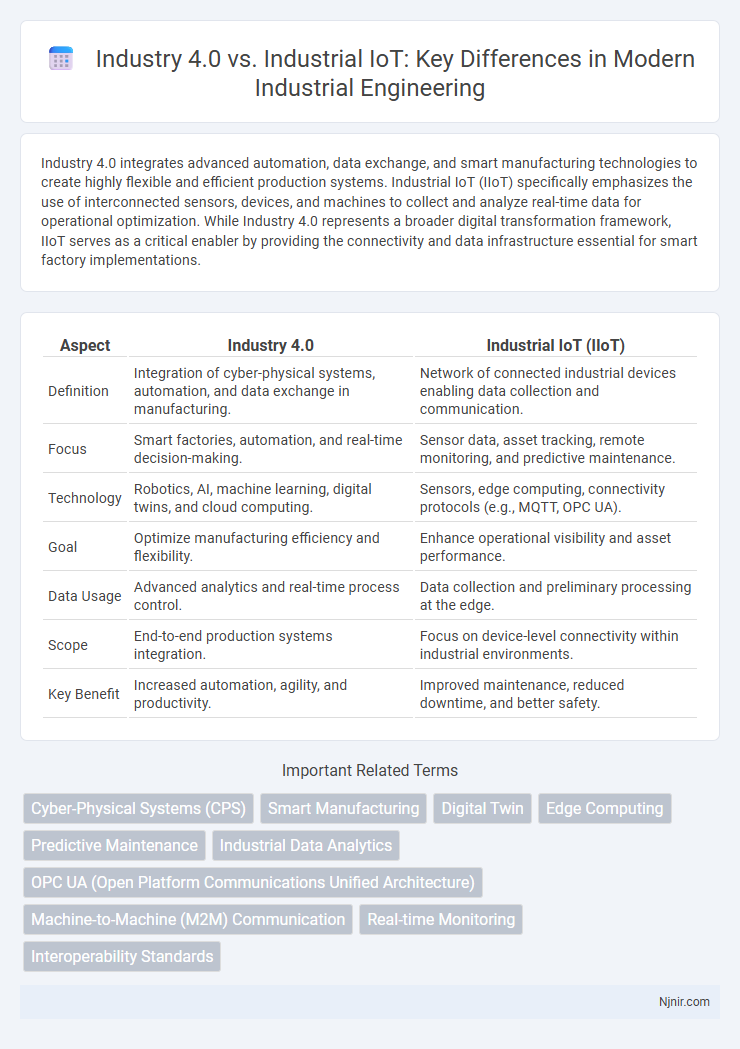
Industry 4.0 integrates advanced automation, data exchange, and smart manufacturing technologies to create highly flexible and efficient production systems. Industrial IoT (IIoT) specifically emphasizes the use of interconnected sensors, devices, and machines to collect and analyze real-time data for operational optimization. While Industry 4.0 represents a broader digital transformation framework, IIoT serves as a critical enabler by providing the connectivity and data infrastructure essential for smart factory implementations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Industry 4.0 | Industrial IoT (IIoT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of cyber-physical systems, automation, and data exchange in manufacturing. | Network of connected industrial devices enabling data collection and communication. |
| Focus | Smart factories, automation, and real-time decision-making. | Sensor data, asset tracking, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance. |
| Technology | Robotics, AI, machine learning, digital twins, and cloud computing. | Sensors, edge computing, connectivity protocols (e.g., MQTT, OPC UA). |
| Goal | Optimize manufacturing efficiency and flexibility. | Enhance operational visibility and asset performance. |
| Data Usage | Advanced analytics and real-time process control. | Data collection and preliminary processing at the edge. |
| Scope | End-to-end production systems integration. | Focus on device-level connectivity within industrial environments. |
| Key Benefit | Increased automation, agility, and productivity. | Improved maintenance, reduced downtime, and better safety. |
Understanding Industry 4.0: Definition and Principles
Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution characterized by the integration of cyber-physical systems, automation, and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It emphasizes smart factories, where interconnected machines and real-time data analytics optimize production efficiency and flexibility. Key principles include interoperability, information transparency, decentralized decision-making, and technical assistance, driving a new era of intelligent manufacturing beyond traditional Industrial IoT applications.
What is Industrial IoT? Key Concepts and Components
Industrial IoT (IIoT) refers to interconnected sensors, instruments, and devices networked together within industrial contexts to collect, exchange, and analyze data for improved operational efficiency and productivity. Key components include edge devices, sensors, cloud computing platforms, data analytics, and cybersecurity systems that enable real-time monitoring and automation. IIoT is integral to Industry 4.0, providing the foundational technology layer that drives smart manufacturing, predictive maintenance, and enhanced decision-making processes.
Comparing Industry 4.0 and Industrial IoT: Core Differences
Industry 4.0 represents a broader transformation of manufacturing through digitization, integration of cyber-physical systems, and smart factory concepts, while Industrial IoT (IIoT) specifically focuses on connecting industrial devices and equipment via the internet to enable real-time data exchange. Industry 4.0 encompasses advanced automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning for holistic process optimization, whereas IIoT primarily provides the infrastructure for data collection, connectivity, and remote monitoring. The core difference lies in Industry 4.0's comprehensive approach to intelligent production ecosystems versus Industrial IoT's role as the enabling technology for device communication and data acquisition.
Technology Stack in Industry 4.0 vs Industrial IoT
Industry 4.0 technology stack centers on integrating cyber-physical systems, advanced robotics, and smart manufacturing platforms with edge computing, AI, and big data analytics to enable real-time decision-making. Industrial IoT technology stack emphasizes sensor networks, connectivity protocols like MQTT and OPC UA, cloud computing, and machine learning for monitoring, predictive maintenance, and asset management. Both frameworks leverage digital twins and augmented reality but differ in their core approach: Industry 4.0 is a holistic manufacturing transformation, while Industrial IoT focuses on connecting and optimizing devices within industrial environments.
Data Collection and Analytics: Contrasting Approaches
Industry 4.0 emphasizes the integration of cyber-physical systems for comprehensive data collection across smart factories, leveraging advanced analytics to optimize production processes. Industrial IoT focuses more specifically on interconnected sensors and devices to gather real-time operational data, enabling immediate insights through cloud-based analytics platforms. Both approaches utilize big data and machine learning, but Industry 4.0 prioritizes holistic system-wide analytics, whereas Industrial IoT targets device-level performance and condition monitoring.
Integration with Legacy Systems: Challenges and Solutions
Industry 4.0 and Industrial IoT (IIoT) both emphasize the integration of smart technologies with existing manufacturing processes, but integrating legacy systems remains a significant challenge due to differences in data protocols, communication standards, and hardware compatibility. Solutions include deploying middleware platforms that enable seamless data exchange, utilizing edge computing to process data locally, and adopting standardized industrial communication protocols like OPC UA to bridge the gap between old and new systems. Effective integration enhances operational efficiency, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance without requiring a complete overhaul of legacy infrastructure.
Security Considerations in Industry 4.0 vs Industrial IoT
Industry 4.0 integrates cyber-physical systems and smart manufacturing processes, requiring robust cybersecurity measures to protect complex, interconnected production environments from data breaches and operational disruptions. Industrial IoT emphasizes networked sensors and devices across industrial settings, creating expansive attack surfaces vulnerable to unauthorized access and real-time data manipulation. Effective security frameworks for both involve multi-layered defenses, including encryption, anomaly detection, and secure authentication protocols tailored to the unique risks of smart factories and IoT-driven industrial applications.
Potential Use Cases: Real-World Applications
Industry 4.0 leverages advanced automation, data exchange, and smart manufacturing technologies in factories to enhance productivity and efficiency, while Industrial IoT (IIoT) focuses on connecting industrial devices and systems through the internet for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Potential use cases for Industry 4.0 include automated production lines, digital twins for virtual simulation, and AI-driven quality control, whereas IIoT excels in asset tracking, remote equipment diagnostics, and energy management via sensor networks. Both concepts drive digital transformation but apply differently, with Industry 4.0 emphasizing integrated smart systems and IIoT enabling enhanced connectivity and data analytics across industrial environments.
Industry 4.0 and IIoT: Benefits and ROI Comparison
Industry 4.0 integrates advanced automation, AI, and cyber-physical systems to enhance manufacturing efficiency, while Industrial IoT (IIoT) focuses on connecting machines and devices through networks for real-time data exchange. Industry 4.0 delivers higher ROI by enabling predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, and optimizing production processes through smart factories. IIoT benefits include improved asset utilization and detailed operational analytics, but Industry 4.0's broader scope typically results in more substantial long-term cost savings and productivity gains.
Future Trends: Convergence and Innovation in Industrial Automation
Industry 4.0 and Industrial IoT (IIoT) are rapidly converging to drive unprecedented innovation in industrial automation, leveraging advanced AI, edge computing, and digital twin technologies for enhanced operational efficiency. Future trends emphasize seamless integration of cyber-physical systems with cloud platforms, enabling predictive maintenance, real-time data analytics, and autonomous decision-making. This convergence fosters smart factories with adaptive manufacturing processes, improved supply chain resilience, and sustainable production methods.
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
Industry 4.0 integrates Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) to enable smart factories, while Industrial IoT primarily uses CPS for real-time data exchange and machine connectivity, enhancing automation and predictive maintenance.
Smart Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 integrates Industrial IoT technologies such as connected sensors and AI analytics to enhance smart manufacturing through real-time data monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated decision-making.
Digital Twin
Digital Twin technology in Industry 4.0 enables real-time simulation and optimization of manufacturing processes through Industrial IoT sensor data integration.
Edge Computing
Edge computing in Industry 4.0 enhances Industrial IoT by enabling real-time data processing and reducing latency for smarter, faster decision-making on connected factory floors.
Predictive Maintenance
Industry 4.0 leverages Industrial IoT technologies for predictive maintenance by integrating real-time sensor data, advanced analytics, and machine learning to minimize downtime and optimize equipment performance.
Industrial Data Analytics
Industrial Data Analytics leverages Industrial IoT to enhance Industry 4.0 by enabling real-time insights, predictive maintenance, and optimized operational efficiency through advanced data processing and machine learning algorithms.
OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture)
OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture) serves as a critical communication standard enabling seamless interoperability, secure data exchange, and real-time integration between Industry 4.0 systems and Industrial IoT devices, driving efficient smart manufacturing processes.
Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Communication
Industry 4.0 integrates advanced cyber-physical systems and AI for smart manufacturing, while Industrial IoT specifically enhances Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication by enabling seamless data exchange between connected devices to optimize operational efficiency.
Real-time Monitoring
Industry 4.0 leverages Industrial IoT technologies to enable real-time monitoring by integrating smart sensors, edge computing, and advanced data analytics for optimized manufacturing processes.
Interoperability Standards
Interoperability standards in Industry 4.0, such as OPC UA and RAMI 4.0, enable seamless integration and communication across diverse Industrial IoT devices, enhancing efficiency and data exchange.
Industry 4.0 vs Industrial IoT Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com