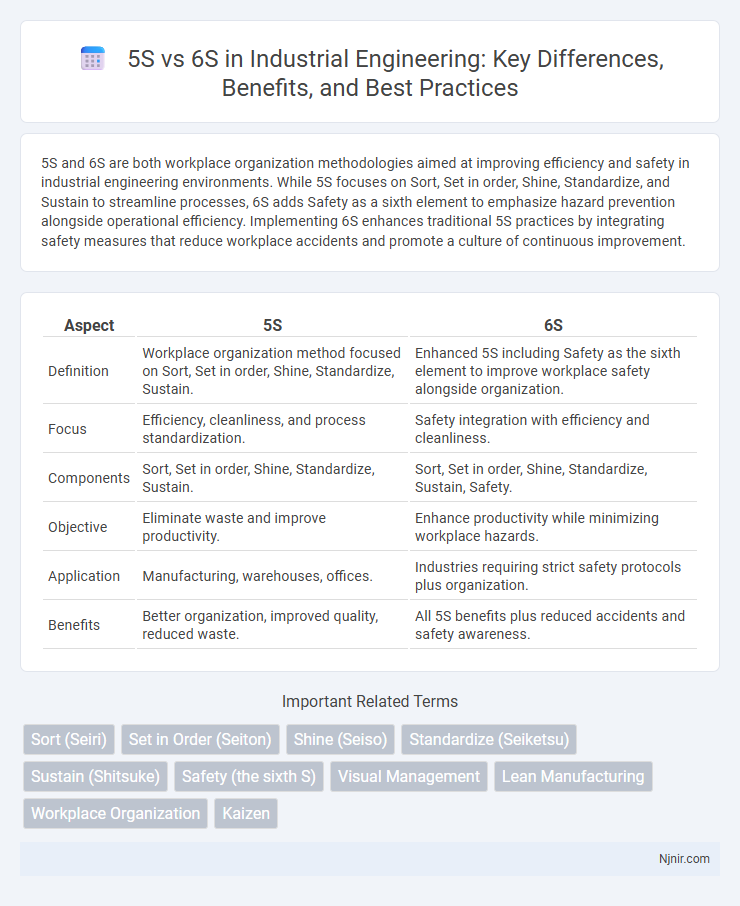
5S and 6S are both workplace organization methodologies aimed at improving efficiency and safety in industrial engineering environments. While 5S focuses on Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain to streamline processes, 6S adds Safety as a sixth element to emphasize hazard prevention alongside operational efficiency. Implementing 6S enhances traditional 5S practices by integrating safety measures that reduce workplace accidents and promote a culture of continuous improvement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | 5S | 6S |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Workplace organization method focused on Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain. | Enhanced 5S including Safety as the sixth element to improve workplace safety alongside organization. |
| Focus | Efficiency, cleanliness, and process standardization. | Safety integration with efficiency and cleanliness. |
| Components | Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain. | Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain, Safety. |
| Objective | Eliminate waste and improve productivity. | Enhance productivity while minimizing workplace hazards. |
| Application | Manufacturing, warehouses, offices. | Industries requiring strict safety protocols plus organization. |
| Benefits | Better organization, improved quality, reduced waste. | All 5S benefits plus reduced accidents and safety awareness. |
Introduction to 5S and 6S Methodologies
5S is a workplace organization method originating from Japan, emphasizing Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain to improve efficiency and safety. The 6S methodology builds upon 5S by adding Safety as a crucial sixth element, further enhancing workplace hazard prevention and creating a safer working environment. Both methodologies aim to streamline processes, reduce waste, and foster continuous improvement in industrial and office settings.
Core Principles of the 5S System
The core principles of the 5S system include Sort (Seiri), Set in Order (Seiton), Shine (Seiso), Standardize (Seiketsu), and Sustain (Shitsuke), which collectively aim to improve workplace organization, efficiency, and safety. While 5S focuses on establishing a clean and orderly workspace, 6S adds a sixth element, Safety, emphasizing hazard identification and prevention to create a safer work environment. Implementing 5S or 6S enhances operational performance by reducing waste, minimizing downtime, and fostering continuous improvement within manufacturing and service industries.
The Addition of Safety in 6S
The 6S methodology enhances the traditional 5S framework by explicitly incorporating Safety as a critical element, ensuring a safer workplace environment. This addition emphasizes hazard identification, risk reduction, and employee awareness, leading to fewer accidents and improved operational efficiency. By integrating Safety into Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain, 6S fosters a culture of continuous safety improvement alongside organization and cleanliness.
Key Differences Between 5S and 6S
5S consists of Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain, primarily focusing on workplace organization and efficiency. 6S includes all 5S steps plus Safety, emphasizing a safer work environment alongside improved productivity. The key difference lies in 6S's integration of safety as a core principle, enhancing risk management and accident prevention within lean manufacturing practices.
Benefits of Implementing 5S
Implementing 5S methodology enhances workplace organization, leading to significant improvements in productivity and safety by eliminating waste and reducing errors. The systematic approach of Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain fosters a culture of continuous improvement and accountability among employees. Improved efficiency and reduced downtime resulting from 5S contribute to higher quality output and lower operational costs.
Advantages of 6S in Industrial Environments
6S builds on the traditional 5S methodology by adding Safety as a core principle, significantly reducing workplace accidents and enhancing employee well-being in industrial environments. The inclusion of Safety fosters a proactive culture, leading to fewer injuries, lower downtime, and improved compliance with regulatory standards like OSHA. This results in higher productivity, better quality control, and a more sustainable operational framework compared to the 5S system.
Challenges in Adopting 5S or 6S
Implementing 5S or 6S frameworks often faces challenges such as resistance to change from employees accustomed to existing workflows and the difficulty in sustaining disciplined, consistent practices over time. Proper training and ongoing management commitment are critical to overcoming these obstacles, ensuring that the principles of Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain, and Safety (in 6S) become ingrained in the organizational culture. Additionally, allocating sufficient resources and continuously measuring performance metrics are essential to address the complexity and enhance the long-term effectiveness of 5S or 6S adoption.
Steps to Transition from 5S to 6S
Transitioning from 5S to 6S involves integrating the Safety step into the existing framework of Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. Begin by conducting a comprehensive safety audit to identify hazards and implement controls alongside organizational improvements. Training employees on safety protocols while maintaining ongoing 5S practices ensures a seamless evolution towards a safer, more efficient workplace.
Case Studies: 5S vs 6S in Industry
Case studies comparing 5S and 6S methodologies reveal significant improvements in workplace safety and efficiency when the sixth component, Safety, is explicitly integrated. Industries adopting 6S report a 30% reduction in workplace accidents and a 20% increase in operational productivity compared to traditional 5S implementations. Manufacturers in automotive and electronics sectors demonstrate enhanced employee engagement and compliance with regulatory standards under 6S frameworks.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Facility
Choosing between 5S and 6S depends on your facility's specific needs for workplace organization and safety. While 5S emphasizes Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain to improve efficiency and reduce waste, 6S incorporates Safety as the sixth pillar, making it ideal for environments where accident prevention and hazard control are critical. Facilities in manufacturing or chemical industries benefit most from 6S due to its comprehensive approach to both operational excellence and employee safety.
Sort (Seiri)
Sort (Seiri) in 5S eliminates unnecessary items to improve workplace efficiency, while 6S extends this principle by integrating Safety measures to enhance overall organizational effectiveness.
Set in Order (Seiton)
Set in Order (Seiton) in 5S focuses on organizing tools and materials for efficiency, while in 6S it includes strict safety measures to ensure an orderly and hazard-free workspace.
Shine (Seiso)
Shine (Seiso) in 5S emphasizes thorough cleaning to identify and eliminate dirt and defects, while 6S incorporates Shine with added safety protocols to ensure a cleaner, safer workplace environment.
Standardize (Seiketsu)
The 5S methodology emphasizes Standardize (Seiketsu) to maintain consistency and sustain improvements, while 6S incorporates Safety alongside Standardize to enhance workplace safety protocols systematically.
Sustain (Shitsuke)
The key difference between 5S and 6S lies in the added Safety component, while the Sustain (Shitsuke) phase in both methodologies emphasizes maintaining discipline and continuous adherence to standardized workplace practices.
Safety (the sixth S)
6S enhances workplace organization by integrating Safety as the sixth element, emphasizing hazard identification and risk reduction beyond the traditional 5S framework.
Visual Management
5S emphasizes workplace organization through Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain, while 6S adds Safety to enhance visual management by ensuring hazard awareness and creating a safer, more efficient work environment.
Lean Manufacturing
5S enhances Lean Manufacturing by organizing the workplace through Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain, while 6S adds Safety as the sixth pillar to further prevent accidents and improve efficiency.
Workplace Organization
5S focuses on Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain for workplace organization, while 6S adds Safety as a critical component to improve overall workplace efficiency and hazard prevention.
Kaizen
5S and 6S methodologies both enhance workplace organization by implementing Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain, with 6S adding Safety to further drive continuous improvement through Kaizen principles.
5S vs 6S Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com