Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems offer a comprehensive solution integrating various business processes, while Material Requirements Planning (MRP) focuses specifically on inventory control and production scheduling. ERP encompasses MRP functions but also extends to finance, human resources, and customer relationship management, providing a unified platform for industrial operations. Choosing ERP over MRP enhances data visibility, process automation, and decision-making efficiency in manufacturing environments.
Table of Comparison
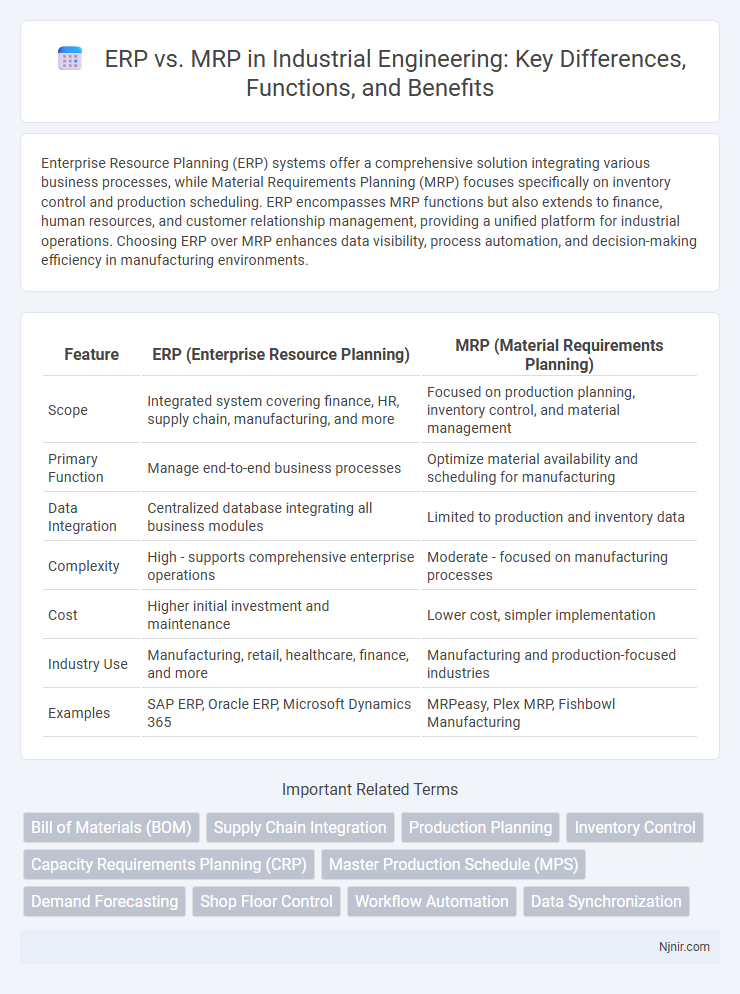
| Feature | ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) | MRP (Material Requirements Planning) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Integrated system covering finance, HR, supply chain, manufacturing, and more | Focused on production planning, inventory control, and material management |
| Primary Function | Manage end-to-end business processes | Optimize material availability and scheduling for manufacturing |
| Data Integration | Centralized database integrating all business modules | Limited to production and inventory data |
| Complexity | High - supports comprehensive enterprise operations | Moderate - focused on manufacturing processes |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and maintenance | Lower cost, simpler implementation |
| Industry Use | Manufacturing, retail, healthcare, finance, and more | Manufacturing and production-focused industries |
| Examples | SAP ERP, Oracle ERP, Microsoft Dynamics 365 | MRPeasy, Plex MRP, Fishbowl Manufacturing |
Introduction to ERP and MRP Systems
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems integrate core business processes including finance, HR, supply chain, and manufacturing into a unified platform, enhancing overall operational efficiency. MRP (Material Requirements Planning) systems specifically focus on production planning, inventory control, and scheduling to ensure materials are available for manufacturing. While MRP is limited to material management and production scheduling, ERP offers a comprehensive solution that consolidates multiple business functions into a single system.
Core Differences Between ERP and MRP
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) integrates multiple business functions including finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management into a unified system, while MRP (Material Requirements Planning) specializes exclusively in managing inventory levels, production scheduling, and procurement processes. ERP systems offer broader organizational transparency and real-time data analytics across departments, whereas MRP focuses on optimizing manufacturing workflow and material availability to reduce stockouts and production delays. The core difference lies in ERP's comprehensive enterprise-wide scope compared to MRP's concentrated functionality in manufacturing resource planning.
Key Features of ERP in Industrial Engineering
ERP systems in industrial engineering integrate key features such as real-time data analytics, supply chain management, and production scheduling to streamline operations and enhance decision-making. They consolidate modules for inventory control, procurement, quality management, and financial reporting, enabling comprehensive visibility across manufacturing processes. Advanced ERP platforms support scalability, automation, and compliance with industry standards, driving efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Essential Functions of MRP in Manufacturing
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) plays a crucial role in manufacturing by managing inventory levels, scheduling production processes, and ensuring timely procurement of raw materials to meet production demands. It calculates material needs based on sales forecasts and bills of materials, optimizing workflow to reduce waste and prevent stockouts. By automating demand planning and inventory control, MRP enhances production efficiency and supports just-in-time manufacturing strategies.
Integration Capabilities: ERP vs MRP
ERP systems offer comprehensive integration capabilities that unify various business functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management into a single platform, enabling real-time data sharing and streamlined operations. MRP systems focus primarily on manufacturing-related processes, including material requirement planning, inventory control, and production scheduling, limiting their integration scope to shop floor operations. The broader integration capabilities of ERP facilitate improved cross-departmental collaboration and data accuracy compared to the more specialized, narrower integration of MRP systems.
Scalability and Flexibility: Which System Wins?
ERP systems offer superior scalability and flexibility compared to MRP, as they integrate multiple business processes beyond manufacturing, including finance, human resources, and customer relationship management. MRP systems primarily focus on production planning and inventory control, limiting their adaptability in dynamic business environments. Companies seeking long-term growth and versatile operations benefit more from ERP's comprehensive and scalable architecture.
Cost Implications: ERP versus MRP Adoption
ERP systems typically involve higher upfront costs due to their comprehensive features and integration capabilities compared to MRP, which focuses primarily on manufacturing resource planning. While MRP solutions often require less investment and can be implemented faster, their limited scope may lead to additional expenses for integrating complementary systems. Over time, ERP adoption can result in greater cost savings by streamlining operations, reducing redundancies, and enabling data-driven decision-making across multiple departments.
Data Management and Analytics Comparison
ERP systems integrate comprehensive data management across multiple business functions, enabling real-time analytics and unified reporting for enhanced decision-making. MRP primarily focuses on inventory control and production planning, offering data management limited to materials requirements without extensive cross-departmental analytics. The advanced data analysis capabilities of ERP provide deeper insights into financial performance, supply chain efficiency, and customer relations compared to the more narrowly focused MRP systems.
Industry-Specific Applications of ERP and MRP
ERP systems offer comprehensive industry-specific modules tailored for sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and construction, integrating financials, supply chain, and human resources to streamline complex operations. MRP solutions concentrate primarily on manufacturing environments, focusing on inventory management, production scheduling, and materials planning to optimize shop floor efficiency. Industry-specific ERP platforms extend beyond MRP capabilities by incorporating advanced analytics, customer relationship management, and compliance features, addressing unique regulatory requirements and operational workflows across diverse industries.
Choosing the Right Solution for Industrial Engineering
Selecting the right solution between ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and MRP (Material Requirements Planning) depends on the scope of industrial engineering needs, where ERP offers a comprehensive integration of business processes including finance, HR, and supply chain, while MRP specializes in production planning and inventory control. Industries requiring extensive coordination across multiple departments and real-time data analytics benefit more from ERP systems, which enhance operational efficiency and decision-making. For manufacturing environments focused primarily on managing production schedules and raw materials, MRP systems provide targeted functionality with simpler implementation and cost-effectiveness.
Bill of Materials (BOM)
ERP systems integrate comprehensive Bill of Materials (BOM) management across multiple departments for enhanced production planning, while MRP primarily focuses on BOM-driven material requirement calculations to optimize inventory control.
Supply Chain Integration
ERP integrates comprehensive supply chain functions including procurement, inventory, and order management, while MRP primarily focuses on production scheduling and materials planning for supply chain optimization.
Production Planning
ERP systems integrate comprehensive production planning modules that streamline resource allocation and workflow management, while MRP systems primarily focus on material requirements planning to optimize inventory levels and scheduling.
Inventory Control
ERP systems offer comprehensive inventory control by integrating real-time data across multiple departments, while MRP primarily focuses on inventory planning and scheduling based on demand forecasts.
Capacity Requirements Planning (CRP)
Capacity Requirements Planning (CRP) in ERP systems provides real-time, integrated resource capacity analysis across multiple departments, whereas traditional MRP systems offer limited, isolated capacity checks primarily focused on production scheduling.
Master Production Schedule (MPS)
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) in ERP systems integrates real-time data across departments for dynamic production planning, while MRP relies primarily on inventory levels and demand forecasts for scheduling.
Demand Forecasting
ERP systems integrate comprehensive demand forecasting tools that leverage real-time data across multiple departments, whereas MRP primarily uses historical sales and inventory data to generate demand forecasts.
Shop Floor Control
ERP systems provide comprehensive shop floor control by integrating real-time production scheduling, inventory management, and quality tracking, whereas MRP primarily focuses on material requirements planning without extensive shop floor visibility.
Workflow Automation
ERP systems automate complex workflows across multiple departments, streamlining business processes beyond the manufacturing focus of MRP systems, which primarily automate inventory and production scheduling.
Data Synchronization
ERP systems provide comprehensive data synchronization across all business functions, while MRP focuses primarily on synchronizing data related to manufacturing and inventory management.
ERP vs MRP Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com