Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems oversee broad organizational functions like finance, supply chain, and human resources, integrating data across departments for strategic planning. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) concentrate on the shop floor, managing real-time production processes, quality control, and equipment monitoring to optimize operational efficiency. Combining ERP and MES enhances data visibility and decision-making, bridging the gap between high-level business management and detailed manufacturing execution in industrial engineering.
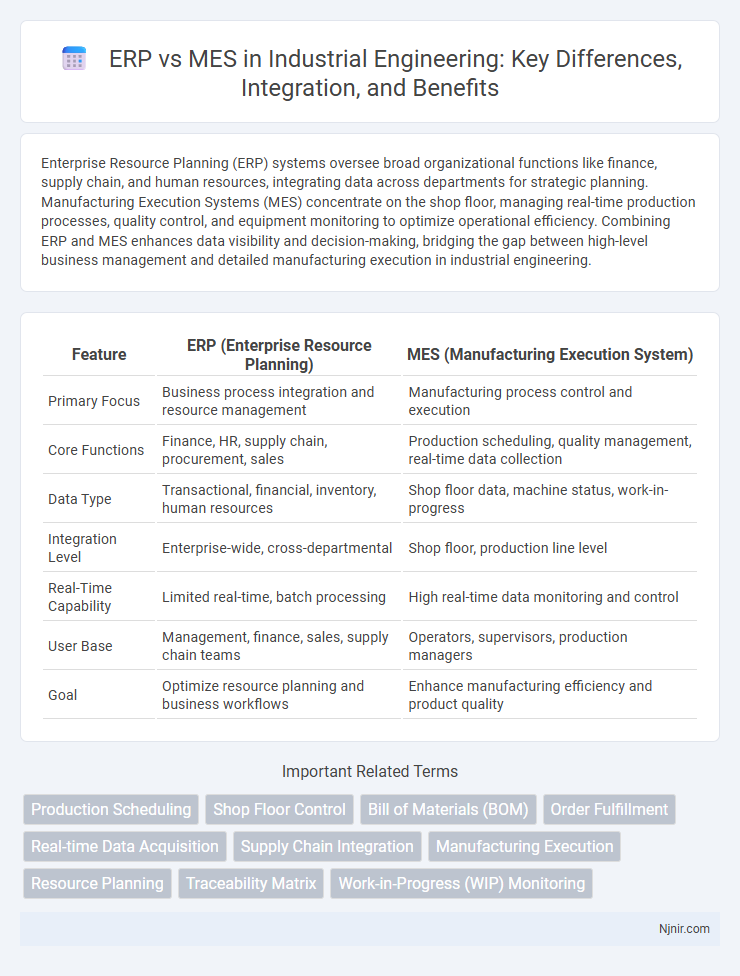
Table of Comparison
| Feature | ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) | MES (Manufacturing Execution System) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Business process integration and resource management | Manufacturing process control and execution |
| Core Functions | Finance, HR, supply chain, procurement, sales | Production scheduling, quality management, real-time data collection |
| Data Type | Transactional, financial, inventory, human resources | Shop floor data, machine status, work-in-progress |
| Integration Level | Enterprise-wide, cross-departmental | Shop floor, production line level |
| Real-Time Capability | Limited real-time, batch processing | High real-time data monitoring and control |
| User Base | Management, finance, sales, supply chain teams | Operators, supervisors, production managers |
| Goal | Optimize resource planning and business workflows | Enhance manufacturing efficiency and product quality |
Understanding ERP and MES: Core Definitions
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems centralize core business processes like finance, supply chain, and human resources to streamline organizational operations and improve decision-making. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) specialize in managing and monitoring production activities on the shop floor, focusing on real-time data collection, scheduling, and quality control. Understanding that ERP supports broad enterprise functions while MES targets detailed manufacturing execution is essential for integrating these systems effectively.
Key Functions of ERP in Manufacturing
ERP in manufacturing focuses on integrating core business processes such as finance, supply chain management, procurement, and human resources to enhance operational efficiency. It centralizes data management, enabling real-time visibility into inventory levels, production planning, and order processing. Key ERP functions streamline manufacturing workflows by coordinating demand forecasting, resource allocation, and compliance with regulatory standards.
MES: Bridging the Shop Floor and Management
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) bridges the gap between the shop floor and management by providing real-time data on production processes, equipment status, and workforce performance. Unlike ERP systems that focus on enterprise-wide resource planning, MES delivers actionable insights to optimize manufacturing operations, improve product quality, and reduce downtime. This integration enhances decision-making by offering precise control over workflows, inventory tracking, and compliance with industry standards.
Main Differences Between ERP and MES
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) primarily manages business-wide processes such as finance, procurement, and human resources by integrating data across departments, while MES (Manufacturing Execution System) focuses on real-time production monitoring, scheduling, and shop floor control. ERP systems handle strategic planning and resource allocation across the enterprise, whereas MES provides operational control and detailed tracking of manufacturing operations to improve efficiency and product quality. The main difference lies in their scope: ERP addresses overall business management, and MES targets execution and optimization of manufacturing processes.
Integration Challenges: ERP vs MES
Integration challenges between ERP and MES systems often arise due to differences in data formats, real-time processing needs, and system architectures. ERP systems prioritize financial and resource planning data with batch processing, while MES requires real-time production and operational data, creating synchronization difficulties. Effective integration demands customized middleware or APIs to ensure seamless data flow, minimize latency, and maintain data consistency across both platforms.
Data Flow: How ERP and MES Exchange Information
The data flow between ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and MES (Manufacturing Execution System) is critical for seamless production management and operational efficiency. ERP systems provide MES with high-level data like production orders, inventory levels, and scheduling, while MES supplies ERP with real-time manufacturing data, including machine status, production progress, and quality metrics. This bidirectional exchange enables synchronized planning, execution, and reporting across the enterprise, enhancing decision-making and reducing downtime.
Benefits of Implementing ERP in Industrial Settings
Implementing ERP in industrial settings streamlines operations by integrating core business processes such as supply chain management, finance, and production planning into a single platform. This unified system enhances data accuracy and real-time visibility, enabling more informed decision-making and improved resource allocation. ERP solutions also boost operational efficiency, reduce costs, and support compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Advantages of MES for Production Optimization
MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) offer real-time production monitoring, enabling immediate adjustments that enhance efficiency and reduce downtime. They provide detailed traceability and data collection at the shop floor level, improving quality control and compliance with industry standards. Unlike ERP systems, MES directly integrates with machinery, optimizing workflow and resource allocation to maximize output and minimize waste.
Choosing Between ERP and MES: Factors to Consider
Choosing between ERP and MES depends on specific business needs such as production complexity, real-time shop floor control, and integration requirements. ERP systems excel in managing financials, supply chain, and business processes, while MES provides detailed monitoring and execution of manufacturing operations. Companies should evaluate scalability, data accuracy, and operational visibility to determine the best fit for improving efficiency and decision-making.
Future Trends: ERP-MES Convergence in Industry 4.0
ERP-MES convergence is driving Industry 4.0 by integrating enterprise resource planning systems with manufacturing execution systems to enhance real-time data exchange and operational efficiency. Future trends emphasize AI-powered analytics and IoT connectivity, enabling predictive maintenance and adaptive production scheduling. This seamless integration supports smarter, more agile supply chains and fosters digital transformation in manufacturing environments.
Production Scheduling
ERP systems provide overarching production scheduling by integrating financial and resource planning, while MES offers real-time, detailed shop-floor scheduling to optimize manufacturing execution and workflow efficiency.
Shop Floor Control
MES enhances shop floor control by providing real-time production tracking and operational visibility, while ERP focuses on overall resource planning and business process integration.
Bill of Materials (BOM)
ERP systems manage high-level Bill of Materials (BOM) for procurement and costing, while MES focuses on detailed, real-time BOM execution and tracking on the manufacturing floor.
Order Fulfillment
MES enhances order fulfillment by providing real-time shop floor control and production tracking, while ERP manages order processing, inventory, and customer data to streamline overall business operations.
Real-time Data Acquisition
MES enables real-time data acquisition on the shop floor, providing instantaneous production insights that ERP systems primarily analyze retrospectively.
Supply Chain Integration
ERP systems centralize supply chain planning and financial management while MES platforms optimize real-time production execution and workflow integration for seamless supply chain synchronization.
Manufacturing Execution
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) optimize real-time production processes and floor-level operations, while Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems manage broader business functions like finance and supply chain.
Resource Planning
ERP systems optimize enterprise-wide resource planning by integrating financials, HR, and supply chain management, while MES focuses on real-time production resource scheduling and execution on the manufacturing floor.
Traceability Matrix
The Traceability Matrix in ERP systems links business requirements to system capabilities, while in MES it connects production processes to real-time manufacturing data for enhanced operational traceability.
Work-in-Progress (WIP) Monitoring
MES provides real-time Work-in-Progress (WIP) monitoring with granular production data, while ERP systems offer broader WIP inventory tracking integrated with financial and supply chain management.
ERP vs MES Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com