Discrete event simulation models complex systems by focusing on the chronological sequence of events, ideal for analyzing queueing and inventory systems in industrial engineering. Agent-based simulation captures the behavior and interactions of autonomous agents, allowing for exploration of adaptive and emergent phenomena in manufacturing processes and supply chains. Choosing between these approaches depends on whether system dynamics or individual agent behaviors drive the analysis goals.
Table of Comparison
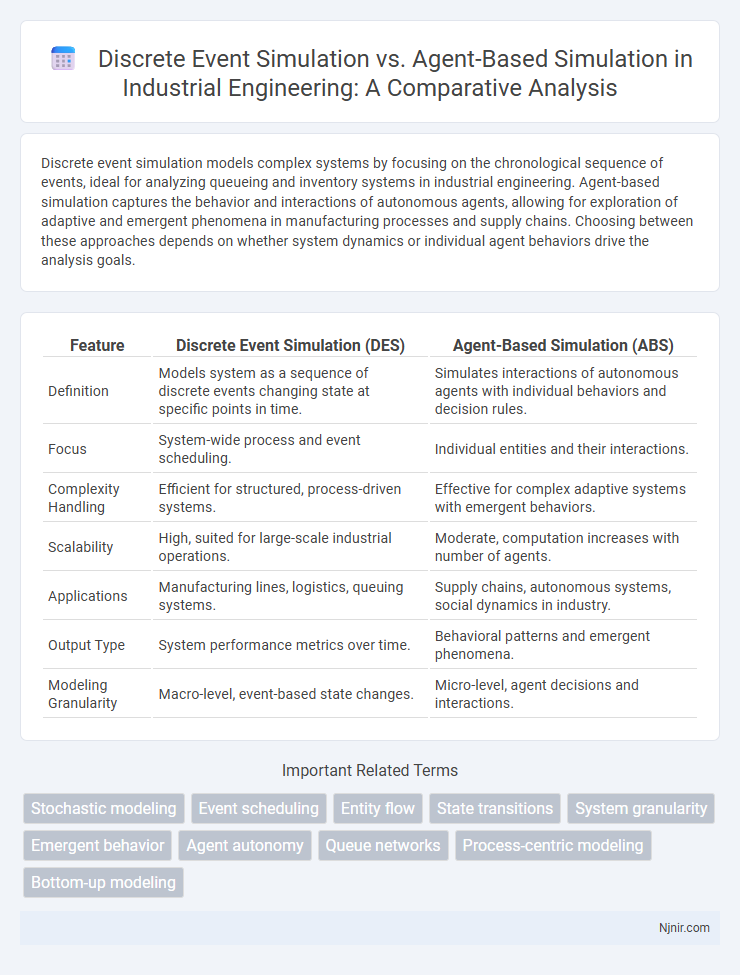
| Feature | Discrete Event Simulation (DES) | Agent-Based Simulation (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Models system as a sequence of discrete events changing state at specific points in time. | Simulates interactions of autonomous agents with individual behaviors and decision rules. |
| Focus | System-wide process and event scheduling. | Individual entities and their interactions. |
| Complexity Handling | Efficient for structured, process-driven systems. | Effective for complex adaptive systems with emergent behaviors. |
| Scalability | High, suited for large-scale industrial operations. | Moderate, computation increases with number of agents. |
| Applications | Manufacturing lines, logistics, queuing systems. | Supply chains, autonomous systems, social dynamics in industry. |
| Output Type | System performance metrics over time. | Behavioral patterns and emergent phenomena. |
| Modeling Granularity | Macro-level, event-based state changes. | Micro-level, agent decisions and interactions. |
Introduction to Simulation Modeling in Industrial Engineering
Discrete event simulation models system behavior by representing changes at specific points in time, ideal for analyzing manufacturing processes, queuing systems, and logistics in industrial engineering. Agent-based simulation focuses on individual entities with autonomous behaviors, capturing complex interactions and adaptive decision-making relevant to workforce dynamics and supply chain management. Both approaches enable optimization of industrial operations but differ in granularity, with discrete event simulation emphasizing process flow and agent-based simulation highlighting individual agent interactions.
Overview of Discrete Event Simulation (DES)
Discrete Event Simulation (DES) models systems as sequences of events occurring at discrete points in time, focusing on the state changes triggered by these events. DES is widely used in manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare to analyze complex processes by tracking queues, resources, and workflows. This approach contrasts with Agent-Based Simulation by emphasizing system-level event scheduling over individual autonomous agents' behaviors.
Overview of Agent-Based Simulation (ABS)
Agent-Based Simulation (ABS) models complex systems through autonomous agents with defined behaviors and interactions, emphasizing individual decision-making and heterogeneity within the population. Unlike Discrete Event Simulation (DES), which focuses on processes and queues, ABS captures emergent phenomena arising from localized interactions in dynamic environments. This approach is particularly effective for studying social systems, ecosystems, and market dynamics where agent variability and adaptive behaviors drive system outcomes.
Key Differences Between DES and ABS
Discrete Event Simulation (DES) models systems as sequences of distinct events that change the state at specific points in time, emphasizing process flow and resource allocation. Agent-Based Simulation (ABS) focuses on individual entities or agents with autonomous behaviors and interactions, enabling the study of emergent phenomena and decentralized decision-making. DES is typically used for system-level analysis with fixed event dynamics, while ABS excels in capturing complex adaptive behaviors and heterogeneous agent interactions.
Use Cases for Discrete Event Simulation in Industry
Discrete event simulation (DES) excels in modeling manufacturing systems, logistics, and supply chain processes by representing complex workflows and resource constraints with precise event-based timelines. Industries leverage DES to optimize machine scheduling, reduce bottlenecks, and improve throughput in assembly lines and distribution centers. The ability to simulate queuing systems and inventory management makes DES indispensable for operational efficiency in sectors such as automotive, electronics, and retail.
Applications of Agent-Based Simulation in Industrial Engineering
Agent-based simulation in industrial engineering is extensively applied for optimizing manufacturing processes, supply chain management, and workforce scheduling by modeling individual agents such as machines, products, and workers with autonomous behaviors. This simulation approach enables detailed analysis of complex systems, capturing interactions and emergent phenomena that traditional discrete event simulation may overlook. Industries leverage agent-based models to improve production efficiency, predict system bottlenecks, and enhance decision-making through dynamic scenario testing.
Comparative Analysis: DES vs. ABS in Manufacturing Systems
Discrete Event Simulation (DES) models manufacturing systems by representing processes as a sequence of events, emphasizing process flow and queuing dynamics, which allows for detailed analysis of system throughput and resource utilization. Agent-Based Simulation (ABS) focuses on autonomous agents such as machines, workers, or products, capturing complex interactions and adaptive behaviors within the manufacturing environment, enhancing the understanding of decentralized decision-making and emergent phenomena. DES excels in predictable, process-centric production lines, while ABS provides superior insights in flexible, human-centric manufacturing systems involving collaboration and negotiation among agents.
Advantages and Limitations of Discrete Event Simulation
Discrete event simulation (DES) efficiently models complex systems with clear, sequential events and well-defined processes, offering advantages such as reduced computational complexity and easier validation compared to agent-based simulation (ABS). However, DES limitations include reduced flexibility in representing adaptive behavior and individual heterogeneity, which ABS handles better through modeling autonomous agents with diverse characteristics. DES excels in manufacturing, logistics, and queuing systems where event timing drives outcomes, but struggles with scenarios requiring intricate interactions or emergent system dynamics.
Strengths and Challenges of Agent-Based Simulation
Agent-based simulation excels in modeling complex systems with heterogeneous agents exhibiting individual behaviors and interactions, allowing detailed analysis of emergent phenomena in social, economic, and biological contexts. This approach offers flexibility in capturing adaptive behaviors and local interactions that discrete event simulation may oversimplify or miss. Challenges include high computational demands, need for extensive data to accurately define agent rules, and difficulties in model validation due to the complexity and stochastic nature of agent interactions.
Choosing the Right Simulation Approach for Industrial Engineering Problems
Discrete event simulation excels in modeling systems with clearly defined events and queues, ideal for manufacturing lines and logistics processes in industrial engineering. Agent-based simulation offers granular insights by representing individual entities with autonomous behaviors, suitable for complex adaptive systems like supply chain networks and workforce dynamics. Selecting the appropriate approach depends on the level of system detail needed, interaction complexity, and the specific industrial engineering problem being addressed.
Stochastic modeling
Discrete event simulation models system behavior through stochastic event timing and state changes, while agent-based simulation incorporates stochastic interactions among autonomous agents to capture emergent system dynamics.
Event scheduling
Discrete event simulation utilizes event scheduling to manage system state changes at specific points in time, whereas agent-based simulation focuses on individual agents' behaviors and interactions without centralized event scheduling.
Entity flow
Discrete event simulation models entity flow through predefined queues and events, while agent-based simulation captures individual agent interactions and autonomous behaviors driving system dynamics.
State transitions
Discrete event simulation models system state changes through scheduled events occurring at specific times, while agent-based simulation captures state transitions driven by individual agents' autonomous interactions and behaviors.
System granularity
Discrete event simulation models system behavior at an aggregate level using event-driven state changes, while agent-based simulation captures fine-grained interactions by modeling individual agents and their behaviors within the system.
Emergent behavior
Agent-based simulation captures emergent behavior by modeling individual agents and their interactions, whereas discrete event simulation focuses on system-level events without explicitly representing emergent phenomena.
Agent autonomy
Agent-based simulation emphasizes individual agent autonomy with independent decision-making, whereas discrete event simulation models system-level events without autonomous agent behavior.
Queue networks
Discrete event simulation models queue networks by representing system changes at distinct events, while agent-based simulation captures individual entity behaviors and interactions within the same networks for more detailed analysis.
Process-centric modeling
Discrete event simulation emphasizes process-centric modeling by representing systems as sequences of events altering discrete states, whereas agent-based simulation models individual autonomous entities interacting within an environment.
Bottom-up modeling
Agent-based simulation excels in bottom-up modeling by representing individual entities and their interactions, whereas discrete event simulation focuses on system-level events and state changes.
discrete event simulation vs agent-based simulation Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com