On-demand production minimizes inventory costs and reduces waste by manufacturing products only when customer orders are confirmed, enhancing responsiveness in dynamic markets. Forecast-driven production relies on demand predictions to optimize resources and streamline supply chains, though it risks overproduction or stockouts if forecasts are inaccurate. Balancing both approaches allows industrial engineers to improve efficiency and meet customer demands effectively.
Table of Comparison
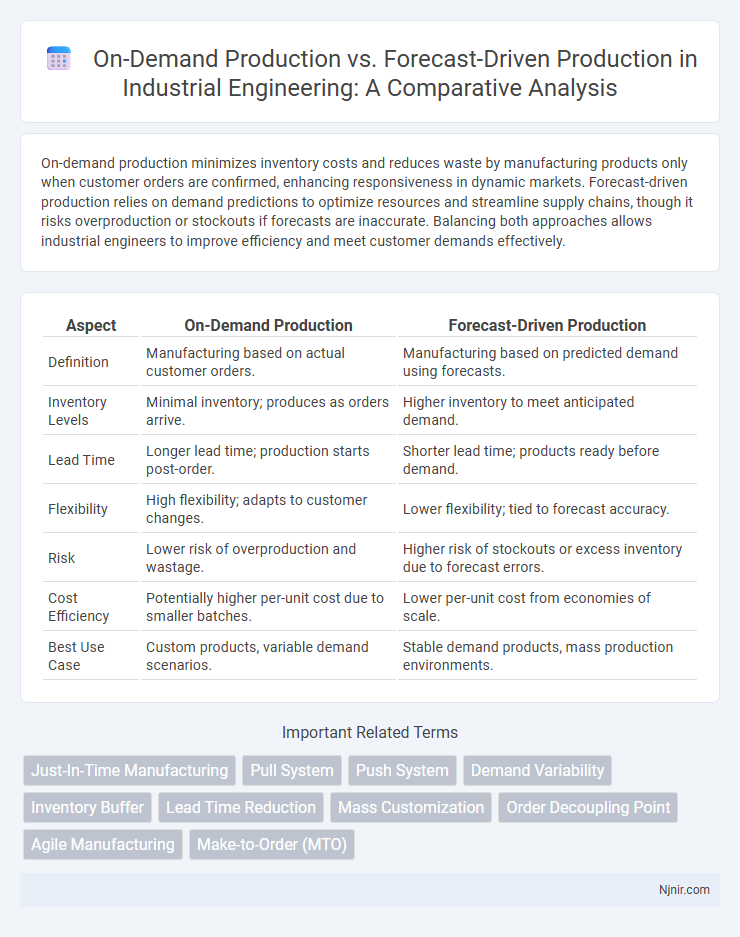
| Aspect | On-Demand Production | Forecast-Driven Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturing based on actual customer orders. | Manufacturing based on predicted demand using forecasts. |
| Inventory Levels | Minimal inventory; produces as orders arrive. | Higher inventory to meet anticipated demand. |
| Lead Time | Longer lead time; production starts post-order. | Shorter lead time; products ready before demand. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; adapts to customer changes. | Lower flexibility; tied to forecast accuracy. |
| Risk | Lower risk of overproduction and wastage. | Higher risk of stockouts or excess inventory due to forecast errors. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially higher per-unit cost due to smaller batches. | Lower per-unit cost from economies of scale. |
| Best Use Case | Custom products, variable demand scenarios. | Stable demand products, mass production environments. |
Introduction to On-Demand and Forecast-Driven Production
On-demand production centers on manufacturing products only when customer orders are received, minimizing inventory costs and reducing waste. Forecast-driven production relies on analyzing market trends and historical data to predict demand and produce goods in advance, aiming to optimize supply chain efficiency. Both methods require precise data management systems to balance responsiveness with cost-effectiveness in meeting market needs.
Key Principles of On-Demand Production
On-demand production centers on manufacturing products only after receiving customer orders, minimizing inventory costs and reducing waste. Key principles include rapid response to customer demand, flexibility in production processes, and lean supply chain management to ensure timely delivery. This approach enhances customization capabilities and aligns production output directly with market needs, improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Fundamentals of Forecast-Driven Production
Forecast-driven production relies on historical sales data and predictive analytics to estimate future demand, facilitating inventory planning and resource allocation. This approach aims to minimize stockouts and overproduction by aligning manufacturing schedules with anticipated market needs. Effective forecast accuracy and demand variability management are fundamental to optimizing supply chain efficiency in forecast-driven production.
Comparative Analysis: Flexibility and Responsiveness
On-demand production offers superior flexibility by enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to real-time customer orders, minimizing inventory costs and reducing waste. Forecast-driven production relies on predictive analytics to plan inventory and production schedules, which can lead to inefficiencies if demand forecasts are inaccurate. In terms of responsiveness, on-demand production adapts immediately to market fluctuations, while forecast-driven approaches may experience delays due to reliance on prior demand data.
Impact on Inventory Management
On-demand production significantly reduces inventory holding costs by manufacturing products only when orders are received, minimizing stock levels and the risk of obsolescence. Forecast-driven production relies on predictive analytics and historical sales data to anticipate demand, leading to higher inventory levels to buffer against uncertainties. Effective inventory management in on-demand systems requires rapid replenishment and flexible supply chains, while forecast-driven systems depend heavily on accurate demand forecasting to optimize stock levels and prevent overproduction or stockouts.
Cost Implications: Efficiency and Waste Reduction
On-demand production minimizes inventory holding costs and reduces waste by producing goods only as needed, enhancing operational efficiency. Forecast-driven production often requires maintaining larger inventories, leading to higher storage expenses and potential excess stock that may become obsolete. Cost implications favor on-demand models where just-in-time manufacturing limits overproduction and aligns production closely with actual consumer demand.
Technology Enablers for Modern Production Models
On-demand production relies heavily on advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and cloud computing to dynamically adjust manufacturing processes in real-time, minimizing waste and inventory costs. Forecast-driven production uses machine learning algorithms and big data platforms to predict demand patterns, optimize supply chain operations, and schedule production runs efficiently. Both models benefit from digital twins and automation technologies that enhance flexibility, accuracy, and responsiveness in modern manufacturing environments.
Quality Control in On-Demand vs Forecast-Driven Systems
On-demand production ensures superior quality control by focusing on smaller batch sizes and real-time monitoring, reducing defects and waste. Forecast-driven production often involves large-scale manufacturing, which can lead to overproduction and higher chances of quality inconsistencies due to inventory aging. Implementing agile quality checkpoints in on-demand systems allows for immediate corrective actions, enhancing overall product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Sustainability Considerations in Production Strategies
On-demand production significantly reduces waste by manufacturing only what is needed, minimizing inventory excess and lowering resource consumption. Forecast-driven production often leads to overproduction, increasing the risk of unsold stock and higher carbon footprints due to storage and disposal. Emphasizing sustainable supply chains, on-demand models align better with circular economy principles and help companies meet environmental regulations and consumer expectations.
Future Trends in Industrial Production Approaches
Future trends in industrial production increasingly favor on-demand production due to advancements in AI, IoT, and real-time data analytics, enabling more agile and customized manufacturing processes. Forecast-driven production faces challenges from market volatility and supply chain disruptions, prompting a shift towards flexible, just-in-time systems that reduce inventory costs and waste. Integration of smart factories and digital twins supports the transition, enhancing responsiveness and efficiency in meeting dynamic consumer demands.
Just-In-Time Manufacturing
Just-In-Time Manufacturing minimizes inventory costs by producing goods on-demand, contrasting with forecast-driven production that relies on predictive inventory stocking to meet anticipated demand.
Pull System
On-demand production, driven by a pull system, reduces inventory costs and enhances responsiveness by producing goods only after receiving customer orders, unlike forecast-driven production which relies on predictions and can lead to excess stock.
Push System
Push systems in forecast-driven production rely on scheduled inventory replenishment based on demand predictions, often leading to overproduction and higher holding costs compared to on-demand pull production.
Demand Variability
On-demand production minimizes the impact of demand variability by producing goods only as ordered, while forecast-driven production relies on predictions that can lead to overstock or shortages due to inaccurate demand estimates.
Inventory Buffer
On-demand production minimizes inventory buffer by manufacturing products only upon order, whereas forecast-driven production requires maintaining larger inventory buffers to mitigate demand uncertainty.
Lead Time Reduction
On-demand production significantly reduces lead time by eliminating inventory buildup and enabling immediate response to customer orders, unlike forecast-driven production which relies on predictive scheduling and often results in longer waiting periods.
Mass Customization
On-demand production enables mass customization by manufacturing products only after customer orders are placed, reducing inventory costs and increasing responsiveness compared to forecast-driven production that relies on predicted demand.
Order Decoupling Point
The Order Decoupling Point in on-demand production is positioned closer to the customer to enable customization and reduce inventory, whereas in forecast-driven production, it is set upstream to focus on efficiency and batch processing based on demand predictions.
Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing leverages on-demand production to minimize inventory costs and rapidly respond to market changes, contrasting with forecast-driven production's reliance on predictive models that may lead to overproduction or stockouts.
Make-to-Order (MTO)
Make-to-Order (MTO) production leverages on-demand manufacturing to minimize inventory costs and enhance customization, contrasting with forecast-driven production that relies on demand predictions and often results in excess stock.
On-demand production vs Forecast-driven production Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com