Flexible manufacturing systems enable rapid adaptation to varying product designs through automated machinery and programmable controls, enhancing production efficiency and reducing downtime. Mass customization combines the low unit costs of mass production with the ability to tailor products to individual customer specifications, often relying on flexible manufacturing as a foundational technology. Both strategies aim to balance cost-effectiveness and responsiveness, but flexible manufacturing prioritizes operational agility while mass customization emphasizes personalized value.
Table of Comparison
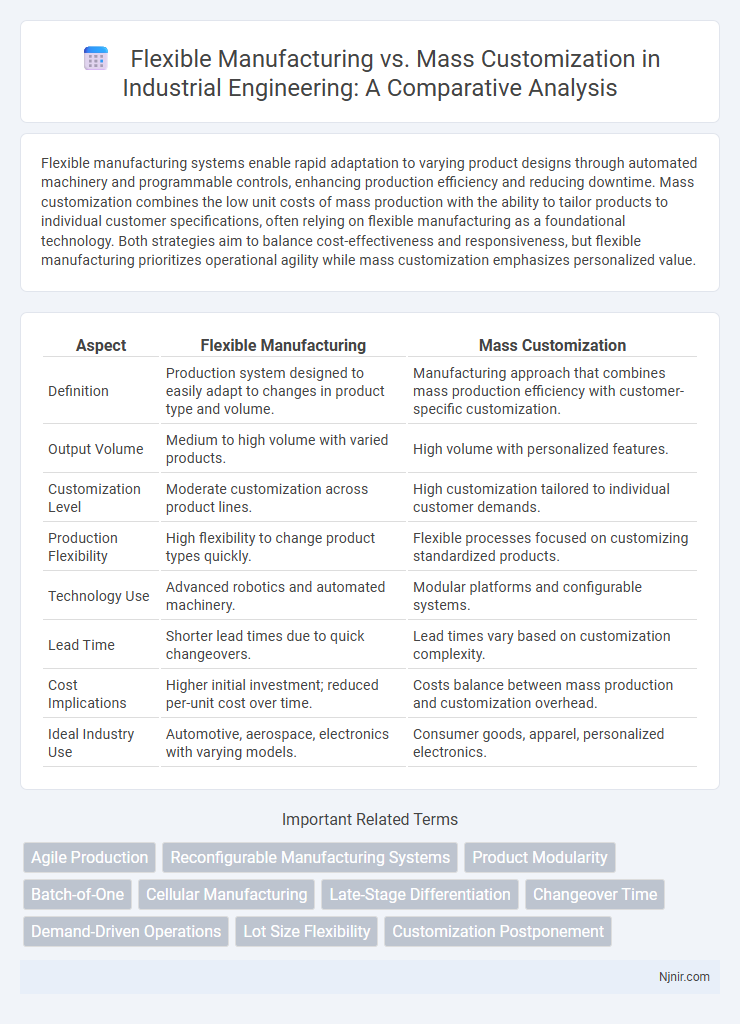
| Aspect | Flexible Manufacturing | Mass Customization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production system designed to easily adapt to changes in product type and volume. | Manufacturing approach that combines mass production efficiency with customer-specific customization. |
| Output Volume | Medium to high volume with varied products. | High volume with personalized features. |
| Customization Level | Moderate customization across product lines. | High customization tailored to individual customer demands. |
| Production Flexibility | High flexibility to change product types quickly. | Flexible processes focused on customizing standardized products. |
| Technology Use | Advanced robotics and automated machinery. | Modular platforms and configurable systems. |
| Lead Time | Shorter lead times due to quick changeovers. | Lead times vary based on customization complexity. |
| Cost Implications | Higher initial investment; reduced per-unit cost over time. | Costs balance between mass production and customization overhead. |
| Ideal Industry Use | Automotive, aerospace, electronics with varying models. | Consumer goods, apparel, personalized electronics. |
Introduction to Flexible Manufacturing and Mass Customization
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) enable rapid adaptation of production processes to produce a variety of products with minimal downtime, utilizing automated machinery and computer-controlled operations. Mass customization combines the efficiency of mass production with the personalization capabilities of custom manufacturing, allowing individualized products to be produced at scale. Both approaches enhance responsiveness to market demand, with FMS emphasizing operational flexibility and mass customization focusing on customer-specific product differentiation.
Core Principles of Flexible Manufacturing
Flexible manufacturing centers on adaptable systems that can efficiently switch between different product types with minimal downtime, emphasizing modular tooling, automated machinery, and real-time process control. This approach enables rapid response to market changes and varying customer demands without sacrificing production efficiency. In contrast, mass customization combines mass production scale with customer-specific variations, often relying on flexible manufacturing principles to balance customization with economies of scale.
Fundamentals of Mass Customization
Mass customization integrates flexible manufacturing systems to produce personalized products at near mass production efficiency by leveraging modular design, rapid reconfiguration, and real-time customer feedback. It fundamentally relies on adaptable production processes that can switch between varied product specifications without sacrificing throughput or quality. This approach contrasts with traditional flexible manufacturing, which emphasizes broad product variety but may not fully tailor to individual customer preferences.
Technology Enablers in Modern Manufacturing
Flexible manufacturing systems leverage advanced robotics, IoT sensors, and real-time data analytics to rapidly adapt production lines for diverse product variants, enhancing responsiveness and reducing downtime. Mass customization relies heavily on modular design software, additive manufacturing (3D printing), and AI-driven customer preference analysis to deliver personalized products at scale without sacrificing efficiency. Both approaches utilize cloud computing and digital twins to optimize workflows and enable seamless transitions between product configurations, driving innovation in modern manufacturing ecosystems.
Production Efficiency: Flexibility vs. Customization
Flexible manufacturing systems prioritize adaptability by enabling rapid shifts in production processes to accommodate varying product types, which enhances overall production efficiency through reduced downtime and tooling costs. Mass customization focuses on delivering tailored products to meet individual customer specifications without sacrificing the economies of scale, leveraging modular design and advanced digital technologies to maintain efficient volume production. Balancing flexibility and customization allows manufacturers to optimize resource utilization while satisfying diverse market demands through scalable and responsive production strategies.
Cost Implications and Investment Strategies
Flexible manufacturing systems require higher initial capital investment in advanced machinery and adaptable technology to enable rapid product changes, resulting in increased fixed costs but lower per-unit production costs over time. Mass customization demands investments in both flexible production processes and sophisticated IT systems for customer interaction and order management, driving up variable costs due to personalized components and smaller batch sizes. Cost implications of flexible manufacturing focus on long-term savings through efficiency and scalability, while mass customization involves balancing upfront technology expenditures with premium pricing strategies to offset complexity and customization expenses.
Impact on Supply Chain and Inventory Management
Flexible manufacturing enhances supply chain agility by enabling rapid product switching and reducing lead times, which minimizes excess inventory and lowers holding costs. Mass customization requires highly responsive supply chains and sophisticated inventory management strategies to balance personalized product demand with supply variability. Both approaches drive the need for advanced forecasting, real-time data analytics, and integrated supplier networks to optimize inventory turnover and reduce stockouts.
Quality Assurance in Diverse Manufacturing Models
Flexible manufacturing emphasizes adaptive production processes that maintain consistent quality assurance by integrating real-time monitoring and automated inspection systems to handle diverse product variants efficiently. Mass customization prioritizes personalized product quality by leveraging modular design and scalable quality control methods, ensuring each customized item meets stringent standards without sacrificing manufacturing speed. Both models rely on advanced data analytics and feedback loops to detect defects early, optimize process parameters, and uphold high-quality output across varied product demands.
Market Responsiveness and Customer Satisfaction
Flexible manufacturing enhances market responsiveness by enabling rapid adaptation to fluctuating demand and product variations, resulting in shorter lead times and improved customer satisfaction through timely delivery. Mass customization combines the efficiency of mass production with personalized product options, directly addressing individual customer preferences and significantly boosting satisfaction levels. Both approaches leverage advanced technologies like CNC machines and digital platforms to balance operational efficiency with tailored market needs.
Future Trends: Integrating Flexibility and Customization
Future trends in manufacturing emphasize the integration of flexibility and mass customization through advanced digital technologies such as AI, IoT, and additive manufacturing. Smart factories leverage real-time data analytics to dynamically adjust production lines, enabling rapid shifts between customized and mass-produced goods. This convergence drives efficiency, reduces waste, and enhances customer-centric product delivery in Industry 4.0 environments.
Agile Production
Agile production integrates flexible manufacturing with mass customization by enabling rapid adaptation to customer-specific demands while maintaining efficiency in high-volume output.
Reconfigurable Manufacturing Systems
Reconfigurable Manufacturing Systems enable flexible manufacturing by swiftly adapting production lines for customized mass production, enhancing efficiency and reducing lead times compared to traditional mass customization approaches.
Product Modularity
Flexible manufacturing leverages product modularity to efficiently produce diverse product variants, while mass customization uses modular design to tailor products to individual customer preferences without sacrificing economies of scale.
Batch-of-One
Batch-of-One production enables flexible manufacturing systems to efficiently deliver mass customization by producing individualized products on demand without sacrificing cost or speed.
Cellular Manufacturing
Cellular manufacturing enhances flexible manufacturing by organizing workstations into self-contained cells, enabling efficient mass customization through rapid product changeovers and reduced lead times.
Late-Stage Differentiation
Late-stage differentiation in flexible manufacturing enables cost-effective mass customization by postponing product variation until final production phases.
Changeover Time
Flexible manufacturing systems significantly reduce changeover time compared to mass customization by enabling rapid shifts between product types without extensive retooling.
Demand-Driven Operations
Demand-driven operations prioritize flexible manufacturing to rapidly adjust production processes while mass customization enables personalized products at scale by leveraging modular designs and real-time customer data.
Lot Size Flexibility
Flexible manufacturing enables rapid adjustment to varying lot sizes, whereas mass customization excels in producing personalized products with high lot size flexibility tailored to individual customer demands.
Customization Postponement
Flexible manufacturing enables customization postponement by allowing production systems to delay final product configuration until customer-specific details are known, contrasting with mass customization which integrates variety early in the production process.
Flexible manufacturing vs Mass customization Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com