SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Dies) streamlines setup times by minimizing equipment changeover to under ten minutes, enhancing production efficiency. Poka-Yoke emphasizes error-proofing processes to prevent defects and ensure quality control through mistake-proof designs. Combining SMED and Poka-Yoke in industrial engineering maximizes operational efficiency by reducing downtime and eliminating process errors.
Table of Comparison
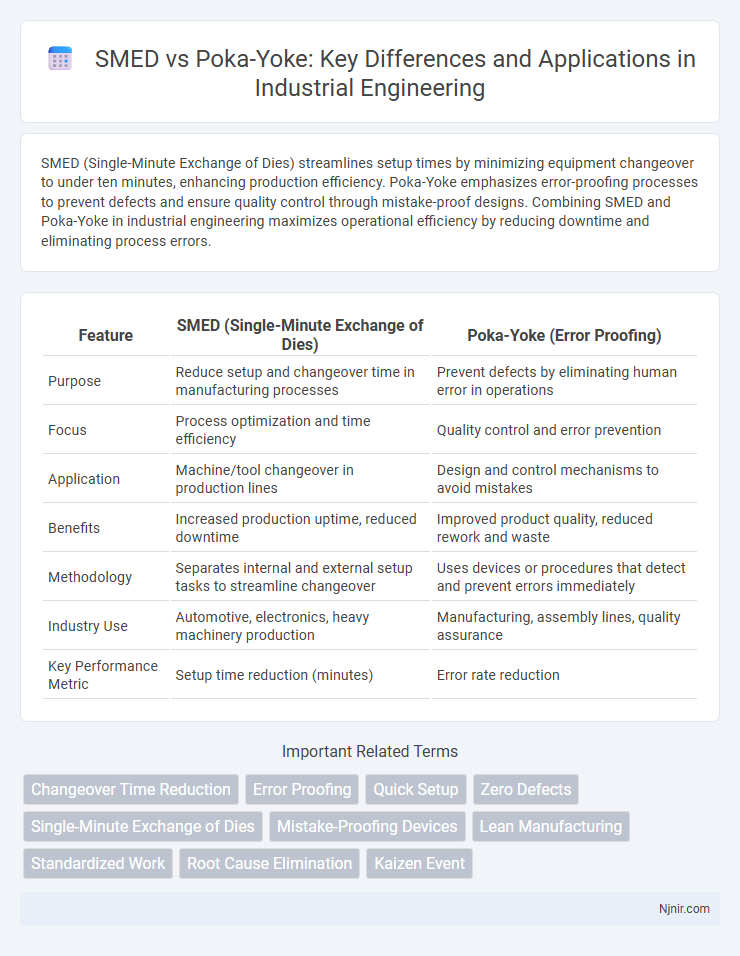
| Feature | SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Dies) | Poka-Yoke (Error Proofing) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduce setup and changeover time in manufacturing processes | Prevent defects by eliminating human error in operations |
| Focus | Process optimization and time efficiency | Quality control and error prevention |
| Application | Machine/tool changeover in production lines | Design and control mechanisms to avoid mistakes |
| Benefits | Increased production uptime, reduced downtime | Improved product quality, reduced rework and waste |
| Methodology | Separates internal and external setup tasks to streamline changeover | Uses devices or procedures that detect and prevent errors immediately |
| Industry Use | Automotive, electronics, heavy machinery production | Manufacturing, assembly lines, quality assurance |
| Key Performance Metric | Setup time reduction (minutes) | Error rate reduction |
Introduction to SMED and Poka-Yoke
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) is a lean manufacturing methodology aimed at reducing equipment setup times to less than 10 minutes, thereby increasing production efficiency and flexibility. Poka-Yoke, also known as mistake-proofing, involves designing processes and systems to prevent errors and defects before they occur, enhancing quality control and minimizing rework. Both SMED and Poka-Yoke are essential tools in lean manufacturing, directly contributing to waste reduction and continuous improvement.
Fundamental Principles of SMED
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Dies) emphasizes the reduction of setup times by separating internal and external setup activities to enable quicker changeovers, thereby enhancing manufacturing efficiency. The fundamental principles of SMED involve converting internal setup tasks into external ones, streamlining operations through standardized procedures, and employing quick-release mechanisms to minimize downtime. In contrast, Poka-Yoke focuses on error prevention by designing fail-safe systems that detect and correct mistakes during the manufacturing process to improve product quality.
Core Concepts of Poka-Yoke
Poka-Yoke centers on error-proofing processes by designing mechanisms that prevent mistakes or immediately detect defects to enhance quality control in manufacturing. Its core concepts include mistake prevention through control methods and detection methods, which trigger alerts or automatically correct errors to minimize human error. Compared to SMED, which focuses on reducing setup time to increase efficiency, Poka-Yoke emphasizes ensuring process reliability and defect-free production by embedding failsafe techniques.
Key Differences Between SMED and Poka-Yoke
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) primarily targets reducing equipment setup and changeover times to improve production efficiency, while Poka-Yoke focuses on mistake-proofing processes to prevent defects and errors. SMED involves systematic steps to separate and streamline internal and external setup activities, whereas Poka-Yoke uses devices or methods to detect and eliminate human errors during operation. The key difference lies in SMED optimizing time for equipment readiness, whereas Poka-Yoke enhances quality assurance through error prevention.
Applications of SMED in Manufacturing
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Dies) significantly reduces equipment setup times in manufacturing, enabling faster changeovers and increased production flexibility. This method is essential in industries such as automotive and electronics, where minimizing downtime directly impacts output efficiency and cost savings. Poka-Yoke complements SMED by focusing on error-proofing processes to prevent defects during production, but SMED's primary application lies in streamlining changeover procedures to boost overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Poka-Yoke Techniques for Error Prevention
Poka-Yoke techniques focus on error prevention through simple, fail-safe mechanisms that detect and correct human mistakes during the manufacturing process. Common methods include mistake-proof fixtures, control devices, and warning signals that ensure tasks are performed correctly or immediately halt the process to prevent defects. These techniques enhance product quality, reduce rework, and improve overall operational efficiency by minimizing the risk of errors at the source.
Benefits of Implementing SMED
Implementing SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Dies) drastically reduces equipment setup and changeover times, leading to increased production flexibility and higher overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). This efficiency improvement minimizes downtime and inventory levels, enabling faster response to market demands and reducing lead times. SMED also supports continuous improvement processes by standardizing and streamlining changeover procedures, which enhances workflow consistency and decreases operational costs.
Advantages of Integrating Poka-Yoke
Integrating Poka-Yoke with SMED significantly enhances error-proofing during rapid changeovers, reducing defects and minimizing downtime. This synergy improves production quality by preventing human errors in setup processes, ensuring consistent machine performance. Combining these methodologies leads to smoother transitions, higher efficiency, and lower waste in manufacturing environments.
Case Studies: SMED vs Poka-Yoke in Industry
Case studies in manufacturing showcase SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Dies) dramatically reducing setup times, such as Toyota's press shop cutting changeover from hours to under 10 minutes, boosting productivity. Poka-Yoke implementations, like in automotive assembly lines at Ford, have significantly decreased defects by preventing human errors through error-proofing mechanisms. Comparing both, SMED optimizes machine utilization by minimizing downtime, while Poka-Yoke enhances quality control by eliminating error occurrences, demonstrating complementary benefits in industrial process improvement.
Selecting the Right Method: SMED or Poka-Yoke
Selecting the right method between SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) and Poka-Yoke depends on the specific operational challenge faced. SMED effectively reduces setup times and accelerates changeover processes in manufacturing environments, optimizing production flow and minimizing downtime. Poka-Yoke, on the other hand, focuses on error-proofing by preventing defects and ensuring quality control, making it ideal for processes where mistake prevention is critical.
Changeover Time Reduction
SMED drastically reduces changeover time by streamlining internal and external setup tasks, while Poka-Yoke enhances changeover accuracy by preventing errors during the process.
Error Proofing
Poka-Yoke enhances error proofing by designing processes to prevent defects, while SMED focuses on reducing setup time to improve efficiency without directly targeting error prevention.
Quick Setup
SMED reduces machine setup time from hours to minutes by streamlining changeover steps, while Poka-Yoke prevents errors during quick setups through fail-safe mechanisms.
Zero Defects
SMED streamlines setup time to enhance efficiency while Poka-Yoke implements error-proofing techniques to achieve zero defects in manufacturing processes.
Single-Minute Exchange of Dies
Single-Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED) significantly reduces equipment setup time by streamlining changeover processes, enhancing manufacturing efficiency compared to Poka-Yoke's primary focus on error-proofing to prevent defects.
Mistake-Proofing Devices
Mistake-proofing devices in Poka-Yoke systems effectively prevent errors during production, while SMED primarily optimizes changeover times to enhance manufacturing efficiency.
Lean Manufacturing
SMED minimizes setup times to boost Lean Manufacturing efficiency, while Poka-Yoke enhances defect prevention and quality assurance within Lean processes.
Standardized Work
Standardized Work enables SMED to reduce setup times efficiently while Poka-Yoke enhances error-proofing by embedding fail-safe mechanisms within standardized processes.
Root Cause Elimination
SMED accelerates setup times to reduce production delays while Poka-Yoke eliminates root causes of errors by implementing fail-safes for quality assurance.
Kaizen Event
Kaizen events emphasize SMED for rapid setup reductions and Poka-Yoke for error-proofing processes to enhance continuous improvement and operational efficiency.
SMED vs Poka-Yoke Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com