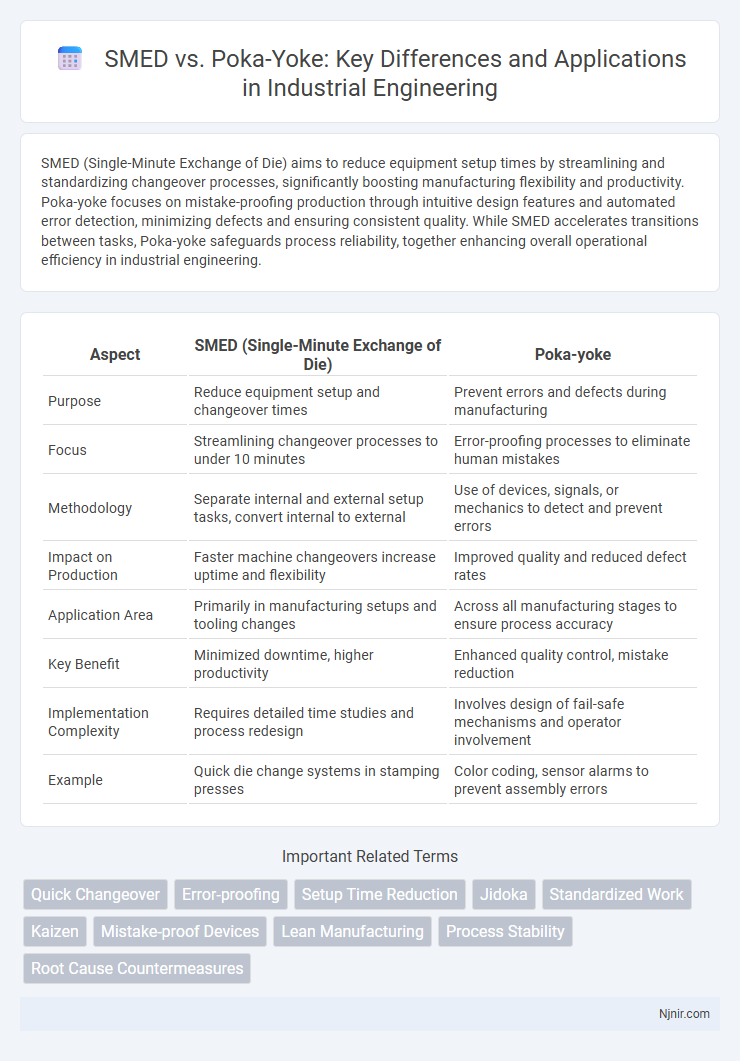
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) aims to reduce equipment setup times by streamlining and standardizing changeover processes, significantly boosting manufacturing flexibility and productivity. Poka-yoke focuses on mistake-proofing production through intuitive design features and automated error detection, minimizing defects and ensuring consistent quality. While SMED accelerates transitions between tasks, Poka-yoke safeguards process reliability, together enhancing overall operational efficiency in industrial engineering.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) | Poka-yoke |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduce equipment setup and changeover times | Prevent errors and defects during manufacturing |
| Focus | Streamlining changeover processes to under 10 minutes | Error-proofing processes to eliminate human mistakes |
| Methodology | Separate internal and external setup tasks, convert internal to external | Use of devices, signals, or mechanics to detect and prevent errors |
| Impact on Production | Faster machine changeovers increase uptime and flexibility | Improved quality and reduced defect rates |
| Application Area | Primarily in manufacturing setups and tooling changes | Across all manufacturing stages to ensure process accuracy |
| Key Benefit | Minimized downtime, higher productivity | Enhanced quality control, mistake reduction |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires detailed time studies and process redesign | Involves design of fail-safe mechanisms and operator involvement |
| Example | Quick die change systems in stamping presses | Color coding, sensor alarms to prevent assembly errors |
Introduction to Industrial Engineering Lean Tools
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) streamlines manufacturing by reducing setup times to under 10 minutes, significantly enhancing production flexibility and minimizing downtime. Poka-yoke, or error-proofing, focuses on preventing defects by integrating simple, fail-safe mechanisms directly into processes to ensure quality control. Both Lean tools are crucial in Industrial Engineering for optimizing operational efficiency and maintaining continuous improvement in production systems.
Understanding SMED: Definition and Principles
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) is a lean manufacturing methodology aimed at reducing equipment setup times to less than 10 minutes, thereby increasing production efficiency and flexibility. It focuses on separating internal and external setup activities, streamlining changeover processes, and standardizing operations to minimize downtime. Poka-yoke, in contrast, is a mistake-proofing technique designed to prevent errors during production, highlighting distinct roles where SMED enhances setup speed while Poka-yoke ensures quality control.
Poka-yoke: Concept and Importance in Manufacturing
Poka-yoke is a Japanese term meaning "mistake-proofing" used in manufacturing to prevent errors and defects during production processes. By incorporating simple and cost-effective mechanisms such as sensors, alarms, or visual cues, Poka-yoke ensures processes are performed correctly the first time, reducing rework and increasing product quality. This method is crucial in enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing downtime, making it an integral part of lean manufacturing and continuous improvement strategies.
Key Objectives: SMED vs Poka-yoke
SMED aims to drastically reduce equipment setup and changeover times to less than 10 minutes, enhancing manufacturing flexibility and reducing downtime. Poka-yoke focuses on preventing errors by designing processes and tools that avoid mistakes or make them immediately obvious, thereby improving product quality and minimizing defects. Both methodologies target efficiency improvements, with SMED emphasizing speed in changeover and Poka-yoke ensuring error-free production.
Process Optimization: Reducing Setup Time with SMED
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) significantly reduces setup time by streamlining and standardizing changeover steps, transforming internal tasks into external ones to achieve faster transitions. In contrast, Poka-yoke focuses on error-proofing processes to prevent defects rather than directly minimizing setup durations. Implementing SMED enhances process optimization by enabling rapid and efficient equipment switches, which increases production flexibility and reduces downtime.
Error Prevention: Role of Poka-yoke Systems
Poka-yoke systems play a critical role in error prevention by detecting and eliminating defects during the production process, ensuring that mistakes are corrected before they result in defects. Unlike SMED, which focuses on reducing setup times to increase manufacturing efficiency, poka-yoke targets process reliability by preventing human errors through simple, fail-safe mechanisms. Implementing poka-yoke devices leads to higher product quality and reduced rework by providing immediate feedback and forcing operators to follow correct procedures.
Implementation Strategies: SMED and Poka-yoke
SMED implementation strategies focus on reducing setup and changeover times by separating internal and external tasks, streamlining workflows, and standardizing procedures to achieve rapid die changes within minutes. Poka-yoke implementation emphasizes error-proofing through simple, often mechanical or visual devices that prevent mistakes or immediately highlight defects, integrating controls directly into the process to ensure quality at the source. Combining SMED and Poka-yoke strategies can drastically enhance operational efficiency by minimizing downtime and virtually eliminating human errors during manufacturing transitions.
Comparative Benefits: Efficiency and Quality Outcomes
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) drastically reduces setup times by streamlining equipment changeovers, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and increased machine uptime. Poka-yoke focuses on error-proofing processes to prevent defects, thereby improving product quality and reducing rework costs. Combining SMED's rapid changeover benefits with Poka-yoke's mistake-proofing mechanisms results in optimized production workflows that maximize both efficiency and quality outcomes.
Case Studies: Real-world Applications of SMED and Poka-yoke
Case studies of SMED demonstrate drastically reduced changeover times, exemplified by Toyota's implementation where die exchange times dropped from hours to minutes, significantly boosting production efficiency. Poka-yoke applications, such as in automotive assembly lines at Honda, reveal how error-proofing mechanisms prevent defects by automatically detecting incorrect part placements, thereby reducing rework rates and enhancing product quality. Integrating SMED with Poka-yoke in manufacturing environments confirms synergies that minimize downtime and defects concurrently, as evidenced by companies like Bosch improving both throughput and defect reduction through combined approaches.
Integration and Synergy: Leveraging Both Tools for Lean Success
SMED streamlines changeover times by reducing setup to single-digit minutes, significantly boosting production efficiency, while Poka-yoke focuses on error prevention through mistake-proofing mechanisms. Integrating SMED with Poka-yoke enhances lean manufacturing by combining rapid transitions with quality assurance, minimizing downtime and defect rates simultaneously. This synergy accelerates workflow, reduces operational costs, and improves overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), driving sustainable lean success.
Quick Changeover
SMED drastically reduces setup time by streamlining changeover processes, while Poka-yoke enhances quick changeover by preventing errors during equipment adjustments.
Error-proofing
SMED reduces setup time by streamlining changeover processes, while Poka-yoke enhances error-proofing by preventing mistakes through immediate defect detection and correction.
Setup Time Reduction
SMED reduces setup time by streamlining and standardizing changeover processes, while Poka-yoke minimizes errors during setup through mistake-proofing mechanisms that enhance setup efficiency.
Jidoka
Jidoka enhances SMED efficiency by integrating Poka-yoke mechanisms to automate defect detection and prevent errors during rapid equipment changeovers.
Standardized Work
SMED accelerates standardized work by minimizing setup times, while Poka-yoke enhances standardized work through mistake-proofing processes to ensure consistent quality.
Kaizen
SMED accelerates setup time by streamlining changeover processes, while Poka-yoke enhances quality through error-proofing, both integral to Kaizen's continuous improvement methodology.
Mistake-proof Devices
SMED reduces changeover time by streamlining setup processes, while Poka-yoke employs mistake-proof devices to prevent errors during production.
Lean Manufacturing
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) reduces equipment setup times to improve Lean Manufacturing efficiency, while Poka-yoke focuses on error prevention to enhance product quality and minimize defects.
Process Stability
SMED enhances process stability by minimizing downtime during equipment changeovers, while Poka-yoke ensures process stability through error prevention and defect reduction in production.
Root Cause Countermeasures
SMED reduces changeover time by streamlining setup processes to address root causes of delays, while Poka-yoke prevents errors by implementing fail-safe mechanisms targeting root causes of defects.
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) vs Poka-yoke Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com