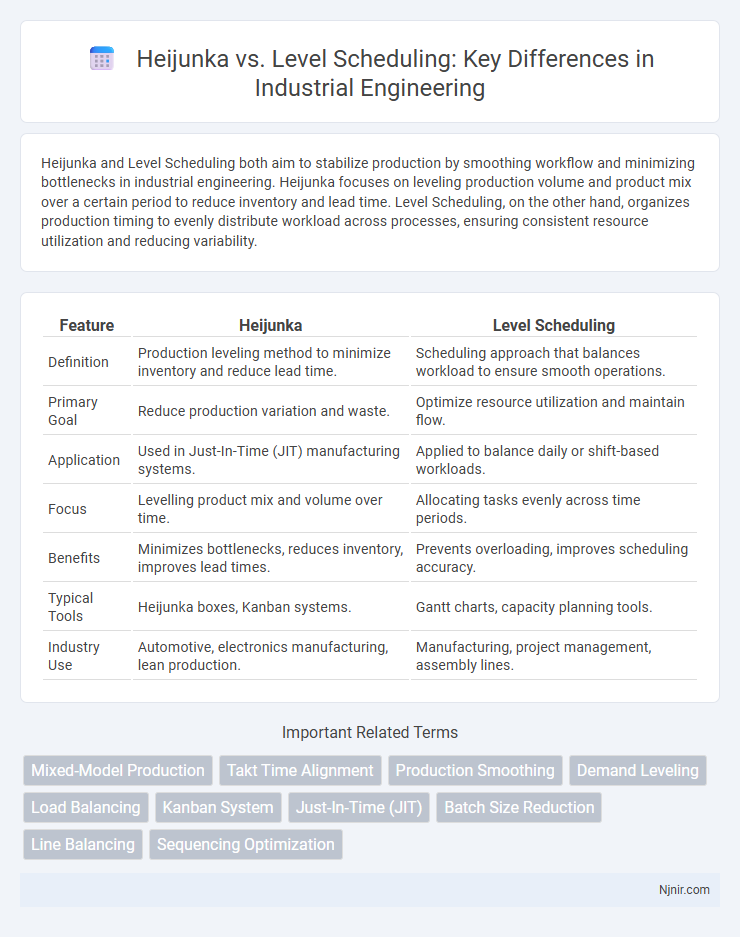
Heijunka and Level Scheduling both aim to stabilize production by smoothing workflow and minimizing bottlenecks in industrial engineering. Heijunka focuses on leveling production volume and product mix over a certain period to reduce inventory and lead time. Level Scheduling, on the other hand, organizes production timing to evenly distribute workload across processes, ensuring consistent resource utilization and reducing variability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heijunka | Level Scheduling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production leveling method to minimize inventory and reduce lead time. | Scheduling approach that balances workload to ensure smooth operations. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce production variation and waste. | Optimize resource utilization and maintain flow. |
| Application | Used in Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing systems. | Applied to balance daily or shift-based workloads. |
| Focus | Levelling product mix and volume over time. | Allocating tasks evenly across time periods. |
| Benefits | Minimizes bottlenecks, reduces inventory, improves lead times. | Prevents overloading, improves scheduling accuracy. |
| Typical Tools | Heijunka boxes, Kanban systems. | Gantt charts, capacity planning tools. |
| Industry Use | Automotive, electronics manufacturing, lean production. | Manufacturing, project management, assembly lines. |
Introduction to Heijunka and Level Scheduling
Heijunka is a Japanese production leveling technique designed to reduce unevenness in manufacturing by smoothing out workflow and minimizing inventory fluctuations. Level Scheduling, closely related to Heijunka, involves organizing production tasks to maintain a consistent pace, aligning output with customer demand without significant delays or bottlenecks. Both methods optimize efficiency and flexibility in lean manufacturing environments by promoting balanced workloads and timely delivery.
Historical Background in Industrial Engineering
Heijunka, originating from the Toyota Production System in the mid-20th century, revolutionized manufacturing by promoting production leveling to reduce waste and improve efficiency. Level scheduling, developed in parallel but distinct in application, emphasizes consistent workflow and inventory balance across various industrial engineering contexts. Both methodologies emerged as pivotal responses to the challenges of mass production and demand variability during Japan's post-war industrial growth.
Core Principles of Heijunka
Heijunka centers on smoothing production by leveling both volume and product mix to reduce waste and enable consistent workflow, contrasting with traditional Level Scheduling that primarily focuses on timing. Core principles of Heijunka include producing a stable and predictable output, balancing workload evenly across processes, and minimizing inventory buildup. This approach enhances operational efficiency by aligning production with demand variability, leading to improved resource utilization and shorter lead times.
Fundamentals of Level Scheduling
Level Scheduling focuses on evenly distributing production orders to match customer demand, minimizing fluctuations in the workflow. It prioritizes consistent production volumes by sequencing tasks to balance workload, reduce inventory, and improve efficiency. Heijunka complements this by smoothing production across all product types and volumes, ensuring stability in operations.
Key Differences: Heijunka vs Level Scheduling
Heijunka is a production leveling technique that smooths out workloads by distributing manufacturing orders evenly over time to reduce waste and inventory. Level Scheduling, often used interchangeably with Heijunka, specifically refers to the sequencing of production to match customer demand patterns more precisely. The key difference lies in Heijunka's broader approach to balancing production volume and variety, while Level Scheduling focuses more narrowly on the timing and order of tasks to achieve a stable workflow.
Benefits of Heijunka in Production Systems
Heijunka, a key lean manufacturing technique, smooths production by leveling output, reducing variability and minimizing inventory costs compared to traditional level scheduling. It enables consistent workflow, balances demand fluctuations, and decreases lead times, increasing overall operational efficiency. Implementing Heijunka improves resource utilization, enhances quality control, and supports just-in-time production by promoting continuous, stable processes.
Advantages of Level Scheduling for Manufacturers
Level Scheduling streamlines production by distributing workloads evenly over time, reducing bottlenecks and minimizing inventory costs. Manufacturers benefit from enhanced flexibility to respond to demand fluctuations while maintaining consistent output rates. This approach improves resource utilization and supports just-in-time manufacturing principles for greater operational efficiency.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Heijunka implementation challenges often include managing demand variability and balancing production loads across different product types, which can lead to complexity in scheduling and resource allocation. Level scheduling faces difficulties in maintaining consistent production despite fluctuating order volumes, requiring robust forecasting and flexible workforce management. Solutions involve integrating advanced demand forecasting tools, implementing flexible work cells, and adopting real-time production monitoring systems to enhance responsiveness and maintain production stability.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case studies reveal that Heijunka significantly improves production flow by leveling both volume and product mix, as demonstrated in Toyota's manufacturing plants where reduced inventory and lead times were achieved. In contrast, level scheduling is widely applied in industries like electronics assembly to stabilize workforce and resource allocation, resulting in consistent output and minimized downtime. Companies implementing Heijunka report enhanced flexibility and responsiveness to demand fluctuations, while level scheduling excels in environments requiring strict adherence to fixed schedules and capacity constraints.
Future Trends in Production Leveling Strategies
Heijunka and Level Scheduling continue to evolve with advancements in AI-driven analytics and real-time data integration, enabling more precise demand forecasting and adaptive production pacing. Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and machine learning, optimize Heijunka's workload distribution to minimize inventory and reduce lead times. Future production leveling strategies emphasize digital twins and autonomous scheduling systems to enhance responsiveness and efficiency across complex manufacturing environments.
Mixed-Model Production
Heijunka optimizes mixed-model production by smoothing workflow and reducing inventory, while level scheduling ensures consistent takt time for synchronized multi-model output.
Takt Time Alignment
Heijunka optimizes production smoothing by aligning with takt time to balance workflow, while Level Scheduling structures tasks to match takt time intervals for consistent output.
Production Smoothing
Heijunka enables production smoothing by evenly distributing workloads and minimizing inventory, while Level Scheduling sequences tasks to maintain consistent output rates and reduce bottlenecks.
Demand Leveling
Heijunka and Level Scheduling both focus on demand leveling by smoothing production volume and variety to minimize waste and improve workflow efficiency.
Load Balancing
Heijunka optimizes load balancing by smoothing production volumes to reduce inventory and lead time variability, while Level Scheduling focuses on sequencing tasks to evenly distribute workloads and resources across the production process.
Kanban System
The Kanban system enhances Heijunka by visually controlling work-in-progress and ensuring smooth, level scheduling that balances production flow and demand variability.
Just-In-Time (JIT)
Heijunka optimizes Just-In-Time (JIT) production by leveling work volume and variety to minimize waste, while Level Scheduling implements this by sequencing production tasks to ensure consistent flow and timely delivery.
Batch Size Reduction
Heijunka reduces batch size by leveling production volume and variety to minimize inventory and lead times, while level scheduling focuses on uniformly distributing tasks over time to enhance workflow efficiency without necessarily minimizing batch size.
Line Balancing
Heijunka enhances line balancing by smoothing production volume and mix over time, while Level Scheduling ensures consistent workflow by sequencing tasks to optimize resource utilization and minimize bottlenecks.
Sequencing Optimization
Heijunka optimizes sequencing by leveling production volume and mix to reduce muda, while Level Scheduling focuses on maintaining consistent workflow timing for improved sequencing efficiency.
Heijunka vs Level Scheduling Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com