Machine vision systems offer consistent and rapid inspection capabilities that significantly reduce human error and increase production efficiency. Unlike human inspection, these automated systems can analyze complex patterns and detect minute defects with higher accuracy under varying lighting and environmental conditions. Integrating machine vision into industrial processes enhances quality control while minimizing labor costs and inspection time.
Table of Comparison
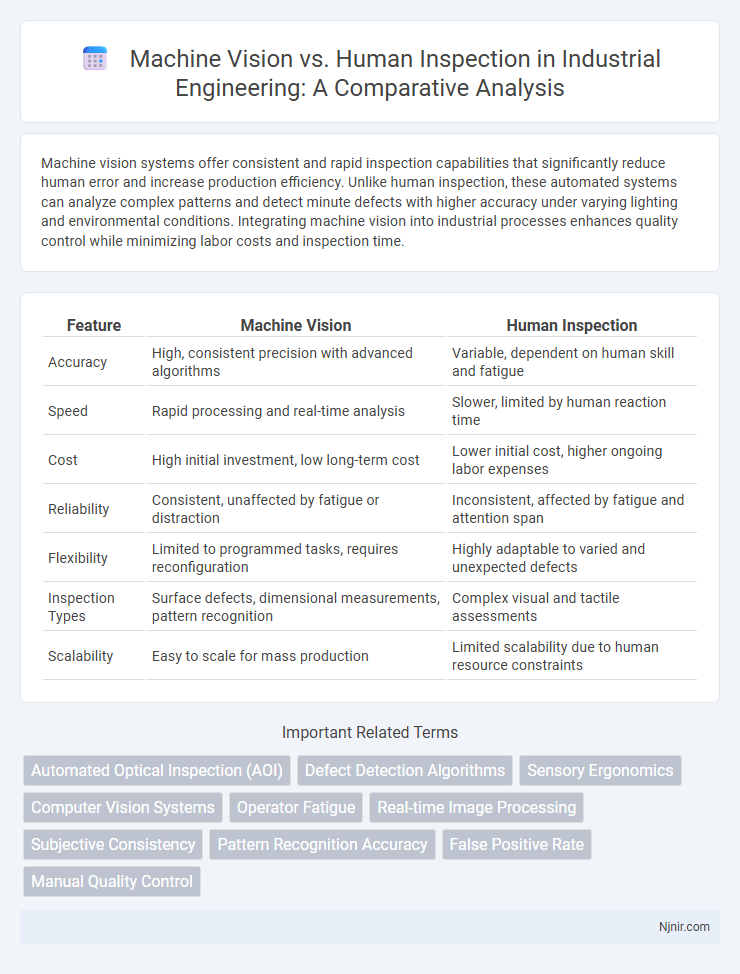
| Feature | Machine Vision | Human Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High, consistent precision with advanced algorithms | Variable, dependent on human skill and fatigue |
| Speed | Rapid processing and real-time analysis | Slower, limited by human reaction time |
| Cost | High initial investment, low long-term cost | Lower initial cost, higher ongoing labor expenses |
| Reliability | Consistent, unaffected by fatigue or distraction | Inconsistent, affected by fatigue and attention span |
| Flexibility | Limited to programmed tasks, requires reconfiguration | Highly adaptable to varied and unexpected defects |
| Inspection Types | Surface defects, dimensional measurements, pattern recognition | Complex visual and tactile assessments |
| Scalability | Easy to scale for mass production | Limited scalability due to human resource constraints |
Introduction to Machine Vision and Human Inspection
Machine vision systems use cameras, sensors, and artificial intelligence to automate the process of visual inspection, enabling faster and more consistent detection of defects in manufacturing and quality control. Human inspection relies on manual observation, leveraging human expertise and flexibility to identify subtle irregularities and complex visual patterns. Combining machine vision with human inspection can enhance overall accuracy and efficiency in quality assessment tasks.
Key Differences Between Machine Vision and Human Inspection
Machine vision systems deliver consistent, high-speed analysis using advanced cameras and algorithms, while human inspection relies on subjective judgment and slower manual evaluation. Machine vision excels in detecting minute defects and performing repetitive tasks without fatigue, whereas human inspectors provide contextual understanding and adaptability to unforeseen issues. Integration of machine vision reduces errors and boosts productivity, but complex decision-making and nuanced assessments still benefit from human expertise.
Accuracy and Consistency in Quality Control
Machine vision systems deliver superior accuracy and consistency in quality control by utilizing high-resolution cameras and advanced algorithms that detect defects with precision beyond human capability. Unlike human inspection, machine vision eliminates variability caused by fatigue, distraction, or subjective judgment, ensuring uniform results across large production volumes. The integration of real-time data processing in machine vision enhances defect detection rates and reduces false positives, providing a reliable and scalable solution for maintaining stringent quality standards.
Speed and Efficiency of Inspection Processes
Machine vision systems significantly outperform human inspection in speed, processing thousands of images per minute with consistent accuracy. Automated inspection reduces cycle time and eliminates fatigue-related errors, enhancing overall efficiency in production lines. High-speed cameras and real-time image analysis enable immediate defect detection, accelerating decision-making and minimizing downtime.
Adaptability to Complex or Variable Tasks
Machine vision systems excel in processing repetitive tasks with high accuracy but often struggle with adaptability to complex or variable tasks due to limited contextual understanding and inflexible programming. Human inspection offers superior adaptability, leveraging cognitive abilities and experience to interpret subtle variations and novel conditions in real-time. Combining machine vision with human oversight enhances efficiency, enabling the automation of routine inspections while addressing intricate or unpredictable scenarios effectively.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Gains
Machine vision systems require a higher initial investment due to hardware, software, and integration costs but offer significant long-term savings through increased inspection speed, consistency, and reduced labor expenses. Human inspection entails lower upfront costs but incurs ongoing expenses related to wages, training, and potential errors leading to rework or product recalls. Evaluating cost-benefit analysis reveals machine vision provides superior returns over time by enhancing productivity and reducing quality control failures.
Human Factors: Fatigue, Training, and Error Rates
Human inspection often struggles with fatigue, leading to decreased accuracy and increased error rates over prolonged periods, which machine vision systems do not experience. Training requirements for human inspectors can be extensive and variable, impacting consistency and reliability, whereas machine vision relies on standardized algorithms that maintain performance once properly calibrated. Error rates in human inspection tend to be higher and less predictable due to cognitive and physical limitations, while machine vision offers more consistent precision through automated image analysis.
Integration of Machine Vision in Industrial Workflows
Integration of machine vision in industrial workflows enhances precision and accelerates quality control by automating defect detection and measurement tasks traditionally performed by human inspectors. Machine vision systems combine high-speed image processing with artificial intelligence to consistently analyze complex patterns and produce real-time insights, reducing human error and increasing production efficiency. Leveraging these technologies supports scalable inspection processes, improves traceability, and enables seamless data integration across manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications and Outcomes
Case studies reveal that machine vision systems outperform human inspection in high-speed manufacturing environments by delivering consistent accuracy and reducing defect rates by up to 90%. In automotive assembly lines, machine vision detects micro-defects and alignment issues that human inspectors often miss, enhancing product quality and lowering recall costs. Conversely, complex visual tasks requiring adaptive judgment, like textile inspection, still benefit from human oversight, demonstrating a hybrid approach achieves optimal outcomes across industries.
Future Trends: Collaborative Inspection and AI Integration
Future trends in machine vision emphasize collaborative inspection, where AI-powered systems work alongside human inspectors to enhance accuracy and efficiency in quality control. Integration of advanced AI algorithms enables real-time decision-making, defect detection, and adaptive learning from human feedback, driving continuous improvement in inspection processes. This fusion of human expertise and machine intelligence is transforming manufacturing industries by reducing errors and accelerating production cycles.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) leverages machine vision technology to provide faster, more accurate, and consistent defect detection in manufacturing processes compared to traditional human inspection.
Defect Detection Algorithms
Machine vision defect detection algorithms achieve higher accuracy and consistency than human inspection by utilizing advanced image processing techniques and real-time data analysis.
Sensory Ergonomics
Machine vision enhances sensory ergonomics by reducing human exposure to visual fatigue and repetitive strain during inspection tasks.
Computer Vision Systems
Computer vision systems outperform human inspection by providing faster, more accurate defect detection and consistent quality control in industrial applications.
Operator Fatigue
Machine vision significantly reduces operator fatigue by automating repetitive visual inspections, thereby enhancing accuracy and consistency compared to human inspection.
Real-time Image Processing
Machine vision systems outperform human inspection in real-time image processing by delivering faster, more accurate defect detection through advanced algorithms and high-speed cameras.
Subjective Consistency
Machine vision ensures objective and consistent inspection results by eliminating human subjectivity and variability common in human inspection processes.
Pattern Recognition Accuracy
Machine vision systems achieve higher pattern recognition accuracy than human inspection by consistently analyzing complex visual data with precise algorithms and minimal error rates.
False Positive Rate
Machine vision systems typically achieve a lower false positive rate than human inspection by consistently applying predefined criteria without fatigue or subjective bias.
Manual Quality Control
Manual quality control relies on human inspection to identify defects, but machine vision offers faster, more consistent, and highly accurate detection, reducing errors and enhancing production efficiency.
Machine vision vs Human inspection Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com