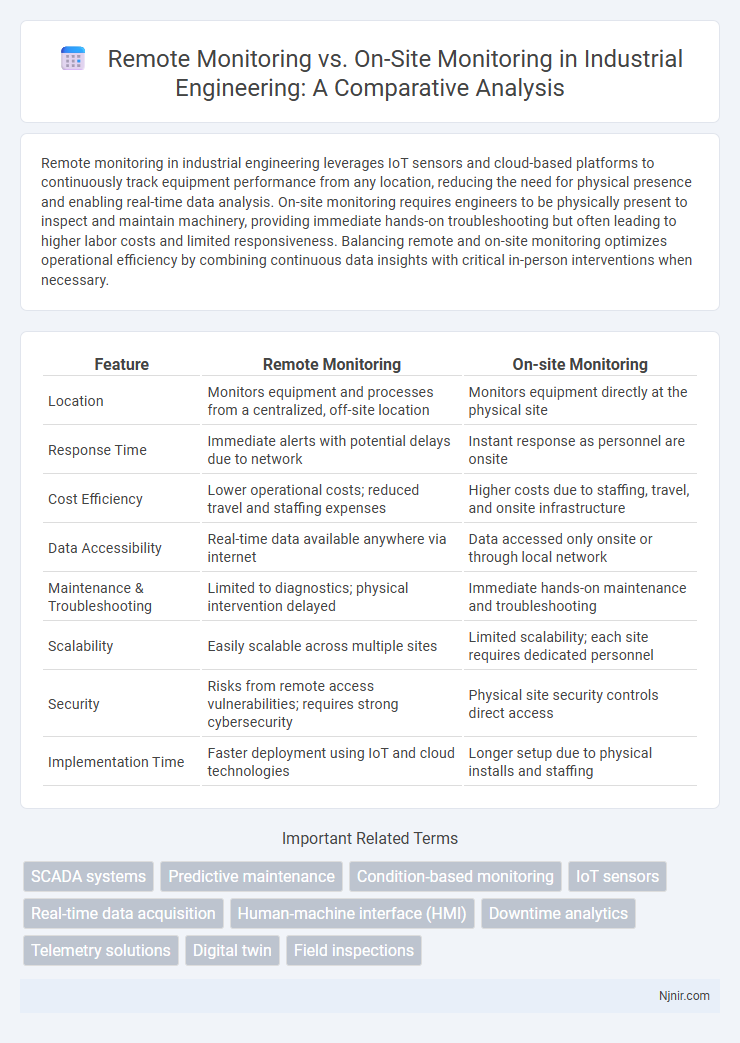
Remote monitoring in industrial engineering leverages IoT sensors and cloud-based platforms to continuously track equipment performance from any location, reducing the need for physical presence and enabling real-time data analysis. On-site monitoring requires engineers to be physically present to inspect and maintain machinery, providing immediate hands-on troubleshooting but often leading to higher labor costs and limited responsiveness. Balancing remote and on-site monitoring optimizes operational efficiency by combining continuous data insights with critical in-person interventions when necessary.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Remote Monitoring | On-site Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Monitors equipment and processes from a centralized, off-site location | Monitors equipment directly at the physical site |
| Response Time | Immediate alerts with potential delays due to network | Instant response as personnel are onsite |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs; reduced travel and staffing expenses | Higher costs due to staffing, travel, and onsite infrastructure |
| Data Accessibility | Real-time data available anywhere via internet | Data accessed only onsite or through local network |
| Maintenance & Troubleshooting | Limited to diagnostics; physical intervention delayed | Immediate hands-on maintenance and troubleshooting |
| Scalability | Easily scalable across multiple sites | Limited scalability; each site requires dedicated personnel |
| Security | Risks from remote access vulnerabilities; requires strong cybersecurity | Physical site security controls direct access |
| Implementation Time | Faster deployment using IoT and cloud technologies | Longer setup due to physical installs and staffing |
Overview of Remote and On-site Monitoring in Industrial Engineering
Remote monitoring in industrial engineering utilizes IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and cloud platforms to supervise equipment performance and process conditions from distant locations, enhancing predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. On-site monitoring involves direct physical inspection and instrumentation control by personnel, allowing immediate response to operational anomalies and ensuring hands-on management of critical systems. Integrating remote and on-site monitoring optimizes reliability, safety, and operational efficiency in industrial environments.
Key Technologies in Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring leverages advanced technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI) to enable real-time data collection and analysis without physical presence. Key technologies include wireless sensor networks that transmit detailed operational data, machine learning algorithms for predictive maintenance, and cloud-based platforms facilitating centralized monitoring across multiple locations. These innovations enhance efficiency and reduce the need for frequent on-site visits compared to traditional on-site monitoring methods.
Core Components of On-site Monitoring Systems
On-site monitoring systems primarily rely on physical sensors, data acquisition units, and real-time control interfaces to ensure accurate and immediate data collection within the monitored environment. Core components include temperature and humidity sensors, motion detectors, and centralized monitoring consoles that facilitate prompt detection and response to anomalies. These systems provide direct oversight and reduce latency compared to remote monitoring setups, which depend heavily on cloud connectivity and network infrastructure.
Advantages of Remote Monitoring for Industrial Operations
Remote monitoring for industrial operations offers real-time data access and continuous system oversight, enhancing predictive maintenance and reducing equipment downtime. It enables centralized control across multiple locations, improving operational efficiency and minimizing the need for onsite personnel. Advanced sensor technologies and IoT integration facilitate early anomaly detection, optimizing resource allocation and safety management in industrial environments.
Benefits of Traditional On-site Monitoring
Traditional on-site monitoring provides direct access to study sites, enabling immediate verification of data accuracy and compliance with protocols. It facilitates face-to-face communication and rapid resolution of issues, enhancing oversight and quality control in clinical trials. On-site visits also allow for thorough inspection of facilities and equipment, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards.
Challenges Associated with Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring faces challenges such as data security concerns, limited real-time access to critical equipment, and dependency on reliable internet connectivity. On-site monitoring allows for immediate physical inspections and troubleshooting, which remote methods may struggle to replicate accurately. Remote systems often require advanced technology investments and skilled personnel to interpret data effectively, complicating seamless operational oversight.
Limitations of On-site Monitoring Approaches
On-site monitoring approaches face significant limitations due to their dependency on physical presence, which restricts real-time data access and delays critical decision-making. High operational costs and logistical challenges often result in limited frequency and scope of inspections, potentially overlooking intermittent issues. Furthermore, the inability to continuously track dynamic or remote environments reduces the effectiveness of on-site monitoring compared to remote monitoring technologies.
Cost Comparison: Remote vs On-site Monitoring
Remote monitoring significantly reduces costs by eliminating travel expenses, lowering labor hours, and enabling real-time data access, making it more budget-friendly than on-site monitoring. On-site monitoring incurs higher costs due to travel, accommodation, and time spent physically at the location, alongside increased logistical coordination. Companies adopting remote monitoring solutions often report up to 40-60% savings in operational expenses compared to traditional on-site methods.
Security and Data Privacy Considerations
Remote monitoring utilizes encrypted data transmission and secure cloud storage to protect sensitive information, but may pose risks due to potential cyberattacks and network vulnerabilities. On-site monitoring offers greater control over data access and physical security measures, minimizing exposure to external threats but requiring stringent internal protocols and regular audits. Organizations must assess their security infrastructure, compliance requirements such as GDPR or HIPAA, and risk tolerance when choosing between remote and on-site monitoring solutions.
Future Trends in Industrial Monitoring Solutions
Future trends in industrial monitoring solutions emphasize the integration of AI-driven remote monitoring systems that enhance real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance capabilities. On-site monitoring continues to evolve with advanced sensor networks and edge computing, enabling faster local decision-making and reduced latency. Hybrid models combining remote and on-site monitoring are gaining traction, improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime in smart manufacturing environments.
SCADA systems
Remote monitoring of SCADA systems enables real-time data analysis and fault detection from centralized locations, while on-site monitoring provides direct hardware inspection and maintenance, optimizing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
Predictive maintenance
Remote monitoring enables real-time data analysis for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and costs compared to traditional on-site monitoring methods.
Condition-based monitoring
Condition-based monitoring enhances remote monitoring by enabling real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance, reducing the need for frequent on-site inspections and minimizing downtime.
IoT sensors
IoT sensors enable remote monitoring by providing real-time data collection and analysis, reducing the need for frequent on-site visits and enhancing efficiency in industrial and environmental applications.
Real-time data acquisition
Remote monitoring enables real-time data acquisition through continuous digital transmission, while on-site monitoring relies on periodic manual data collection, limiting immediacy.
Human-machine interface (HMI)
Remote monitoring leverages advanced Human-machine interface (HMI) technologies to provide real-time data visualization and control from any location, whereas on-site monitoring relies on local HMI systems for direct, immediate interaction and troubleshooting.
Downtime analytics
Remote monitoring provides real-time downtime analytics with continuous data collection, enabling faster issue detection and reduced operational interruptions compared to periodic, manually gathered on-site monitoring reports.
Telemetry solutions
Telemetry solutions in remote monitoring enable real-time data transmission and analysis, offering faster response times and reduced operational costs compared to traditional on-site monitoring methods.
Digital twin
Digital twin technology enhances remote monitoring by providing real-time, accurate virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling continuous data analysis and predictive maintenance without the need for on-site presence.
Field inspections
Remote monitoring enhances field inspections by enabling real-time data collection and analysis from multiple locations, whereas on-site monitoring requires physical presence for direct observation and manual data gathering.
Remote monitoring vs On-site monitoring Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com