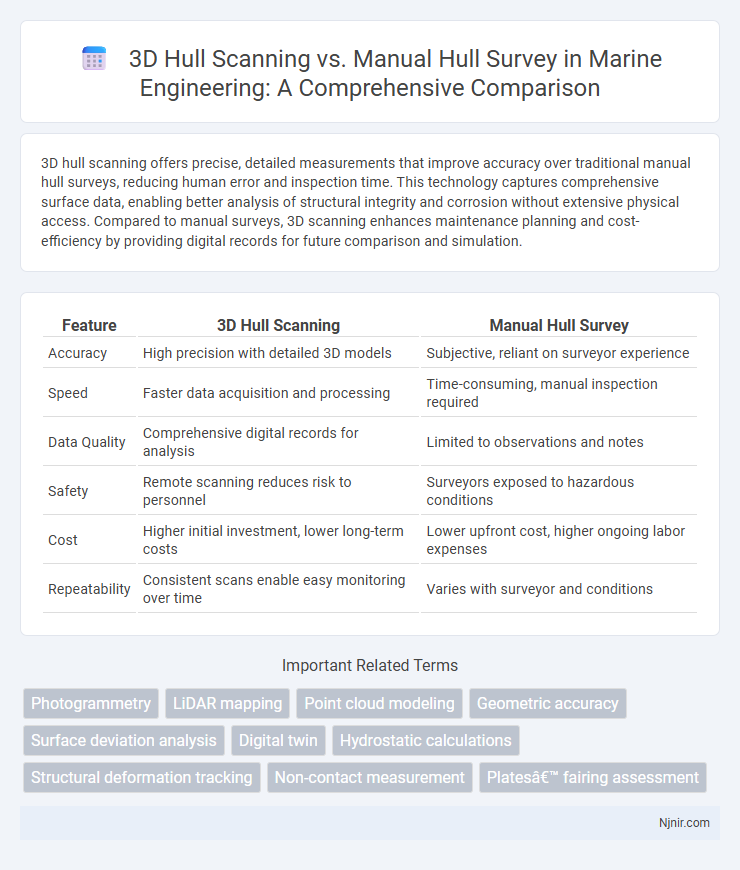
3D hull scanning offers precise, detailed measurements that improve accuracy over traditional manual hull surveys, reducing human error and inspection time. This technology captures comprehensive surface data, enabling better analysis of structural integrity and corrosion without extensive physical access. Compared to manual surveys, 3D scanning enhances maintenance planning and cost-efficiency by providing digital records for future comparison and simulation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Hull Scanning | Manual Hull Survey |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High precision with detailed 3D models | Subjective, reliant on surveyor experience |
| Speed | Faster data acquisition and processing | Time-consuming, manual inspection required |
| Data Quality | Comprehensive digital records for analysis | Limited to observations and notes |
| Safety | Remote scanning reduces risk to personnel | Surveyors exposed to hazardous conditions |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower long-term costs | Lower upfront cost, higher ongoing labor expenses |
| Repeatability | Consistent scans enable easy monitoring over time | Varies with surveyor and conditions |
Introduction to Hull Inspection Methods
3D hull scanning utilizes advanced laser technology to create precise digital models of a vessel's hull, enabling detailed analysis of structural integrity and corrosion without physical contact. Manual hull surveys rely on expert inspectors visually examining the hull, often requiring physical access to all sections, which can be time-consuming and less accurate. The integration of 3D scanning offers enhanced accuracy, speed, and comprehensive coverage compared to traditional manual inspections.
Overview of 3D Hull Scanning Technology
3D hull scanning technology employs advanced laser or photogrammetry systems to capture detailed and precise digital representations of a ship's hull, enabling faster and more accurate inspection compared to manual surveys. This method generates high-resolution 3D models that facilitate thorough analysis of surface conditions, deformation, and wear without physical contact, reducing human error and operational risks. The integration of automated data collection and processing streamlines maintenance planning and regulatory compliance, significantly enhancing overall efficiency in hull integrity assessments.
Manual Hull Survey: Traditional Approach
Manual hull surveys rely on physical inspections, where surveyors use tools like thickness gauges and visual checks to assess hull integrity. This traditional approach provides hands-on evaluation of corrosion, damage, and structural weaknesses but can be time-intensive and limited by human error. Despite advancements in technology, manual surveys remain crucial for detailed tactile assessments and immediate anomaly detection.
Accuracy Comparison: 3D Scanning vs Manual Survey
3D hull scanning delivers unparalleled accuracy by capturing millions of precise data points in a digital format, minimizing human error and providing comprehensive coverage of complex hull geometries. Manual hull surveys rely heavily on the surveyor's experience and physical measurements, often resulting in lower precision and potential inconsistencies across different areas of the hull. Advanced 3D scanning technologies enhance repeatability and enable detailed analysis, outperforming traditional manual methods in both speed and measurement fidelity.
Time Efficiency and Project Scheduling
3D hull scanning significantly reduces inspection time by capturing detailed, accurate data in a fraction of the time required for manual hull surveys. This advanced technology enables faster project scheduling and minimizes downtime by providing immediate digital models for analysis and decision-making. Manual surveys, while thorough, often involve longer on-site periods and slower data processing, impacting overall project timelines.
Cost Implications of Each Method
3D hull scanning significantly reduces labor costs by automating data collection and minimizing inspection time compared to manual hull surveys, which require extensive human effort and longer turnaround times. While the initial investment in 3D scanning equipment and software can be high, the technology offers long-term savings through enhanced accuracy, fewer reworks, and rapid report generation. Manual hull surveys may appear less expensive upfront but often incur higher overall costs due to slower processes, increased risk of human error, and potential for incomplete data capture.
Safety Considerations in Both Techniques
3D hull scanning enhances safety by minimizing human exposure to hazardous environments through remote data acquisition, reducing the risk of accidents during inspections. Manual hull surveys require inspectors to work in confined, potentially unstable spaces, increasing the likelihood of physical injuries and exposure to harmful substances. Integrating 3D scanning technology with manual methods offers a balanced approach, leveraging precision data collection while maintaining essential hands-on safety assessments.
Data Documentation and Analysis Capabilities
3D hull scanning provides precise, high-resolution digital models that enable detailed data documentation and comprehensive analysis of hull conditions, including accurate measurements of structural integrity and deformation. Manual hull surveys rely on visual inspections and manual measurements, which can lead to incomplete data and subjective assessments, limiting post-survey analysis and trend tracking. The advanced data capture of 3D scanning facilitates efficient detection of corrosion, cracks, and fouling, enhancing predictive maintenance and lifecycle management compared to traditional survey methods.
Applications in Maintenance and Repair
3D hull scanning offers high-precision geometric data that enables accurate damage assessment, corrosion mapping, and deformations detection, streamlining maintenance and repair planning. Manual hull surveys rely on visual inspection and physical measurements, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error, limiting their accuracy in complex structural analysis. Integrating 3D scanning in maintenance enables predictive repairs, reduces dry-dock time, and enhances the overall lifecycle management of marine vessels.
Future Trends in Marine Hull Inspection
3D hull scanning technology is revolutionizing marine hull inspection by enabling faster, more accurate data collection and real-time damage assessment compared to traditional manual hull surveys. Advanced imaging techniques, such as laser scanning and photogrammetry, facilitate comprehensive digital twins of vessel hulls, improving predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. Future trends highlight increased integration of AI-driven analytics and autonomous drones to enhance inspection precision and operational efficiency.
Photogrammetry
3D hull scanning using photogrammetry provides highly accurate, detailed digital models of ship hulls faster and with less human error compared to traditional manual hull surveys.
LiDAR mapping
LiDAR-based 3D hull scanning delivers highly accurate, detailed digital models faster and with less human error compared to traditional manual hull surveys.
Point cloud modeling
3D hull scanning generates precise point cloud models enabling faster, more accurate inspections compared to time-consuming, subjective manual hull surveys.
Geometric accuracy
3D hull scanning provides significantly higher geometric accuracy than manual hull surveys by capturing precise, detailed digital measurements that minimize human error and improve structural assessment reliability.
Surface deviation analysis
3D hull scanning provides precise surface deviation analysis by capturing high-resolution, accurate digital models that detect minute irregularities missed in manual hull surveys, improving maintenance and performance assessments.
Digital twin
3D hull scanning creates an accurate digital twin of the vessel for precise condition monitoring and maintenance, outperforming manual hull surveys in speed, detail, and data reliability.
Hydrostatic calculations
3D hull scanning provides precise hydrostatic calculations by capturing accurate hull geometry, significantly improving upon the manual hull survey's reliance on less precise measurements and estimations.
Structural deformation tracking
3D hull scanning provides precise, real-time structural deformation tracking with high-resolution data compared to the slower, less accurate manual hull survey methods.
Non-contact measurement
3D hull scanning offers precise, non-contact measurement of ship hulls, enabling faster data acquisition and reducing human error compared to manual hull surveys that rely on direct physical inspection.
Plates’ fairing assessment
3D hull scanning provides precise, high-resolution data for accurate plates' fairing assessment, significantly outperforming the subjective and time-consuming manual hull survey method.
3D hull scanning vs Manual hull survey Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com