Green ship technology dramatically reduces environmental impact by utilizing energy-efficient propulsion systems, alternative fuels like LNG and hydrogen, and advanced hull designs to minimize drag. Conventional ship systems typically rely on heavy fuel oil engines that emit higher levels of greenhouse gases and pollutants, contributing significantly to marine pollution. Adoption of green technologies enhances sustainability in maritime operations, cutting emissions and complying with increasingly strict environmental regulations.
Table of Comparison
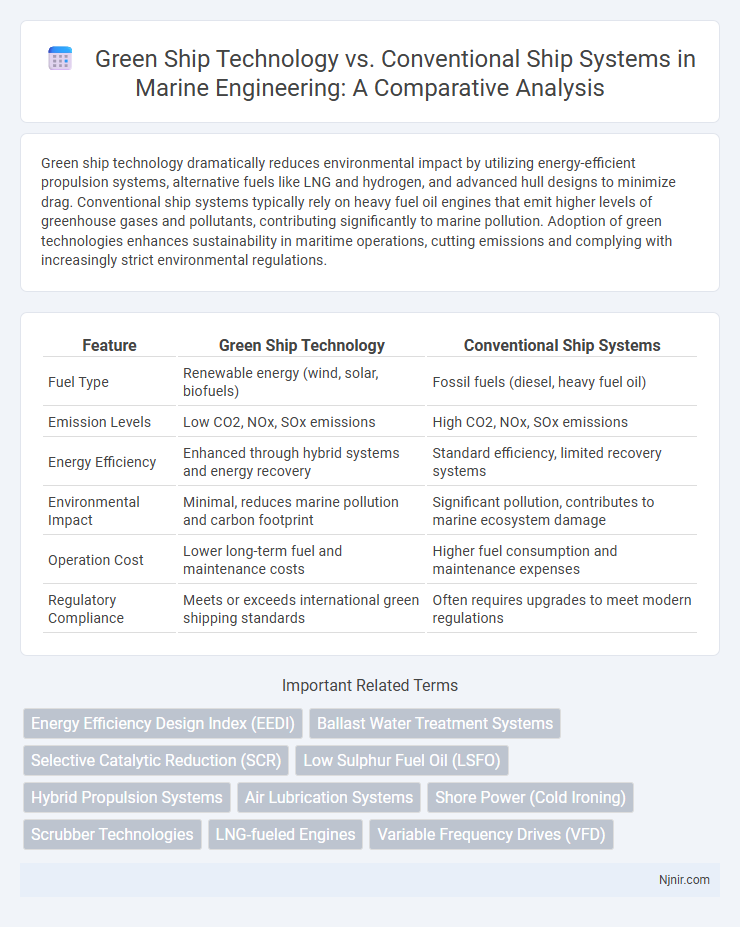
| Feature | Green Ship Technology | Conventional Ship Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Renewable energy (wind, solar, biofuels) | Fossil fuels (diesel, heavy fuel oil) |
| Emission Levels | Low CO2, NOx, SOx emissions | High CO2, NOx, SOx emissions |
| Energy Efficiency | Enhanced through hybrid systems and energy recovery | Standard efficiency, limited recovery systems |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal, reduces marine pollution and carbon footprint | Significant pollution, contributes to marine ecosystem damage |
| Operation Cost | Lower long-term fuel and maintenance costs | Higher fuel consumption and maintenance expenses |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets or exceeds international green shipping standards | Often requires upgrades to meet modern regulations |
Introduction to Green Ship Technology and Conventional Ship Systems
Green ship technology incorporates eco-friendly innovations aimed at reducing emissions, fuel consumption, and environmental impact through advanced propulsion systems, energy-efficient hull designs, and alternative fuels such as LNG and hydrogen. Conventional ship systems primarily rely on fossil fuel-powered engines and traditional navigation and propulsion methods that contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and marine pollution. The transition to green ship technology represents a critical shift in maritime operations toward sustainability, regulatory compliance, and cost-efficient energy use.
Key Environmental Impacts of Traditional Ship Systems
Traditional ship systems rely heavily on fossil fuels such as heavy fuel oil and marine diesel, leading to significant emissions of sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter that contribute to air pollution and acid rain. These ships often discharge untreated ballast water, causing marine ecosystem disruptions through the introduction of invasive species. Moreover, conventional ships produce large amounts of greenhouse gases, primarily CO2, exacerbating global climate change and ocean acidification.
Core Principles of Green Ship Technology
Green ship technology centers on energy efficiency, emission reduction, and sustainable resource use through advanced propulsion systems, alternative fuels, and waste management innovations. Core principles include optimizing hull design for hydrodynamic efficiency, integrating renewable energy sources like wind and solar, and employing emission control technologies to meet stringent environmental regulations. These practices contrast conventional ship systems that rely heavily on fossil fuels and emit higher levels of greenhouse gases without comprehensive resource recycling or pollution mitigation.
Fuel Types: Marine Diesel vs. Alternative Fuels
Green ship technology increasingly utilizes alternative fuels such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), hydrogen, ammonia, and biofuels, which significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional marine diesel. Marine diesel, while widely used in conventional ship systems for its energy density and established infrastructure, contributes substantially to sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter pollution. Alternative fuels in green ship systems offer enhanced compliance with International Maritime Organization (IMO) 2020 sulfur cap regulations and promote sustainability by lowering carbon footprints and improving air quality.
Energy Efficiency Measures: Old Practices vs. Modern Innovations
Green ship technology integrates advanced energy efficiency measures such as optimized hull designs, air lubrication systems, and renewable energy integration, significantly reducing fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional ship systems. Traditional practices focus primarily on incremental improvements like engine tuning and paint coatings to reduce drag but lack the comprehensive approach to sustainability seen in modern innovations. Implementation of smart energy management systems and use of alternative fuels such as LNG and hydrogen contribute to a transformative shift from conventional to green maritime operations.
Emission Reduction Technologies: Scrubbers vs. Eco-Friendly Solutions
Scrubbers in conventional ship systems chemically clean exhaust gases, reducing sulfur oxide emissions but still relying on fossil fuel combustion, which limits overall environmental benefits. Green ship technology emphasizes eco-friendly solutions like LNG fuel, battery hybrid systems, and wind-assist propulsion, drastically lowering greenhouse gas and particulate emissions at the source. Emission reduction through green technologies supports compliance with IMO regulations while promoting sustainable maritime operations and minimizing oceanic pollution.
Design Differences: Hull Optimization and Propulsion Systems
Green ship technology emphasizes hull optimization by incorporating streamlined shapes and advanced coatings to reduce hydrodynamic resistance, significantly lowering fuel consumption compared to conventional ship systems. Propulsion systems in green ships often utilize hybrid engines, LNG fuel, or electric drives that maximize energy efficiency and minimize emissions, contrasting with the heavy fuel oil-powered engines common in traditional vessels. These design differences enhance overall sustainability and operational performance, aligning with stricter environmental regulations and global decarbonization goals.
Regulatory Landscape: IMO Standards and Compliance
Green ship technology is increasingly aligned with IMO standards such as MARPOL Annex VI, emphasizing reduced sulfur emissions and energy efficiency to meet stringent environmental regulations. Conventional ship systems often face challenges in compliance due to higher emissions and fuel consumption, prompting shifts toward alternative fuels and emission reduction technologies. IMO's upcoming regulations on carbon intensity and mandatory Greenhouse Gas (GHG) reporting incentivize adoption of innovative green propulsion and energy-saving systems to ensure regulatory compliance and sustainability.
Economic Analysis: Cost Comparison and Operational Lifecycle
Green ship technology presents a significant reduction in fuel consumption and emissions compared to conventional ship systems, resulting in lower operational costs over the vessel's lifecycle. Initial investments in green technologies, such as LNG propulsion or hybrid power systems, are higher but are offset by fuel savings and reduced maintenance expenses throughout the ship's service period. Economic analysis shows that green ships achieve a better total cost of ownership due to regulatory incentives, decreased environmental compliance costs, and potential resale value enhancements.
Future Prospects: Trends and Adoption Challenges in Marine Engineering
Green ship technology is rapidly evolving with innovations such as zero-emission fuels, energy-efficient hull designs, and advanced propulsion systems aiming to reduce carbon footprints in marine engineering. Conventional ship systems, reliant on fossil fuels and traditional engines, face increasing regulatory pressure and cost challenges that drive the shift toward sustainable alternatives. Future prospects highlight widespread adoption impeded by high initial investments, infrastructure limitations, and the need for standardized global regulations to ensure scalable implementation.
Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI)
Green ship technology significantly reduces the Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) compared to conventional ship systems by integrating advanced propulsion, optimized hull designs, and alternative fuels to lower CO2 emissions per transport work.
Ballast Water Treatment Systems
Green ship technology employs advanced Ballast Water Treatment Systems that use eco-friendly methods such as UV sterilization and filtration to prevent marine invasive species, significantly reducing environmental impact compared to conventional ship systems relying on chemical biocides or untreated ballast water discharge.
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) in green ship technology significantly reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by up to 90% compared to conventional ship systems, enhancing environmental compliance and fuel efficiency.
Low Sulphur Fuel Oil (LSFO)
Green ship technology uses advanced Low Sulphur Fuel Oil (LSFO) formulations to reduce sulfur emissions significantly compared to conventional ship systems reliant on higher-sulfur marine fuels.
Hybrid Propulsion Systems
Hybrid propulsion systems integrate electric motors with conventional engines to reduce fuel consumption and emissions in green ship technology compared to traditional ship systems.
Air Lubrication Systems
Air Lubrication Systems in green ship technology reduce drag by creating a layer of air bubbles beneath the hull, lowering fuel consumption and emissions compared to conventional ship systems.
Shore Power (Cold Ironing)
Shore power (cold ironing) in green ship technology reduces emissions and fuel consumption by allowing vessels to connect to onshore electrical grids, unlike conventional ship systems that rely solely on onboard fossil fuel generators while docked.
Scrubber Technologies
Green ship technology employs advanced scrubber systems to reduce sulfur oxide emissions significantly compared to conventional ship systems that rely on traditional fuel combustion without effective exhaust gas cleaning.
LNG-fueled Engines
LNG-fueled engines in green ship technology reduce emissions by up to 90% of sulfur oxides and significantly lower nitrogen oxides compared to conventional diesel-powered ship systems.
Variable Frequency Drives (VFD)
Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) in green ship technology significantly enhance energy efficiency by optimizing motor speed control, reducing fuel consumption and emissions compared to conventional ship systems.
Green ship technology vs Conventional ship systems Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com