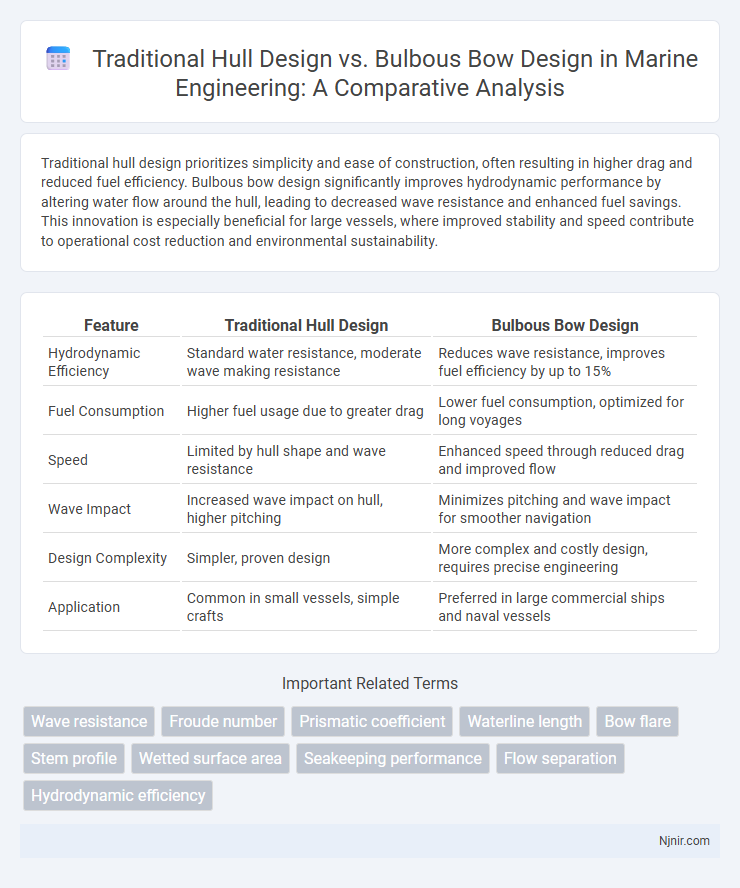
Traditional hull design prioritizes simplicity and ease of construction, often resulting in higher drag and reduced fuel efficiency. Bulbous bow design significantly improves hydrodynamic performance by altering water flow around the hull, leading to decreased wave resistance and enhanced fuel savings. This innovation is especially beneficial for large vessels, where improved stability and speed contribute to operational cost reduction and environmental sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Hull Design | Bulbous Bow Design |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrodynamic Efficiency | Standard water resistance, moderate wave making resistance | Reduces wave resistance, improves fuel efficiency by up to 15% |
| Fuel Consumption | Higher fuel usage due to greater drag | Lower fuel consumption, optimized for long voyages |
| Speed | Limited by hull shape and wave resistance | Enhanced speed through reduced drag and improved flow |
| Wave Impact | Increased wave impact on hull, higher pitching | Minimizes pitching and wave impact for smoother navigation |
| Design Complexity | Simpler, proven design | More complex and costly design, requires precise engineering |
| Application | Common in small vessels, simple crafts | Preferred in large commercial ships and naval vessels |
Introduction to Hull Design in Marine Engineering
Traditional hull design in marine engineering emphasizes streamlined shapes to reduce water resistance and improve stability during navigation. Bulbous bow design introduces a protruding bulb at the ship's front, altering water flow patterns to minimize wave resistance and enhance fuel efficiency. This innovation significantly reduces drag, especially in large vessels, resulting in optimized performance and lower operational costs.
Overview of Traditional Hull Design
Traditional hull design features a rounded or V-shaped bottom that emphasizes stability and straightforward construction, commonly used in older vessels and small boats. This design typically results in higher wave resistance and fuel consumption, particularly at higher speeds, due to its less hydrodynamic shape. Despite these drawbacks, traditional hulls remain favored for their simplicity, durability, and ease of maintenance in various maritime applications.
Evolution of the Bulbous Bow Concept
The evolution of the bulbous bow concept stems from the need to reduce wave resistance and improve fuel efficiency compared to traditional hull designs. Early designs focused on optimizing the underwater shape to interfere constructively with bow waves, creating a wave system that minimizes drag. Advances in computational fluid dynamics and model testing have refined bulbous bow shapes to suit various ship types, significantly enhancing hydrodynamic performance and operational economy.
Hydrodynamic Principles: Traditional vs. Bulbous Bow
Traditional hull design relies on a straightforward bow shape that primarily minimizes wave resistance by smoothly displacing water along the hull, following classic hydrodynamic principles of laminar flow and pressure distribution. Bulbous bow design introduces a protruding bulb below the waterline that creates a wave system out of phase with the hull-generated waves, effectively reducing wave-making resistance and improving fuel efficiency. This hydrodynamic interaction decreases drag and enhances vessel speed by optimizing the pressure waves and flow separation around the bow area.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison
Traditional hull designs often experience higher hydrodynamic resistance, resulting in increased fuel consumption during maritime navigation. Bulbous bow designs significantly reduce wave-making resistance by altering flow patterns around the bow, leading to fuel savings of up to 15% in large vessels at optimal cruising speeds. Enhanced fuel efficiency from bulbous bows contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions and operational costs in commercial shipping.
Impact on Vessel Speed and Stability
Traditional hull design typically features a rounded or V-shaped bow, which generates significant wave resistance, limiting vessel speed and efficiency. In contrast, bulbous bow design reduces wave resistance by altering the flow of water around the hull, leading to improved fuel efficiency and higher speeds at cruising conditions. The bulbous bow also enhances vessel stability by minimizing pitch motion and improving seakeeping in rough waters, making it preferable for modern commercial ships.
Structural Considerations and Construction Challenges
Traditional hull design typically features a smooth, rounded bow that simplifies structural integrity by distributing stress uniformly across the frame, reducing localized strain and easing construction processes. Bulbous bow design introduces complex geometries requiring reinforced framing and precise welding techniques to manage additional hydrodynamic loads and potential stress concentrations at the bulb-hull interface. Construction challenges for bulbous bows include ensuring accurate alignment and integration with the main hull to prevent structural weaknesses and maintain optimal hydrodynamic performance under varying sea conditions.
Applicability to Different Vessel Types
Traditional hull designs remain widely used in small to medium-sized vessels due to their simplicity and lower construction costs, offering reliable performance in diverse water conditions. Bulbous bow designs are predominantly applied in large ships such as tankers, container ships, and cruise liners to reduce wave resistance, improve fuel efficiency, and enhance stability at higher speeds. The effectiveness of bulbous bows depends on vessel length, speed, and operating conditions, making them less suitable for slower or smaller vessels where traditional hull forms provide optimal performance.
Environmental Implications of Hull and Bow Designs
Traditional hull designs typically generate higher wave resistance and increased fuel consumption, leading to greater greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impact. Bulbous bow designs reduce wave drag by altering water flow around the ship's bow, improving fuel efficiency and lowering carbon dioxide emissions significantly across long voyages. Implementation of bulbous bows contributes to sustainable shipping practices by minimizing fuel use and reducing the vessel's overall ecological footprint.
Future Trends in Hull Optimization
Future trends in hull optimization emphasize integrating advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and machine learning algorithms to refine traditional hull designs and bulbous bow configurations for enhanced fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Innovations include adaptive hull structures that adjust shape in real-time based on sea conditions, maximizing hydrodynamic performance while minimizing resistance. The convergence of eco-friendly materials and digital twin technology is accelerating the development of smart hulls optimized for sustainability and operational cost reduction in maritime industries.
Wave resistance
Bulbous bow design significantly reduces wave resistance compared to traditional hull designs by altering water flow and minimizing bow wave formation.
Froude number
Bulbous bow designs reduce wave resistance and improve fuel efficiency at Froude numbers typically between 0.2 and 0.4, unlike traditional hull designs that experience higher drag in this critical speed range.
Prismatic coefficient
Traditional hull designs typically have higher prismatic coefficients around 0.55-0.60, optimizing for lower resistance at moderate speeds, whereas bulbous bow designs feature lower prismatic coefficients near 0.50-0.54 to reduce wave-making resistance and improve fuel efficiency at higher speeds.
Waterline length
Bulbous bow design effectively increases the waterline length compared to traditional hull design, enhancing hull speed and fuel efficiency.
Bow flare
Traditional hull designs often feature pronounced bow flare to deflect waves and improve deck dryness, whereas bulbous bow designs minimize bow flare to reduce wave resistance and enhance fuel efficiency.
Stem profile
Traditional hull designs feature a straight stem profile that increases wave resistance, whereas bulbous bow designs utilize a protruding stem shape to reduce wave drag and improve fuel efficiency.
Wetted surface area
Bulbous bow designs reduce wetted surface area compared to traditional hull designs, resulting in lower hydrodynamic drag and improved fuel efficiency.
Seakeeping performance
Bulbous bow design significantly enhances seakeeping performance by reducing wave resistance and improving stability in rough seas compared to traditional hull designs.
Flow separation
Bulbous bow design reduces flow separation by streamlining water flow around the hull, decreasing drag and enhancing fuel efficiency compared to traditional hull designs.
Hydrodynamic efficiency
Bulbous bow design enhances hydrodynamic efficiency by reducing wave resistance and improving fuel consumption compared to traditional hull designs.
traditional hull design vs bulbous bow design Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com