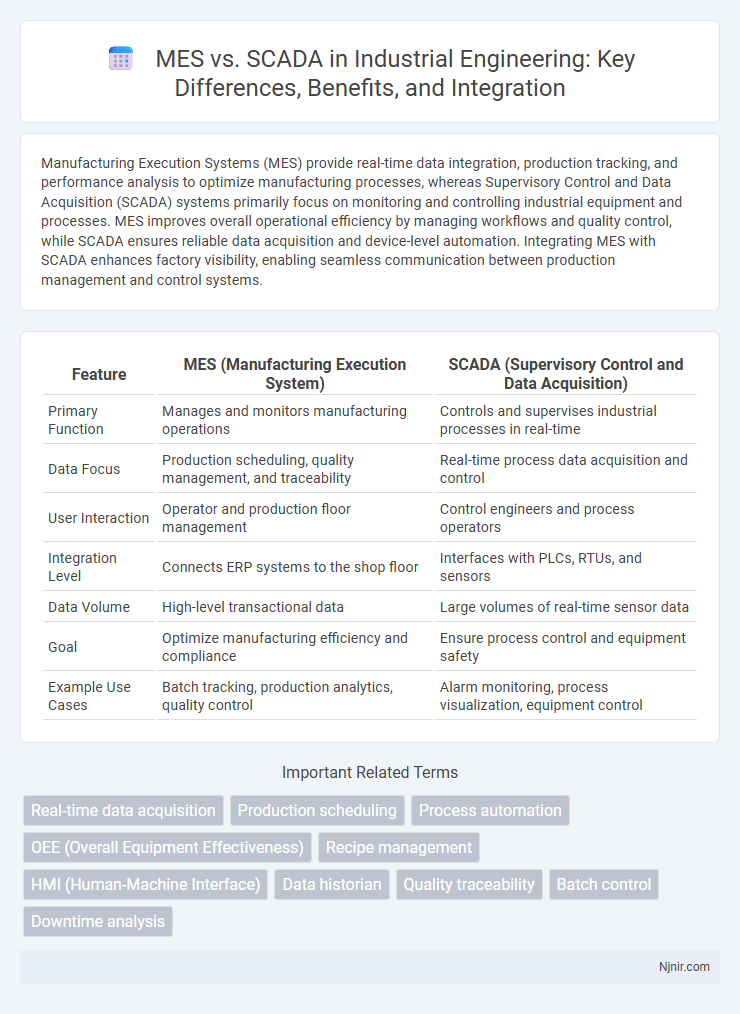
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) provide real-time data integration, production tracking, and performance analysis to optimize manufacturing processes, whereas Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems primarily focus on monitoring and controlling industrial equipment and processes. MES improves overall operational efficiency by managing workflows and quality control, while SCADA ensures reliable data acquisition and device-level automation. Integrating MES with SCADA enhances factory visibility, enabling seamless communication between production management and control systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | MES (Manufacturing Execution System) | SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages and monitors manufacturing operations | Controls and supervises industrial processes in real-time |
| Data Focus | Production scheduling, quality management, and traceability | Real-time process data acquisition and control |
| User Interaction | Operator and production floor management | Control engineers and process operators |
| Integration Level | Connects ERP systems to the shop floor | Interfaces with PLCs, RTUs, and sensors |
| Data Volume | High-level transactional data | Large volumes of real-time sensor data |
| Goal | Optimize manufacturing efficiency and compliance | Ensure process control and equipment safety |
| Example Use Cases | Batch tracking, production analytics, quality control | Alarm monitoring, process visualization, equipment control |
Understanding MES and SCADA: Key Definitions
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are software solutions designed to monitor, track, document, and control the entire production process on the factory floor, ensuring real-time data collection and improved operational efficiency. Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems focus on real-time process control and data acquisition from equipment and sensors in industrial environments, providing visualization and alert functionalities. While MES targets production workflow optimization and traceability, SCADA emphasizes equipment control and monitoring within industrial automation.
Core Functions of MES in Industrial Operations
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) primarily focus on real-time production management by tracking and documenting the transformation of raw materials into finished goods, ensuring operational efficiency and quality control. Core functions include production scheduling, resource allocation, performance analysis, and compliance management, which directly influence manufacturing workflows and product traceability. Unlike SCADA systems that monitor and control industrial processes, MES integrates production data with business systems to optimize manufacturing operations and enhance decision-making.
SCADA Systems: Capabilities and Applications
SCADA systems provide real-time monitoring, control, and data acquisition for industrial processes, enabling operators to respond quickly to equipment status changes and alarms. These systems integrate with sensors, PLCs, and other field devices to optimize production efficiency and ensure safety across sectors like manufacturing, energy, and water management. SCADA capabilities include visualization through human-machine interfaces (HMIs), historical data logging, remote access, and automated control sequences essential for minimizing downtime and improving operational decision-making.
Architecture Differences: MES vs SCADA
MES architecture centers on enterprise-level integration, encompassing real-time production scheduling, quality management, and workflow control, linking ERP systems with shop floor devices. SCADA architecture prioritizes real-time data acquisition and control, utilizing distributed sensors, PLCs, and HMI interfaces to monitor and manage industrial processes. The key architectural difference lies in MES's broader scope for operational management and traceability, while SCADA focuses on centralized process visualization and immediate control.
Data Collection and Processing: A Comparative Overview
MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) excels in real-time data collection and processing by integrating production scheduling, quality management, and inventory tracking to optimize manufacturing workflows. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) focuses on collecting real-time data from sensors, PLCs, and other control devices to monitor and control industrial processes. MES provides higher-level data analysis and process optimization, whereas SCADA emphasizes immediate data acquisition and visualization for operational control.
Integration with ERP and Other Systems
MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) differ significantly in their integration capabilities with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and other business systems. MES acts as a critical intermediary, providing real-time data on production processes, resource allocation, and quality management that seamlessly integrates with ERP for enhanced decision-making and operational efficiency. SCADA primarily handles equipment-level monitoring and control, with limited direct ERP integration, often requiring additional middleware for comprehensive enterprise-wide data exchange and process synchronization.
Real-Time Monitoring: How MES and SCADA Differ
MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) provide real-time monitoring focused on production workflows, tracking work orders, and managing process execution on the shop floor. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems specialize in real-time data acquisition from sensors and control devices, emphasizing equipment status and process variables monitoring. The distinction lies in MES delivering operational insight for manufacturing processes, while SCADA offers detailed control and visualization of industrial equipment in real-time.
Production Control versus Process Control
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) specialize in production control by managing and optimizing workflows, scheduling, and resource allocation on the factory floor, ensuring real-time tracking of production progress and quality compliance. Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems focus on process control by monitoring, controlling, and collecting real-time data from industrial equipment and processes, enabling immediate response to operational anomalies and maintaining system stability. MES integrates production planning with shop floor execution, while SCADA primarily ensures the continuous, safe, and efficient functioning of automated processes.
Implementation Challenges for MES and SCADA
Implementation challenges for MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) often include complex integration with existing ERP systems and real-time data synchronization across production lines, requiring robust middleware solutions. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) implementation struggles typically involve ensuring reliable communication across distributed control systems and managing cybersecurity risks due to its exposure to industrial networks. Both systems demand comprehensive training and change management to align with operational workflows and to maximize their automation and monitoring capabilities.
Choosing the Right System: MES or SCADA for Your Industry
Choosing between MES (Manufacturing Execution System) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) depends on your industry's operational needs and goals. MES excels in managing production workflows, quality control, and real-time data integration across manufacturing processes, making it ideal for complex, multi-step production environments. SCADA systems are better suited for monitoring and controlling infrastructure and equipment in real time, providing crucial data acquisition and process visualization, which benefits industries focused on operational control and asset management.
Real-time data acquisition
MES provides real-time data acquisition for production process control, while SCADA specializes in real-time monitoring and control of industrial equipment and infrastructure.
Production scheduling
MES provides real-time production scheduling and optimization, while SCADA primarily monitors and controls equipment without advanced scheduling capabilities.
Process automation
MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) optimize real-time production process automation by managing workflow and resource allocation, while SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) focuses on monitoring and controlling industrial equipment and processes.
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)
MES systems provide real-time data integration and analysis critical for improving OEE, while SCADA primarily monitors and controls equipment without deep performance optimization.
Recipe management
MES provides advanced recipe management by enabling real-time adjustments, version control, and centralized storage, whereas SCADA primarily supports basic recipe execution and monitoring without comprehensive versioning features.
HMI (Human-Machine Interface)
MES provides comprehensive HMI tools for production scheduling and performance monitoring, while SCADA offers real-time HMI visualization and control of industrial processes.
Data historian
MES systems integrate real-time production data with historical context, while SCADA primarily collects and monitors operational data, with Data historians in MES providing deeper analysis and long-term traceability compared to SCADA's immediate data storage.
Quality traceability
MES provides comprehensive quality traceability by integrating production data and real-time monitoring, whereas SCADA primarily focuses on process control and equipment status without detailed quality lineage.
Batch control
MES optimizes batch control by managing production workflows and traceability, while SCADA focuses on real-time monitoring and control of batch process variables.
Downtime analysis
MES provides detailed downtime analysis by integrating production data across processes, while SCADA focuses on real-time monitoring and control with limited historical downtime insights.
MES vs SCADA Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com