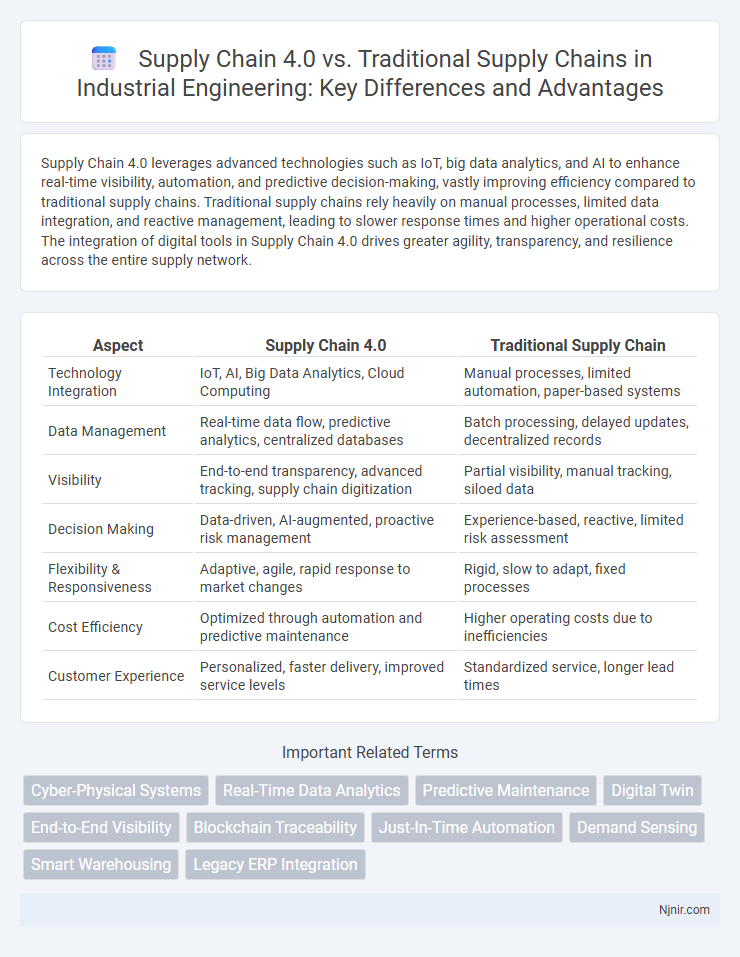
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages advanced technologies such as IoT, big data analytics, and AI to enhance real-time visibility, automation, and predictive decision-making, vastly improving efficiency compared to traditional supply chains. Traditional supply chains rely heavily on manual processes, limited data integration, and reactive management, leading to slower response times and higher operational costs. The integration of digital tools in Supply Chain 4.0 drives greater agility, transparency, and resilience across the entire supply network.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Supply Chain 4.0 | Traditional Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Integration | IoT, AI, Big Data Analytics, Cloud Computing | Manual processes, limited automation, paper-based systems |
| Data Management | Real-time data flow, predictive analytics, centralized databases | Batch processing, delayed updates, decentralized records |
| Visibility | End-to-end transparency, advanced tracking, supply chain digitization | Partial visibility, manual tracking, siloed data |
| Decision Making | Data-driven, AI-augmented, proactive risk management | Experience-based, reactive, limited risk assessment |
| Flexibility & Responsiveness | Adaptive, agile, rapid response to market changes | Rigid, slow to adapt, fixed processes |
| Cost Efficiency | Optimized through automation and predictive maintenance | Higher operating costs due to inefficiencies |
| Customer Experience | Personalized, faster delivery, improved service levels | Standardized service, longer lead times |
Overview of Traditional Supply Chain Management
Traditional supply chain management relies on linear processes, manual data entry, and siloed communication between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, often leading to delays and inefficiencies. Inventory management depends heavily on historical demand forecasts, increasing the risk of stockouts or overstocking. Decision-making typically lacks real-time data integration, resulting in slower response times to market fluctuations and disruptions.
Defining Supply Chain 4.0: Key Features and Technologies
Supply Chain 4.0 integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, big data analytics, and blockchain to create a connected, intelligent, and automated supply network. Key features include real-time data visibility, predictive analytics for demand forecasting, and autonomous decision-making processes that enhance efficiency and agility. Unlike traditional supply chains, Supply Chain 4.0 enables seamless end-to-end integration and adaptive responses to market dynamics.
Digital Transformation in Supply Chain Operations
Supply Chain 4.0 integrates advanced digital technologies like IoT, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics to enhance real-time visibility, predictive maintenance, and automated decision-making in supply chain operations. Traditional supply chains rely heavily on manual processes, limited data sharing, and reactive management, leading to inefficiencies and slower response times. Digital transformation in Supply Chain 4.0 drives greater agility, cost reduction, and improved customer satisfaction by enabling seamless connectivity across suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers.
Real-Time Data and Analytics in Supply Chain 4.0
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to enhance visibility, responsiveness, and decision-making across the entire supply chain network. Unlike traditional supply chains that rely on periodic data collection and manual analysis, Supply Chain 4.0 integrates IoT sensors, AI, and cloud computing to provide continuous, actionable insights. This transformation enables proactive risk management, dynamic inventory optimization, and improved customer satisfaction through faster, data-driven adjustments.
Automation and Smart Factories Integration
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages advanced automation technologies and smart factories integration to enhance efficiency, real-time data exchange, and predictive analytics, surpassing traditional supply chains reliant on manual processes and static data. Automation in Supply Chain 4.0 incorporates robotics, IoT sensors, and AI-driven systems to optimize inventory management, production scheduling, and logistics, enabling faster decision-making and reduced operational costs. Smart factories serve as interconnected hubs within Supply Chain 4.0, utilizing machine-to-machine communication and digital twins to create agile, adaptive manufacturing environments that respond dynamically to market demands and supply fluctuations.
Customer-Centric Approaches: Then and Now
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and big data analytics to create highly responsive, personalized customer experiences by predicting demand and optimizing inventory in real-time. Traditional supply chains often relied on forecast-driven models with limited real-time visibility, resulting in slower response times and less customization. Modern customer-centric approaches emphasize agile fulfillment, end-to-end transparency, and continuous feedback integration to enhance satisfaction and loyalty.
Efficiency and Cost-Reduction Comparisons
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and robotics to enhance real-time data visibility, enabling predictive analytics that optimize inventory management and reduce operational costs. In contrast, traditional supply chains rely on manual processes and limited data integration, resulting in slower response times and higher inefficiencies. Studies indicate that companies adopting Supply Chain 4.0 experience up to 30% cost reduction and 25% improvement in overall efficiency compared to conventional supply chain models.
Risk Management and Resilience in Both Models
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and big data analytics to enhance risk management by enabling real-time visibility and predictive insights, significantly improving resilience against disruptions. Traditional supply chains rely heavily on manual processes and historical data, which limits their ability to anticipate risks and respond swiftly to unforeseen events. The integration of digital tools in Supply Chain 4.0 fosters adaptive decision-making and faster recovery, creating a robust framework for managing complex global supply networks.
Sustainability Practices in Supply Chain 4.0 vs Traditional
Supply Chain 4.0 integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain to enhance transparency, efficiency, and resource optimization, leading to significantly reduced carbon footprints and waste compared to Traditional Supply Chains. Real-time data analytics in Supply Chain 4.0 enable precise demand forecasting and inventory management, minimizing excess production and energy consumption traditionally associated with supply chains. Unlike traditional models that often rely on manual tracking and static processes, Supply Chain 4.0 promotes circular economy principles and sustainable sourcing through automated and intelligent decision-making tools.
Future Trends and Strategic Implications
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain to enable real-time data analytics and enhanced automation, contrasting with the linear and manually intensive processes of traditional supply chains. Future trends emphasize predictive analytics, autonomous vehicles, and digital twins, driving efficiency and agility in end-to-end supply chain management. Strategic implications include increased resilience, customizable customer experiences, and the need for workforce upskilling to harness digital transformation benefits.
Cyber-Physical Systems
Supply Chain 4.0 integrates advanced Cyber-Physical Systems to enable real-time data exchange, automation, and enhanced decision-making, significantly outperforming traditional supply chains reliant on manual processes and limited connectivity.
Real-Time Data Analytics
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages real-time data analytics through IoT sensors and AI algorithms to enhance responsiveness and decision-making, whereas traditional supply chains rely on delayed, manual data processing limiting agility and accuracy.
Predictive Maintenance
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages IoT sensors and AI-driven predictive maintenance to reduce equipment downtime by up to 30%, outperforming traditional supply chains that rely on reactive or scheduled maintenance models.
Digital Twin
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages digital twin technology to create real-time, virtual replicas of physical supply networks, enhancing predictive analytics and operational efficiency compared to traditional supply chains.
End-to-End Visibility
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and AI to provide comprehensive end-to-end visibility, enabling proactive decision-making and enhanced efficiency compared to the limited transparency and slower responsiveness of traditional supply chains.
Blockchain Traceability
Blockchain traceability in Supply Chain 4.0 enables real-time, tamper-proof tracking of goods, significantly enhancing transparency and trust compared to traditional supply chains relying on manual, paper-based records.
Just-In-Time Automation
Just-In-Time automation in Supply Chain 4.0 integrates IoT sensors and AI analytics to optimize inventory levels and reduce lead times, outperforming traditional supply chain methods reliant on manual processes and fixed schedules.
Demand Sensing
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages advanced demand sensing technologies such as AI-driven analytics and IoT data integration to provide real-time demand forecasting, outperforming traditional supply chains that rely on historical data and periodic manual updates.
Smart Warehousing
Smart warehousing in Supply Chain 4.0 leverages IoT, AI, and robotics to enhance inventory accuracy, reduce labor costs, and enable real-time data analysis, outperforming traditional supply chain methods reliant on manual processes and limited visibility.
Legacy ERP Integration
Supply Chain 4.0 leverages advanced IoT, AI, and cloud-based technologies for real-time data integration, enabling seamless Legacy ERP system connectivity and enhanced supply chain visibility compared to traditional supply chains reliant on siloed, manual ERP processes.
Supply Chain 4.0 vs Traditional Supply Chain Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com