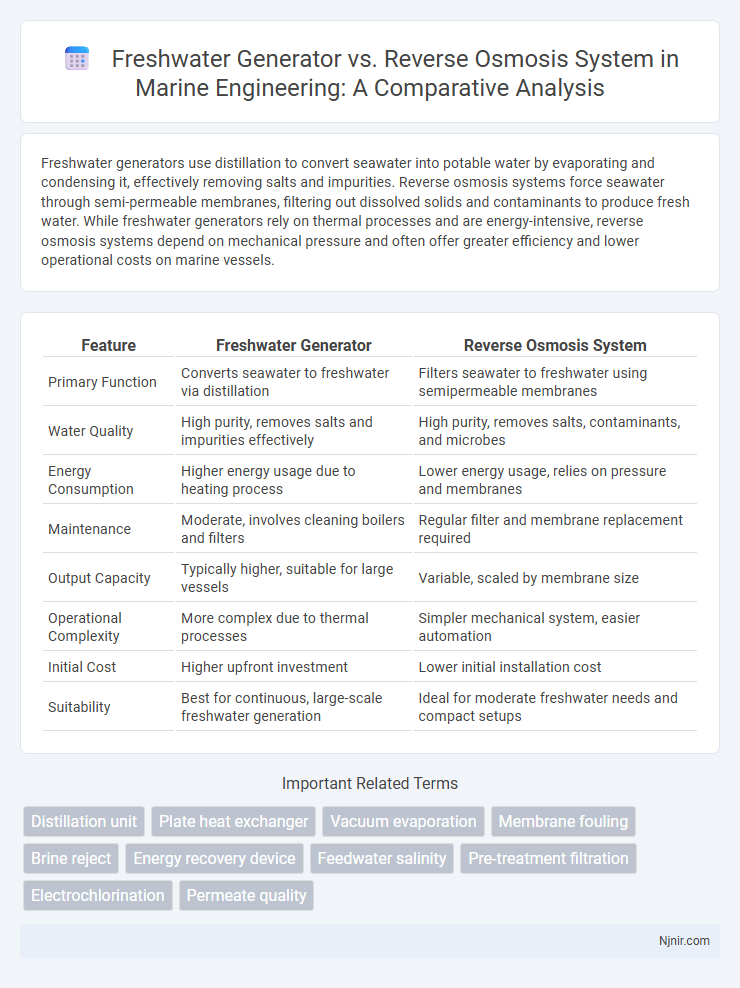
Freshwater generators use distillation to convert seawater into potable water by evaporating and condensing it, effectively removing salts and impurities. Reverse osmosis systems force seawater through semi-permeable membranes, filtering out dissolved solids and contaminants to produce fresh water. While freshwater generators rely on thermal processes and are energy-intensive, reverse osmosis systems depend on mechanical pressure and often offer greater efficiency and lower operational costs on marine vessels.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Freshwater Generator | Reverse Osmosis System |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Converts seawater to freshwater via distillation | Filters seawater to freshwater using semipermeable membranes |
| Water Quality | High purity, removes salts and impurities effectively | High purity, removes salts, contaminants, and microbes |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy usage due to heating process | Lower energy usage, relies on pressure and membranes |
| Maintenance | Moderate, involves cleaning boilers and filters | Regular filter and membrane replacement required |
| Output Capacity | Typically higher, suitable for large vessels | Variable, scaled by membrane size |
| Operational Complexity | More complex due to thermal processes | Simpler mechanical system, easier automation |
| Initial Cost | Higher upfront investment | Lower initial installation cost |
| Suitability | Best for continuous, large-scale freshwater generation | Ideal for moderate freshwater needs and compact setups |
Introduction to Marine Freshwater Production Systems
Marine freshwater production systems are essential for converting seawater into potable water on vessels and offshore platforms. Freshwater generators utilize thermal distillation or membrane distillation processes to evaporate and condense seawater, effectively removing impurities. Reverse osmosis systems employ high-pressure membranes to filter out salts and contaminants, offering energy-efficient and compact solutions for onboard freshwater production.
Overview of Freshwater Generators
Freshwater generators produce potable water by distilling seawater through evaporation and condensation processes, effectively removing salts and impurities. These systems operate continuously and can generate large quantities of fresh water, making them ideal for marine vessels and remote locations. Their low maintenance requirements and resistance to membrane fouling distinguish them from reverse osmosis systems, which rely on high-pressure filtration through semipermeable membranes.
Overview of Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems purify water by forcing it through a semi-permeable membrane, effectively removing contaminants such as salts, bacteria, and heavy metals. These systems are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications due to their high efficiency in producing clean, potable water. Compared to freshwater generators, RO systems typically require less energy and have lower maintenance needs, making them suitable for areas with moderate water salinity and consistent water pressure.
Working Principles: Freshwater Generators vs Reverse Osmosis
Freshwater generators utilize the process of distillation, where seawater is heated to produce steam, which condenses into pure freshwater by separating out salts and impurities. Reverse osmosis systems force seawater through a semipermeable membrane under high pressure, filtering out salt, bacteria, and contaminants to yield potable water. These distinct working principles highlight freshwater generators rely on phase change and condensation, while reverse osmosis depends on membrane filtration and pressure differentials for desalination.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency Comparison
Freshwater generators typically consume more energy due to their reliance on distillation processes that require heating large volumes of water, whereas reverse osmosis systems operate at lower energy levels by using membrane filtration powered by high-pressure pumps. RO systems often achieve higher efficiency by recovering a significant portion of the input water as purified output with less heat loss, making them more suitable for sustainable, energy-conscious applications. Energy consumption for freshwater generators can exceed 10 kWh per 1,000 liters, while RO units generally require around 3-5 kWh per 1,000 liters, reflecting a substantial efficiency advantage in membrane-based purification.
Space and Installation Requirements
Freshwater generators typically require larger installation spaces due to their complex components like evaporators and condensers, making them more suited for vessels with ample room. Reverse osmosis systems have a more compact design and easier installation process, often fitting in smaller areas such as under sinks or tight compartments. The simpler plumbing and lower maintenance demands of reverse osmosis systems further reduce the space and installation challenges compared to freshwater generators.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Freshwater generators require regular monitoring of turbine blades and heat exchangers to prevent fouling and ensure efficient operation, while reverse osmosis (RO) systems demand frequent membrane cleaning or replacement to maintain optimal filtration performance. RO systems typically consume more energy and generate brine waste, necessitating proper disposal, whereas freshwater generators rely on thermal processes with lower chemical handling needs. Maintenance schedules for freshwater generators often involve mechanical checks and water quality testing, contrasting with RO's focus on membrane integrity and pressure system upkeep.
Water Quality: Distillate vs Permeate
Freshwater generators produce distillate water by vaporizing and condensing seawater, resulting in highly pure water free from salts, bacteria, and most contaminants, ideal for critical applications requiring minimal impurities. Reverse osmosis systems create permeate by forcing water through a semipermeable membrane, effectively removing dissolved solids, but some trace minerals and organic compounds may remain, influencing the taste and water quality. Distillate is generally of higher purity compared to permeate, making freshwater generators preferred for applications demanding ultra-pure water, while reverse osmosis is favored for everyday potable water needs with effective contaminant reduction.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Freshwater generators produce potable water by condensing atmospheric moisture, consuming less energy and producing no wastewater, making them more environmentally friendly than reverse osmosis systems, which require significant electricity and generate brine waste that can harm aquatic ecosystems. Reverse osmosis systems also depend heavily on water source availability and often discard 3-4 gallons of water for every gallon purified, reducing overall water efficiency. The sustainable choice leans towards freshwater generators, especially in areas with high humidity and limited freshwater resources, due to their minimal environmental footprint and lower resource depletion.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Investment
Freshwater generators typically have higher upfront costs ranging from $10,000 to $50,000 depending on capacity, while reverse osmosis (RO) systems are generally more affordable initially, averaging between $500 and $5,000. Maintenance expenses for freshwater generators, including energy consumption and filter replacements, can accumulate over time, sometimes exceeding $1,000 annually, whereas RO systems require frequent membrane replacements costing about $100 to $300 per year. Long-term investment in freshwater generators offers continuous, large-scale water production with lower dependency on external water sources, whereas RO systems may incur recurring operational costs and efficiency declines, impacting total cost of ownership over 10 to 20 years.
Distillation unit
Freshwater generators using distillation units efficiently remove salts and impurities through thermal evaporation and condensation, offering higher purity in water compared to reverse osmosis systems that rely on membrane filtration.
Plate heat exchanger
Freshwater generators with plate heat exchangers offer higher thermal efficiency and faster heat transfer compared to reverse osmosis systems, enhancing desalination performance and energy savings.
Vacuum evaporation
Vacuum evaporation freshwater generators produce high-purity water by boiling seawater at low pressure, offering greater energy efficiency and scalability compared to reverse osmosis systems that rely on pressure-driven membrane filtration.
Membrane fouling
Freshwater generators typically experience less membrane fouling compared to reverse osmosis systems due to their lower pressure operation and specialized pre-treatment processes that reduce particulate and biological contamination.
Brine reject
Freshwater generators produce freshwater by distilling seawater and discharge highly concentrated brine reject with minimal energy use, while reverse osmosis systems filter seawater through membranes, generating less brine reject but requiring higher energy consumption and complex maintenance.
Energy recovery device
Freshwater generators with integrated energy recovery devices significantly reduce power consumption compared to reverse osmosis systems by capturing and reusing hydraulic energy during desalination.
Feedwater salinity
Freshwater generators effectively desalinate high-salinity feedwater through thermal distillation, whereas reverse osmosis systems are more efficient with moderately saline feedwater due to membrane limitations.
Pre-treatment filtration
Freshwater generators utilize multi-stage pre-treatment filtration including sediment and carbon filters to protect membranes from fouling, while reverse osmosis systems rely heavily on precise pre-treatment such as cartridge filters and anti-scalant dosing to prevent membrane clogging and extend lifespan.
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination in freshwater generators provides automated, chemical-free disinfection by producing sodium hypochlorite on-site, whereas reverse osmosis systems rely primarily on membrane filtration without inherent microbial control.
Permeate quality
Freshwater generators produce higher-permeate quality water with lower total dissolved solids compared to reverse osmosis systems, ensuring superior purity for critical applications.
Freshwater generator vs reverse osmosis system Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com