FRP hulls offer superior corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance compared to aluminum hulls, making them ideal for prolonged exposure to marine environments. Aluminum hulls provide higher structural strength and better impact resistance, which enhances durability in rough waters and high-speed applications. Choosing between FRP and aluminum hulls depends on the specific vessel requirements, balancing weight, cost, and performance factors.
Table of Comparison
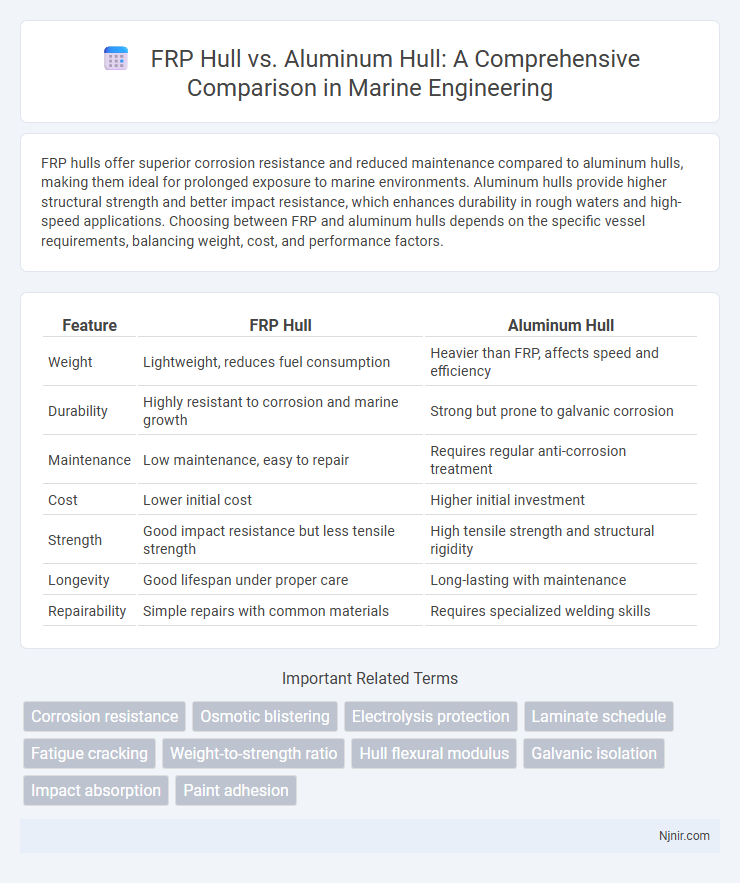
| Feature | FRP Hull | Aluminum Hull |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces fuel consumption | Heavier than FRP, affects speed and efficiency |
| Durability | Highly resistant to corrosion and marine growth | Strong but prone to galvanic corrosion |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to repair | Requires regular anti-corrosion treatment |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial investment |
| Strength | Good impact resistance but less tensile strength | High tensile strength and structural rigidity |
| Longevity | Good lifespan under proper care | Long-lasting with maintenance |
| Repairability | Simple repairs with common materials | Requires specialized welding skills |
Overview of FRP and Aluminum Hull Materials
FRP hulls are composed of fiberglass-reinforced plastic, offering high strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and ease of maintenance, making them ideal for recreational and small to medium-sized vessels. Aluminum hulls provide superior durability, impact resistance, and lightweight properties suitable for commercial, military, and expedition vessels, but require specialized welding and surface treatment to prevent corrosion. Both materials deliver distinct performance characteristics based on application requirements, with FRP excelling in customization and cost-effectiveness, while aluminum offers enhanced structural integrity and longevity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
FRP hulls offer excellent corrosion resistance and impact absorption, making them resistant to harsh marine environments and reducing maintenance needs. Aluminum hulls provide superior structural strength and toughness, with higher resistance to deformation under heavy loads and impacts. However, aluminum is prone to corrosion without proper treatment, while FRP may suffer from stress cracks over time under extreme conditions.
Weight and Performance Implications
FRP hulls offer significantly lighter weight compared to aluminum hulls, enhancing fuel efficiency and acceleration due to reduced displacement. Aluminum hulls provide superior strength and durability, which supports higher performance in rough waters but often results in increased weight and fuel consumption. The choice between FRP and aluminum hulls directly impacts vessel speed, handling characteristics, and operational costs.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
FRP hulls exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum hulls, as fiberglass materials are inherently impervious to rust and electrochemical reactions that commonly affect metals. Aluminum hulls require regular maintenance, including protective coatings and inspections to prevent pitting and galvanic corrosion, especially in saltwater environments. Maintenance for FRP hulls primarily involves surface cleaning and gelcoat repairs, resulting in lower long-term upkeep costs and increased durability in marine conditions.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Lifecycle Expenses
FRP hulls generally have lower initial costs due to cheaper materials and simplified manufacturing processes compared to aluminum hulls, which require more expensive raw materials and specialized fabrication. Over the lifecycle, FRP hulls can incur higher maintenance expenses because of potential issues like osmotic blistering and longer repair times, whereas aluminum hulls benefit from durability and corrosion resistance, reducing long-term maintenance costs despite higher upfront investments. Total cost of ownership analysis often favors aluminum hulls for vessels used in harsh environments or with extended service lives, while FRP remains cost-effective for smaller, less frequently used boats.
Repair and Modifications: Ease and Techniques
FRP hulls are easier to repair and modify due to their moldable fiberglass composition, allowing patching and reshaping with resin and fiberglass cloth, which can be done on-site with minimal equipment. Aluminum hull repairs typically require specialized welding techniques and equipment, making modifications more complex and often necessitating professional intervention. The lightweight and corrosion-resistant nature of aluminum also means any structural alterations must maintain the metal's integrity and protective coatings to prevent degradation.
Environmental Impact of FRP vs Aluminum
FRP hulls generate significant environmental concerns due to their non-recyclable nature and the toxic resins used in manufacturing, leading to long-term waste disposal challenges. Aluminum hulls offer better recyclability and lower carbon footprints in production, contributing to more sustainable lifecycle management. However, the energy-intensive extraction process for aluminum can offset some of these benefits compared to FRP's raw material sourcing.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
FRP hulls offer superior thermal insulation due to their composite structure, which reduces heat transfer and maintains stable internal temperatures compared to aluminum hulls that conduct heat rapidly. Acoustic insulation is also enhanced in FRP hulls, as the material's density and resin matrix effectively dampen vibrations and hull noise, whereas aluminum hulls tend to transmit engine and water sounds more readily. These properties make FRP hulls favorable for applications requiring noise reduction and temperature control, such as luxury yachts and research vessels.
Applications in Commercial and Recreational Vessels
FRP hulls dominate recreational vessels due to their lightweight, corrosion resistance, and ease of molding complex shapes, ideal for yachts and small boats. Aluminum hulls are preferred in commercial vessels such as fishing boats and workboats, offering superior strength, durability, and impact resistance for harsh operating conditions. The choice between FRP and aluminum hulls hinges on factors like vessel size, maintenance costs, and specific commercial or leisure applications.
Future Trends in Hull Material Technology
FRP hulls are increasingly favored for their lightweight properties and corrosion resistance, enabling enhanced fuel efficiency and lower maintenance costs in modern marine vessels. Aluminum hulls offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and impact resistance, making them ideal for high-performance and military applications where durability and speed are critical. Emerging trends include hybrid composites combining FRP with advanced alloys and nanomaterials, aiming to optimize structural integrity, reduce environmental impact, and extend hull lifespan in future marine technologies.
Corrosion resistance
FRP hulls offer superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum hulls, which are prone to oxidation and require frequent maintenance in marine environments.
Osmotic blistering
FRP hulls are prone to osmotic blistering due to water absorption in the resin, while aluminum hulls resist this issue because of their impermeable metal structure.
Electrolysis protection
FRP hulls inherently resist electrolysis better than aluminum hulls, which require advanced sacrificial anodes and regular monitoring to prevent costly corrosion damage.
Laminate schedule
FRP hulls feature a multi-layer laminate schedule with alternating fiberglass and resin layers for strength and corrosion resistance, while aluminum hulls rely on welded metal sheets with minimal layering but benefit from lightweight durability and impact resistance.
Fatigue cracking
FRP hulls exhibit superior resistance to fatigue cracking compared to aluminum hulls due to their composite material structure and flexibility under cyclic stress.
Weight-to-strength ratio
FRP hulls offer a superior weight-to-strength ratio compared to aluminum hulls, providing lighter boats with comparable durability and resilience.
Hull flexural modulus
FRP hulls typically exhibit a lower flexural modulus compared to aluminum hulls, resulting in greater flexibility and impact absorption but less stiffness and strength under load.
Galvanic isolation
FRP hulls naturally provide galvanic isolation by preventing metal-to-metal contact with seawater, whereas aluminum hulls require specialized coatings or sacrificial anodes to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Impact absorption
FRP hulls provide superior impact absorption due to their flexible composite structure, while aluminum hulls offer higher toughness but less energy dissipation upon collision.
Paint adhesion
FRP hulls offer superior paint adhesion due to their porous gelcoat surface compared to the smoother, less porous aluminum hulls that often require specialized primers for effective coating.
FRP Hull vs Aluminum Hull Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com