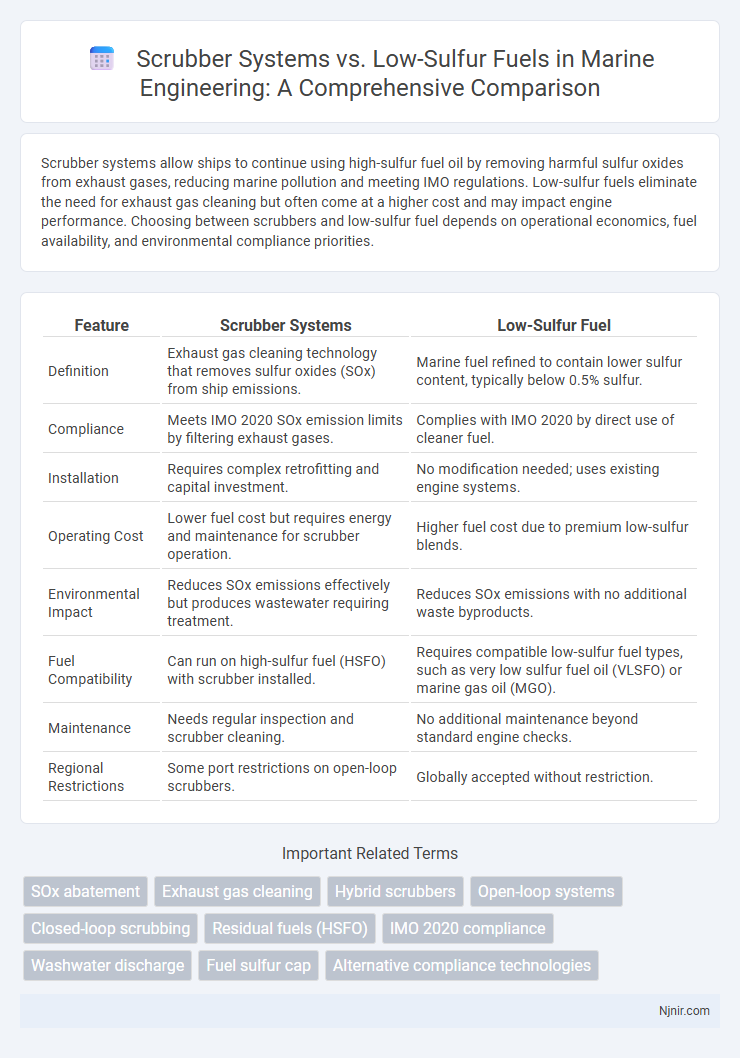
Scrubber systems allow ships to continue using high-sulfur fuel oil by removing harmful sulfur oxides from exhaust gases, reducing marine pollution and meeting IMO regulations. Low-sulfur fuels eliminate the need for exhaust gas cleaning but often come at a higher cost and may impact engine performance. Choosing between scrubbers and low-sulfur fuel depends on operational economics, fuel availability, and environmental compliance priorities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Scrubber Systems | Low-Sulfur Fuel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exhaust gas cleaning technology that removes sulfur oxides (SOx) from ship emissions. | Marine fuel refined to contain lower sulfur content, typically below 0.5% sulfur. |
| Compliance | Meets IMO 2020 SOx emission limits by filtering exhaust gases. | Complies with IMO 2020 by direct use of cleaner fuel. |
| Installation | Requires complex retrofitting and capital investment. | No modification needed; uses existing engine systems. |
| Operating Cost | Lower fuel cost but requires energy and maintenance for scrubber operation. | Higher fuel cost due to premium low-sulfur blends. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces SOx emissions effectively but produces wastewater requiring treatment. | Reduces SOx emissions with no additional waste byproducts. |
| Fuel Compatibility | Can run on high-sulfur fuel (HSFO) with scrubber installed. | Requires compatible low-sulfur fuel types, such as very low sulfur fuel oil (VLSFO) or marine gas oil (MGO). |
| Maintenance | Needs regular inspection and scrubber cleaning. | No additional maintenance beyond standard engine checks. |
| Regional Restrictions | Some port restrictions on open-loop scrubbers. | Globally accepted without restriction. |
Introduction to Marine Sulfur Regulations
Marine sulfur regulations enacted by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) limit sulfur content in fuel to 0.50% m/m outside designated emission control areas, reducing sulfur oxide (SOx) emissions from ships. Scrubber systems, also known as exhaust gas cleaning systems, enable vessels to continue using high-sulfur fuel oil while meeting these limits by removing SOx from exhaust gases. Low-sulfur fuel, such as marine gas oil (MGO) or very low sulfur fuel oil (VLSFO), is an alternative compliant fuel with sulfur levels below the IMO cap, avoiding the need for expensive scrubber installations.
Overview of Scrubber Systems Technology
Scrubber systems technology utilizes advanced exhaust gas cleaning mechanisms to remove sulfur oxides from ship emissions, enabling vessels to continue using high-sulfur fuel oil while complying with IMO sulfur regulations. These systems employ open-loop, closed-loop, or hybrid configurations, effectively reducing sulfur emissions by up to 98% through seawater or freshwater scrubbing processes. Compared to low-sulfur fuel alternatives, scrubbers offer a cost-efficient long-term solution that addresses both environmental compliance and operational flexibility.
Understanding Low-Sulfur Marine Fuels
Low-sulfur marine fuels, such as Very Low Sulfur Fuel Oil (VLSFO) and Marine Gas Oil (MGO), comply with IMO 2020 regulations limiting sulfur content to 0.5%, reducing sulfur oxide (SOx) emissions from ships. These fuels provide a straightforward compliance method but can be more expensive and may impact engine performance due to varying fuel properties. Scrubber systems enable vessels to continue using high-sulfur fuel oil (HSFO) by cleaning exhaust gases, offering cost savings but requiring significant investment and maintenance efforts.
Compliance Pathways: Scrubbers vs Low-Sulfur Fuel
Scrubber systems and low-sulfur fuel represent two primary compliance pathways under IMO 2020 regulations for reducing sulfur oxide emissions from ships. Scrubbers allow vessels to continue using high-sulfur fuel oil (HSFO) by cleaning exhaust gases, while low-sulfur fuel requires switching to fuels with sulfur content below 0.5%. Economically, scrubbers have higher upfront costs but enable cost savings over time with cheaper HSFO, whereas low-sulfur fuel incurs higher operational expenses but avoids scrubber installation and maintenance complexities.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Scrubber systems effectively reduce sulfur dioxide emissions from ships by cleaning exhaust gases, allowing vessels to continue using high-sulfur fuel while meeting environmental regulations. Low-sulfur fuel inherently produces fewer sulfur oxides, minimizing airborne pollutants and preventing acid rain formation, which significantly benefits marine and coastal ecosystems. Lifecycle assessments indicate that scrubbers generate wastewater discharges that may harm marine environments, whereas low-sulfur fuel reduces both air and water pollution without additional effluent concerns.
Operational and Maintenance Considerations
Scrubber systems require continuous monitoring and extensive maintenance to manage corrosion, waste disposal, and chemical consumption, impacting operational costs and crew workload. Low-sulfur fuel reduces emissions compliance complexity but often increases fuel expenses and may affect engine performance due to varying fuel quality. Vessel operators must evaluate long-term maintenance schedules, crew training needs, and the environmental regulatory landscape when choosing between scrubbers and low-sulfur fuels.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Lifetime Expenses
Scrubber systems require significant upfront investment, with installation costs ranging from $2 million to $10 million per vessel depending on size and technology. Over a ship's lifetime, scrubbers often provide cost savings by enabling the continued use of cheaper high-sulfur fuel oil, which can be $100 to $150 per ton less expensive than low-sulfur fuel. However, low-sulfur fuel eliminates operational and maintenance expenses associated with scrubber systems, making it a financially viable option for vessels with lower fuel consumption or limited time at sea.
Fuel Availability and Supply Chain Factors
Scrubber systems enable ships to continue using high-sulfur fuel oil, which benefits supply chain flexibility amid ongoing low-sulfur fuel availability challenges. Low-sulfur fuel availability depends heavily on refinery output capacity and distribution infrastructure, often leading to regional disparities and higher costs. Scrubbers provide a strategic buffer against fuel supply uncertainties by permitting the use of more readily available high-sulfur fuels without compromising compliance with IMO 2020 sulfur regulations.
Future Trends in Emission Reduction Technologies
Scrubber systems continue to evolve with advances in hybrid and closed-loop technologies, significantly reducing sulfur oxide emissions from marine engines while enabling the use of high-sulfur fuel oil. Low-sulfur fuel adoption is growing due to stricter International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations, driving research into alternative fuels like LNG, biofuels, and hydrogen to achieve deeper decarbonization. Future trends emphasize integrating scrubbers with energy-efficient propulsion systems and digital monitoring to optimize emissions control and comply with evolving environmental standards.
Decision Criteria for Ship Operators
Ship operators prioritize scrubber systems when long-term fuel cost savings and compliance with IMO 2020 sulfur limits are critical, especially for vessels with high operational hours and access to open waters. Low-sulfur fuels offer simplicity and lower upfront investment but may increase fuel expenses and supply chain variability. Decisions hinge on factors like initial capital expenditure, operational maintenance, fuel price volatility, regulatory zones, and vessel trading patterns.
SOx abatement
Scrubber systems effectively reduce SOx emissions by cleaning exhaust gases, while low-sulfur fuel minimizes SOx formation at the source, both serving as key strategies for maritime SOx abatement.
Exhaust gas cleaning
Exhaust gas cleaning via scrubber systems effectively reduces sulfur oxide emissions from ships, offering a cost-efficient alternative to low-sulfur fuel by allowing continued use of high-sulfur fuel oil while meeting IMO sulfur regulations.
Hybrid scrubbers
Hybrid scrubber systems offer versatile emissions control by enabling ships to switch between using low-sulfur fuel and high-sulfur fuel with exhaust gas cleaning, optimizing operational costs and regulatory compliance.
Open-loop systems
Open-loop scrubber systems reduce sulfur emissions by treating exhaust gases with seawater but depend on regulatory acceptance and marine water quality, offering a cost-effective alternative to low-sulfur fuel for ships operating in IMO Sulfur Emission Control Areas.
Closed-loop scrubbing
Closed-loop scrubber systems offer an efficient method for ships to meet IMO sulfur emission regulations by continuously treating exhaust gases with recycled water, enabling compliance while using high-sulfur fuel without discharging wash water into the environment.
Residual fuels (HSFO)
Scrubber systems enable ships to continue using high-sulfur residual fuels like HSFO by removing sulfur oxides from exhaust gases, providing a cost-effective alternative to switching to more expensive low-sulfur fuels.
IMO 2020 compliance
Scrubber systems enable ships to comply with IMO 2020 sulfur emissions limits by cleaning exhaust gases, allowing continued use of higher-sulfur fuels compared to the mandatory switch to low-sulfur fuel oil.
Washwater discharge
Scrubber systems generate washwater discharge containing pollutants requiring treatment, whereas low-sulfur fuel significantly reduces sulfur oxide emissions without producing washwater effluent.
Fuel sulfur cap
Scrubber systems enable ships to meet the IMO 2020 fuel sulfur cap of 0.5% by cleaning exhaust gases, allowing continued use of higher-sulfur fuel oils.
Alternative compliance technologies
Scrubber systems and low-sulfur fuel represent key alternative compliance technologies for reducing marine sulfur emissions, with scrubbers enabling vessels to continue using high-sulfur fuel by removing sulfur oxides from exhaust gases and low-sulfur fuel minimizing sulfur content at the source.
Scrubber systems vs low-sulfur fuel Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com