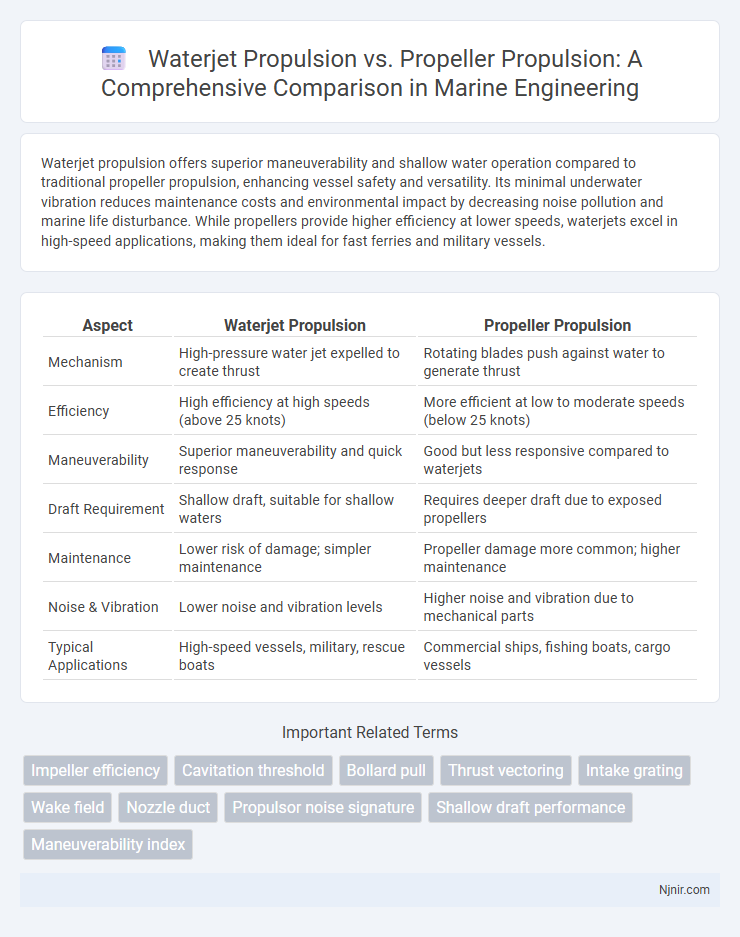
Waterjet propulsion offers superior maneuverability and shallow water operation compared to traditional propeller propulsion, enhancing vessel safety and versatility. Its minimal underwater vibration reduces maintenance costs and environmental impact by decreasing noise pollution and marine life disturbance. While propellers provide higher efficiency at lower speeds, waterjets excel in high-speed applications, making them ideal for fast ferries and military vessels.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Waterjet Propulsion | Propeller Propulsion |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | High-pressure water jet expelled to create thrust | Rotating blades push against water to generate thrust |
| Efficiency | High efficiency at high speeds (above 25 knots) | More efficient at low to moderate speeds (below 25 knots) |
| Maneuverability | Superior maneuverability and quick response | Good but less responsive compared to waterjets |
| Draft Requirement | Shallow draft, suitable for shallow waters | Requires deeper draft due to exposed propellers |
| Maintenance | Lower risk of damage; simpler maintenance | Propeller damage more common; higher maintenance |
| Noise & Vibration | Lower noise and vibration levels | Higher noise and vibration due to mechanical parts |
| Typical Applications | High-speed vessels, military, rescue boats | Commercial ships, fishing boats, cargo vessels |
Introduction to Marine Propulsion Systems
Waterjet propulsion uses high-velocity water jets to generate thrust, offering superior maneuverability and shallow draft capabilities compared to traditional propeller systems. Propeller propulsion relies on rotating blades to push water backward, providing efficient thrust especially at lower speeds and for larger vessels. Marine propulsion systems must balance factors like efficiency, speed, and vessel type, with waterjets favored in high-speed crafts and propellers preferred for bulkier ships.
Overview of Waterjet Propulsion Technology
Waterjet propulsion technology uses high-pressure water jets to generate thrust, offering superior maneuverability and shallow draft capabilities compared to traditional propeller propulsion. This system reduces cavitation risks and enhances vessel speed and efficiency, especially in high-speed applications. Waterjet units are commonly employed in fast ferries, military vessels, and recreational crafts where precision and agility are critical.
Fundamentals of Propeller Propulsion
Propeller propulsion relies on rotating blades that generate thrust by accelerating water backward, creating a reaction force that moves the vessel forward according to Newton's third law of motion. The efficiency of propeller propulsion depends on blade design, pitch, diameter, and rotational speed, which influence thrust generation and hydrodynamic performance. Understanding factors such as cavitation, drag, and torque is fundamental to optimizing propeller propulsion systems for marine applications.
Comparative Efficiency and Performance
Waterjet propulsion offers superior maneuverability and higher speeds in shallow waters compared to traditional propeller propulsion, which excels in fuel efficiency at steady cruising speeds. Waterjets generate thrust by expelling water at high velocity through a narrow nozzle, reducing cavitation and allowing enhanced acceleration and rapid direction changes. Propellers provide better overall efficiency at lower speeds due to continuous thrust generation and simpler mechanics, making them ideal for long-distance and heavy-load marine applications.
Maneuverability and Vessel Control
Waterjet propulsion offers superior maneuverability and vessel control due to its ability to vector thrust in multiple directions, enabling tight turns and rapid acceleration or deceleration. Unlike traditional propeller propulsion, waterjets provide enhanced responsiveness in shallow waters and high-speed conditions, reducing the risk of damage from debris. This makes waterjet systems ideal for high-speed vessels requiring precise handling and quick directional changes.
Shallow Water Operations and Draft Requirements
Waterjet propulsion offers superior shallow water operation capabilities by drawing water from beneath the hull and expelling it at high velocity, reducing the risk of damage from underwater obstacles compared to traditional propeller systems. This technology minimizes draft requirements, often allowing vessels to operate in waters less than one meter deep, whereas propeller-driven boats typically require deeper drafts to avoid grounding and propeller strikes. The increased maneuverability and reduced draft of waterjet systems make them ideal for coastal, riverine, and estuarine environments where depth and debris pose significant operational challenges.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Waterjet propulsion systems generally require less frequent maintenance than traditional propeller propulsion due to fewer exposed moving parts vulnerable to debris damage. The sealed nature of waterjet units reduces corrosion risks and extends component lifespan, enhancing durability in harsh marine environments. However, propeller systems benefit from simpler, more accessible parts that can be repaired or replaced quickly, offering cost-effective long-term maintenance.
Environmental Impact and Noise Emissions
Waterjet propulsion systems generate less underwater noise compared to traditional propeller systems, reducing disturbances to marine life and lowering acoustic pollution in sensitive ecosystems. They minimize cavitation by using high-speed water jets that cause less turbulence, resulting in quieter operation and decreased risk of harming aquatic animals. Waterjet units also reduce the release of harmful emissions as they often improve fuel efficiency in high-speed vessels, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint relative to conventional propeller-driven boats.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Operation
Waterjet propulsion systems generally have higher initial installation costs due to complex engineering and specialized components compared to traditional propeller propulsion. Operational expenses for waterjets tend to be lower, as they require less maintenance, have fewer moving parts prone to wear, and provide better fuel efficiency at high speeds. Propeller systems incur higher ongoing maintenance costs, especially in abrasive or shallow water conditions, increasing long-term operational expenditures.
Application Suitability: Vessels and Use Cases
Waterjet propulsion excels in high-speed vessels, such as patrol boats and jet skis, offering enhanced maneuverability and shallow water operation. Propeller propulsion is better suited for larger ships like cargo vessels and fishing boats, providing higher efficiency at lower speeds and better fuel economy. Choosing between the two depends on vessel size, operational environment, and the need for speed or fuel efficiency.
Impeller efficiency
Waterjet propulsion achieves higher impeller efficiency at increased speeds by minimizing cavitation and optimizing water flow compared to traditional propeller propulsion.
Cavitation threshold
Waterjet propulsion demonstrates a higher cavitation threshold compared to traditional propeller propulsion, reducing blade damage and improving performance in high-speed marine vessels.
Bollard pull
Waterjet propulsion delivers higher bollard pull efficiency in shallow waters by minimizing cavitation and maximizing thrust, whereas propeller propulsion generally provides greater bollard pull at lower speeds with higher vulnerability to damage.
Thrust vectoring
Waterjet propulsion offers superior thrust vectoring capabilities compared to propeller propulsion by enabling precise and rapid directional control through adjustable nozzles, enhancing maneuverability and response time.
Intake grating
Waterjet propulsion features a low-profile intake grating that minimizes debris ingestion and enhances performance in shallow waters compared to the larger, more obstructive intake grids used in propeller propulsion systems.
Wake field
Waterjet propulsion generates a more uniform and less turbulent wake field compared to traditional propeller propulsion, resulting in reduced cavitation, lower drag, and improved vessel maneuverability.
Nozzle duct
Waterjet propulsion features a nozzle duct designed to efficiently accelerate water flow for high-speed maneuverability and shallow water operation, whereas propeller propulsion uses an open propeller without a nozzle, resulting in different thrust characteristics and efficiency profiles.
Propulsor noise signature
Waterjet propulsion generates a lower noise signature than traditional propeller propulsion by minimizing cavitation and mechanical vibration.
Shallow draft performance
Waterjet propulsion provides superior shallow draft performance compared to propeller propulsion by minimizing underwater appendages and reducing the risk of damage in shallow waters.
Maneuverability index
Waterjet propulsion achieves a higher maneuverability index than propeller propulsion due to its enhanced thrust vectoring capabilities and rapid directional response.
waterjet propulsion vs propeller propulsion Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com