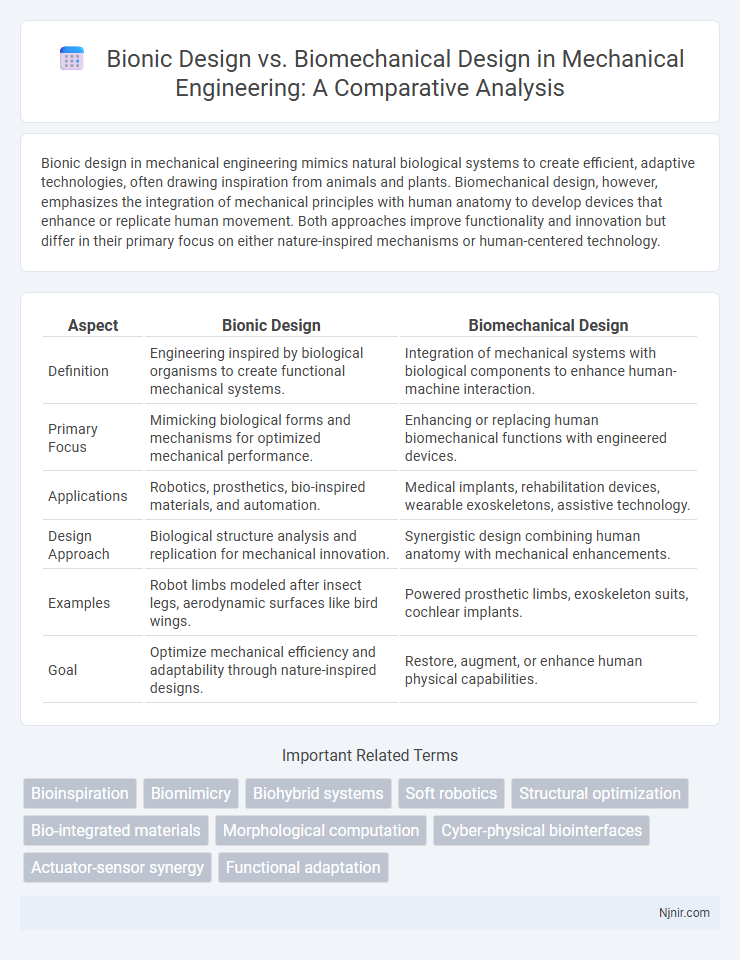
Bionic design in mechanical engineering mimics natural biological systems to create efficient, adaptive technologies, often drawing inspiration from animals and plants. Biomechanical design, however, emphasizes the integration of mechanical principles with human anatomy to develop devices that enhance or replicate human movement. Both approaches improve functionality and innovation but differ in their primary focus on either nature-inspired mechanisms or human-centered technology.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bionic Design | Biomechanical Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engineering inspired by biological organisms to create functional mechanical systems. | Integration of mechanical systems with biological components to enhance human-machine interaction. |
| Primary Focus | Mimicking biological forms and mechanisms for optimized mechanical performance. | Enhancing or replacing human biomechanical functions with engineered devices. |
| Applications | Robotics, prosthetics, bio-inspired materials, and automation. | Medical implants, rehabilitation devices, wearable exoskeletons, assistive technology. |
| Design Approach | Biological structure analysis and replication for mechanical innovation. | Synergistic design combining human anatomy with mechanical enhancements. |
| Examples | Robot limbs modeled after insect legs, aerodynamic surfaces like bird wings. | Powered prosthetic limbs, exoskeleton suits, cochlear implants. |
| Goal | Optimize mechanical efficiency and adaptability through nature-inspired designs. | Restore, augment, or enhance human physical capabilities. |
Introduction to Bionic and Biomechanical Design
Bionic design draws inspiration from natural biological systems to develop innovative technological solutions by mimicking the structure, function, and processes of living organisms. Biomechanical design integrates principles of mechanics with biological systems to analyze and replicate movement, force, and structural performance in both natural and artificial constructs. Both approaches emphasize interdisciplinary research, combining biology, engineering, and material science to advance functionality and efficiency in design applications.
Defining Bionic Design in Mechanical Engineering
Bionic design in mechanical engineering involves emulating biological structures and functions to create efficient, adaptive, and sustainable mechanical systems by analyzing natural models at micro and macro scales. This design approach integrates principles such as energy efficiency, self-repair, and multifunctionality found in living organisms to enhance mechanical performance and innovation. Unlike biomechanical design, which primarily focuses on the interaction between mechanics and biological systems for medical or prosthetic applications, bionic design emphasizes the direct translation of biological intelligence into mechanical engineering solutions.
Understanding Biomechanical Design Principles
Biomechanical design principles focus on replicating the functional mechanics of living organisms by analyzing forces, motion, and material properties to create efficient and adaptive systems. This approach integrates anatomy, physiology, and engineering to optimize performance in prosthetics, robotics, and wearable devices. Understanding biomechanical design enhances the development of solutions that align closely with natural movement and load distribution.
Historical Evolution of Bionic vs. Biomechanical Approaches
Bionic design emerged in the mid-20th century as engineers began mimicking natural biological systems using electronics and robotics, fostering innovations like prosthetic limbs and autonomous machines. Biomechanical design traces back to early anatomical and mechanical studies in the Renaissance, emphasizing the integration of biological principles with mechanical systems for prosthetics, orthopedics, and ergonomic devices. The historical evolution reveals bionic design's focus on electronic and robotic replication of natural functions, while biomechanical design centers on mechanical adaptation and enhancement of human movement and structure.
Key Differences Between Bionic Design and Biomechanical Design
Bionic design focuses on replicating biological systems and natural processes to create sustainable, efficient technologies inspired by organisms, whereas biomechanical design emphasizes the integration of mechanical principles with human or animal anatomy to enhance movement and functionality. Bionic design often applies biomimicry for innovation in engineering and robotics, while biomechanical design is primarily used in prosthetics, orthopedics, and ergonomic devices to improve physical performance and health outcomes. The key difference lies in bionic design's emphasis on nature-inspired innovation versus biomechanical design's focus on mechanical adaptation to biological systems.
Applications of Bionic Design in Modern Engineering
Bionic design integrates principles from biological systems to create innovative engineering solutions, enhancing efficiency and adaptability in fields such as robotics, aerospace, and prosthetics. This approach mimics natural structures and mechanisms, leading to lightweight yet strong materials, energy-efficient machines, and improved ergonomic devices. The application of bionic design in modern engineering drives advancements in sustainable technology, biomimetic drones, and adaptive building materials, revolutionizing product performance and user experience.
Applications of Biomechanical Design in Mechanical Systems
Biomechanical design in mechanical systems significantly enhances prosthetics, exoskeletons, and robotic limbs by mimicking the natural movement and functionality of human anatomy. This approach utilizes biological principles to improve ergonomics, efficiency, and adaptability in devices used for rehabilitation, medical assistance, and human augmentation. Advanced sensors and materials in biomechanical design enable seamless interaction between mechanical systems and the human body, promoting comfort and performance.
Advantages and Limitations of Bionic Design
Bionic design leverages natural biological structures to create efficient, sustainable, and innovative solutions that often outperform conventional mechanical systems in adaptability and energy efficiency. Its advantages include improved ergonomics, enhanced durability through biomimicry, and reduced environmental impact by emulating natural processes. Limitations involve high complexity in replicating biological functions accurately, increased development costs, and challenges in integrating biological components with existing mechanical systems.
Advantages and Limitations of Biomechanical Design
Biomechanical design leverages the integration of biological principles with mechanical systems to create structures and devices that closely mimic natural movement and functionality, offering enhanced adaptability and efficiency in applications such as prosthetics and robotics. Advantages include improved ergonomics, increased comfort for users, and greater energy efficiency, while limitations involve complex material requirements, higher development costs, and challenges in replicating the full range of natural biomechanical behaviors. The need for advanced sensors and control systems also presents technical hurdles, often resulting in longer design cycles compared to purely mechanical approaches.
Future Trends: Integrating Bionic and Biomechanical Concepts
Future trends in design increasingly focus on integrating bionic and biomechanical concepts to enhance human-machine interfaces, combining biological inspiration with mechanical efficiency. Advances in materials science and AI-driven modeling enable more seamless, adaptive systems that mimic natural movement and improve functionality in prosthetics and robotics. This convergence is expected to drive innovations in wearable technology, rehabilitation devices, and autonomous systems, pushing the boundaries of human augmentation and medical applications.
Bioinspiration
Bionic design leverages direct bioinspiration by mimicking natural structures and functions, whereas biomechanical design focuses on applying biological principles to mechanical systems for improved efficiency and adaptability.
Biomimicry
Biomimicry in bionic design replicates natural biological systems for innovation, whereas biomechanical design focuses on the mechanical principles of living organisms to enhance human-machine interfaces.
Biohybrid systems
Biohybrid systems integrate bionic design principles by combining living biological components with engineered biomechanical structures to enhance functionality and adaptability.
Soft robotics
Bionic design in soft robotics mimics natural biological structures to enhance adaptability and flexibility, while biomechanical design integrates mechanical principles with biological functions to improve efficiency and structural support.
Structural optimization
Bionic design leverages nature-inspired principles for structural optimization by mimicking biological forms, while biomechanical design focuses on analyzing mechanical functions of biological systems to enhance structural efficiency.
Bio-integrated materials
Bio-integrated materials in bionic design enhance seamless interaction with biological tissues, whereas biomechanical design primarily emphasizes mechanical function and movement replication.
Morphological computation
Bionic design leverages morphological computation by mimicking biological structures for adaptive functionality, whereas biomechanical design integrates mechanical components with biological systems emphasizing structural efficiency.
Cyber-physical biointerfaces
Cyber-physical biointerfaces integrate bionic design principles that mimic biological systems with biomechanical design focused on mechanical functionality to enhance seamless interaction between humans and machines.
Actuator-sensor synergy
Bionic design enhances actuator-sensor synergy by mimicking natural biological systems for adaptive responsiveness, while biomechanical design focuses on mechanical efficiency and structural optimization to improve actuator-sensor integration.
Functional adaptation
Bionic design replicates biological structures for enhanced functionality by mimicking natural forms, while biomechanical design integrates mechanical principles with biological systems to improve functional adaptation and performance.
Bionic design vs biomechanical design Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com