Helical gears offer smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears due to their angled teeth, which engage gradually, reducing noise and vibration. Their ability to carry higher loads and operate at higher speeds makes them ideal for automotive transmissions and industrial machinery. Spur gears, with their simpler design and ease of manufacturing, are preferred for low-speed applications requiring precise, straightforward power transmission.
Table of Comparison
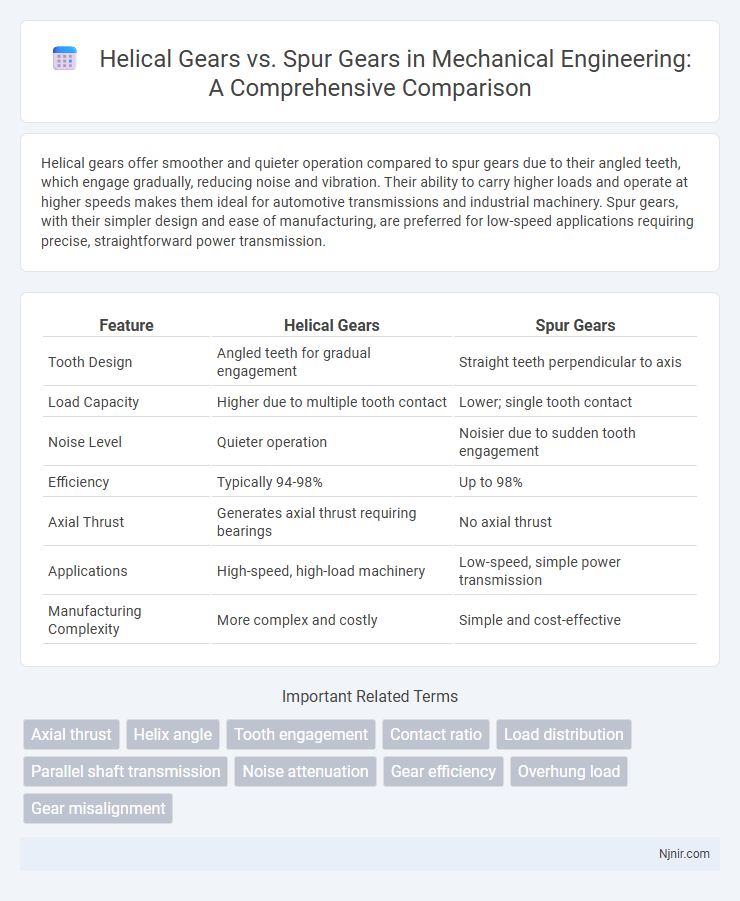
| Feature | Helical Gears | Spur Gears |
|---|---|---|
| Tooth Design | Angled teeth for gradual engagement | Straight teeth perpendicular to axis |
| Load Capacity | Higher due to multiple tooth contact | Lower; single tooth contact |
| Noise Level | Quieter operation | Noisier due to sudden tooth engagement |
| Efficiency | Typically 94-98% | Up to 98% |
| Axial Thrust | Generates axial thrust requiring bearings | No axial thrust |
| Applications | High-speed, high-load machinery | Low-speed, simple power transmission |
| Manufacturing Complexity | More complex and costly | Simple and cost-effective |
Introduction to Helical and Spur Gears
Helical gears feature angled teeth that engage gradually, providing smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears, which have straight teeth that mesh instantly. Spur gears are simpler in design and manufacturing, offering efficient power transmission for applications with lower noise tolerance. Both gear types are essential in mechanical systems, with helical gears preferred for high-speed, high-load conditions and spur gears favored for cost-effective, straightforward usage.
Fundamental Design Differences
Helical gears feature angled teeth cut at a helix angle, enabling gradual engagement and smoother transmission of motion compared to spur gears, which have straight teeth aligned parallel to the gear axis. The angled teeth of helical gears create axial thrust forces, requiring bearings to accommodate these loads, whereas spur gears generate only radial loads due to their tooth design. Helical gears operate more quietly and handle higher loads due to increased tooth contact, while spur gears offer simpler design and manufacturing advantages suitable for lower-speed applications.
Transmission Efficiency Comparison
Helical gears offer higher transmission efficiency than spur gears due to their angled teeth, which engage gradually and reduce impact loads and noise. Spur gears experience more sliding friction and shock loads because of their teeth engaging suddenly, resulting in slightly lower efficiency in high-speed or high-load applications. Efficiency rates for helical gears typically range from 94% to 98%, while spur gears average between 90% and 95%, making helical gears preferable for smoother and quieter power transmission.
Load Capacity and Strength
Helical gears offer higher load capacity and strength compared to spur gears due to their angled teeth, which distribute load more evenly and engage gradually, reducing stress concentrations and noise. Spur gears have straight teeth that create abrupt contact and higher localized stress, limiting their load capacity and durability under heavy or high-speed applications. Consequently, helical gears are preferred in automotive transmissions and industrial machinery where enhanced strength and smoother operation are critical.
Noise and Vibration Characteristics
Helical gears exhibit lower noise and vibration levels compared to spur gears due to their angled teeth, which engage gradually and provide smoother transmission of power. Spur gears generate higher noise and vibration because their teeth engage suddenly, resulting in impact forces during operation. The continuous contact in helical gears reduces acoustic emissions and mechanical vibrations, making them ideal for high-speed and high-load applications.
Applications in Mechanical Systems
Helical gears are widely used in automotive transmissions and industrial machinery requiring smooth, quiet operation and high load capacity due to their angled teeth design, which distributes load gradually. Spur gears find applications in simple machinery, such as conveyor systems and mechanical clocks, where efficiency and ease of manufacturing are prioritized despite higher noise levels. The choice between helical and spur gears depends on factors like load requirements, noise limitations, and gear alignment within mechanical systems.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Helical gears require more precise manufacturing processes due to their angled teeth, leading to higher costs and longer production times compared to spur gears. Spur gears have simpler geometry with straight teeth, allowing for easier machining and reduced manufacturing expenses. The complexity of helical gears also demands more advanced tooling and quality control measures, increasing overall production costs.
Lubrication and Maintenance Needs
Helical gears require specialized lubrication with high-quality oil to accommodate the sliding contact and reduce heat buildup caused by their angled teeth, leading to smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears. Spur gears, having straight teeth and simpler engagement, typically need less complex lubrication but may experience higher noise and wear under heavy loads, necessitating regular inspection and re-lubrication. Maintenance for helical gears often involves monitoring oil viscosity and ensuring proper circulation in enclosed gearboxes, while spur gears benefit from straightforward lubrication routines and frequent cleaning to prevent debris accumulation.
Gear Alignment and Mounting Requirements
Helical gears require more precise alignment and robust mounting due to their angled teeth, which generate axial thrust and increased load on bearings. Spur gears have simpler alignment and mounting needs since their straight teeth produce predominantly radial forces with minimal axial loads. Proper gear alignment in helical gears reduces noise and wear, enhancing operational efficiency compared to the easier installation of spur gears.
Selection Criteria for Industrial Use
Helical gears offer smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears due to their angled teeth, making them ideal for high-speed industrial applications requiring noise reduction. Spur gears are preferred for applications demanding simple design, ease of manufacturing, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for lower-speed or moderate-load conditions. Selection criteria focus on load capacity, noise tolerance, alignment precision, and space constraints within industrial machinery.
Axial thrust
Helical gears generate significant axial thrust due to their angled teeth, requiring bearings designed to handle this force, whereas spur gears produce minimal axial thrust because their teeth are parallel to the gear axis.
Helix angle
Helical gears, characterized by their helix angle ranging from 15 to 30 degrees, offer smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears due to gradual tooth engagement along the angled helix.
Tooth engagement
Helical gears offer smoother and quieter tooth engagement due to their angled teeth, providing gradual contact, whereas spur gears engage teeth abruptly with straight teeth, causing more noise and stress.
Contact ratio
Helical gears have a higher contact ratio than spur gears due to their angled teeth, resulting in smoother and quieter operation.
Load distribution
Helical gears provide superior load distribution through angled teeth engagement, resulting in smoother operation and higher load-carrying capacity compared to spur gears with straight teeth.
Parallel shaft transmission
Helical gears provide smoother, quieter operation and higher load capacity than spur gears in parallel shaft transmission due to their angled teeth design.
Noise attenuation
Helical gears generate significantly less noise than spur gears due to their angled teeth, which provide smoother and quieter operation by distributing contact gradually.
Gear efficiency
Helical gears typically offer higher gear efficiency than spur gears due to their smoother engagement and reduced noise and vibration during operation.
Overhung load
Helical gears generate lower overhung load due to their angled teeth distributing forces more evenly compared to the higher overhung load caused by the straight teeth of spur gears.
Gear misalignment
Helical gears exhibit greater tolerance to gear misalignment than spur gears due to their angled tooth design, which enables smoother engagement and distributes load more evenly.
helical gears vs spur gears Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com