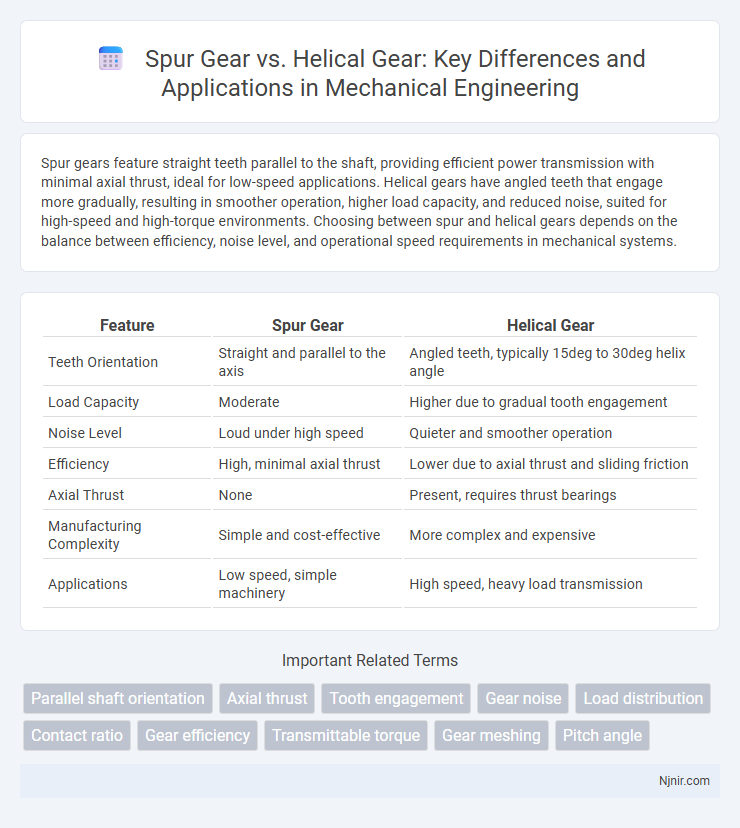
Spur gears feature straight teeth parallel to the shaft, providing efficient power transmission with minimal axial thrust, ideal for low-speed applications. Helical gears have angled teeth that engage more gradually, resulting in smoother operation, higher load capacity, and reduced noise, suited for high-speed and high-torque environments. Choosing between spur and helical gears depends on the balance between efficiency, noise level, and operational speed requirements in mechanical systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spur Gear | Helical Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Teeth Orientation | Straight and parallel to the axis | Angled teeth, typically 15deg to 30deg helix angle |
| Load Capacity | Moderate | Higher due to gradual tooth engagement |
| Noise Level | Loud under high speed | Quieter and smoother operation |
| Efficiency | High, minimal axial thrust | Lower due to axial thrust and sliding friction |
| Axial Thrust | None | Present, requires thrust bearings |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Simple and cost-effective | More complex and expensive |
| Applications | Low speed, simple machinery | High speed, heavy load transmission |
Introduction to Spur and Helical Gears
Spur gears feature straight teeth aligned parallel to the gear axis, making them the simplest and most cost-effective option for transmitting motion between parallel shafts. Helical gears possess angled teeth, which engage gradually, resulting in smoother and quieter operation while handling higher loads. Both gear types are essential in mechanical systems, with spur gears favored for straightforward applications and helical gears preferred for high-speed and high-torque environments.
Fundamental Differences in Gear Design
Spur gears feature straight teeth parallel to the gear axis, resulting in simpler design and efficient power transmission at low speeds with minimal axial thrust. Helical gears have angled teeth that engage gradually, enabling smoother operation, higher load capacity, and reduced noise but generate axial thrust requiring thrust bearings. The fundamental difference lies in tooth geometry and orientation, impacting load distribution, noise levels, and the types of applications each gear suits.
Working Principles of Spur and Helical Gears
Spur gears operate on the principle of direct tooth engagement, where straight teeth mesh along the gear's axis, transmitting torque with minimal axial thrust. Helical gears feature angled teeth that engage gradually, producing smoother and quieter operation while generating axial forces due to the helix angle. The working principle of helical gears allows for higher load capacity and efficiency in power transmission compared to spur gears.
Load Distribution and Stress Analysis
Spur gears exhibit concentrated load distribution along the gear tooth width, resulting in higher localized stress and increased noise during operation, whereas helical gears provide gradual load transfer due to angled teeth, enabling smoother engagement and reduced stress concentrations. The helical gear's load distribution across multiple teeth simultaneously decreases dynamic loads, improving fatigue life and enhancing torque capacity. Stress analysis reveals that helical gears benefit from lower bending stress and contact stress compared to spur gears, making them more suitable for high-speed and heavy-load applications.
Noise and Vibration Characteristics
Spur gears generate higher noise and vibration levels due to their straight teeth engaging suddenly, causing impact forces during meshing. Helical gears produce smoother and quieter operation because their angled teeth engage gradually, distributing load more evenly and reducing impact noise. The continuous tooth engagement in helical gears significantly minimizes vibration, making them ideal for applications requiring quieter performance.
Efficiency and Power Transmission
Spur gears exhibit higher mechanical efficiency due to their simpler tooth design, which minimizes frictional losses during power transmission. Helical gears provide smoother and quieter operation with higher load capacity, but their angled teeth generate axial thrust and increased sliding friction, slightly reducing overall efficiency. In high-speed and high-power applications, helical gears offer better power transmission durability despite a modest efficiency trade-off compared to spur gears.
Manufacturing Complexity and Costs
Spur gears feature simpler manufacturing processes due to their straight teeth, resulting in lower production costs and faster machining times compared to helical gears. Helical gears require more advanced cutting techniques like hobbing or grinding with angled teeth, increasing complexity and manufacturing expenses. The additional precision and material handling in helical gear production lead to higher costs but also offer smoother operation and greater load capacity.
Applications in Mechanical Engineering
Spur gears are widely used in low-speed applications such as conveyor systems, simple machinery, and automotive gearboxes due to their straightforward design and cost-effectiveness. Helical gears, with angled teeth, are preferred in high-speed and high-load scenarios like automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and aerospace equipment because they offer smoother and quieter operation. The choice between spur and helical gears depends on application-specific requirements for noise reduction, load capacity, and efficiency in mechanical engineering projects.
Maintenance and Durability
Spur gears require less maintenance due to their simpler design, but they tend to experience more noise and wear under high loads, leading to reduced durability compared to helical gears. Helical gears, with their angled teeth, distribute load more evenly and operate more quietly, resulting in better longevity and reduced maintenance frequency. Regular lubrication and alignment checks are essential for both gear types to optimize performance and extend service life.
Selection Criteria for Gear Type
Selection criteria for spur gear versus helical gear primarily depend on load capacity, noise levels, and efficiency requirements. Spur gears offer simplicity, high efficiency, and ease of manufacturing, making them ideal for moderate-speed applications with lower noise constraints. Helical gears provide smoother operation and higher load capacity due to angled teeth, suitable for high-speed, heavy-load environments where noise reduction is critical.
Parallel shaft orientation
Spur gears with parallel shaft orientation offer simple design and efficient power transmission, while helical gears provide smoother operation and higher load capacity due to angled teeth engagement.
Axial thrust
Helical gears generate significant axial thrust due to their angled teeth, whereas spur gears produce negligible axial thrust because of their straight teeth.
Tooth engagement
Spur gears engage teeth along the entire width simultaneously, resulting in abrupt contact and noise, while helical gears feature angled teeth that engage gradually, providing smoother and quieter operation.
Gear noise
Helical gears generate less operational noise than spur gears due to their angled teeth producing smoother and quieter meshing action.
Load distribution
Helical gears provide superior load distribution compared to spur gears due to their angled teeth, which engage gradually and distribute forces more evenly along the tooth surface.
Contact ratio
Helical gears typically have a higher contact ratio than spur gears, resulting in smoother operation and increased load capacity.
Gear efficiency
Helical gears typically offer higher gear efficiency than spur gears due to their angled teeth, which provide smoother and quieter operation with reduced friction and wear.
Transmittable torque
Helical gears transmit higher torque than spur gears due to their angled teeth, which provide greater tooth engagement and load distribution.
Gear meshing
Spur gears ensure straightforward gear meshing with parallel teeth providing efficient power transmission, while helical gears offer smoother and quieter gear meshing due to their angled teeth that engage gradually.
Pitch angle
Helical gears have an angled pitch line that creates smoother and quieter meshing compared to the straight pitch angle of spur gears.
Spur gear vs helical gear Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com