Topology optimization leverages computational algorithms to identify the most efficient material layout within a given design space, enhancing performance while reducing weight and material use. Traditional design relies on established heuristics and engineering experience, often resulting in conservative and less material-efficient structures. Integrating topology optimization into mechanical engineering enables innovative solutions that outperform conventional designs in strength, stiffness, and resource utilization.
Table of Comparison
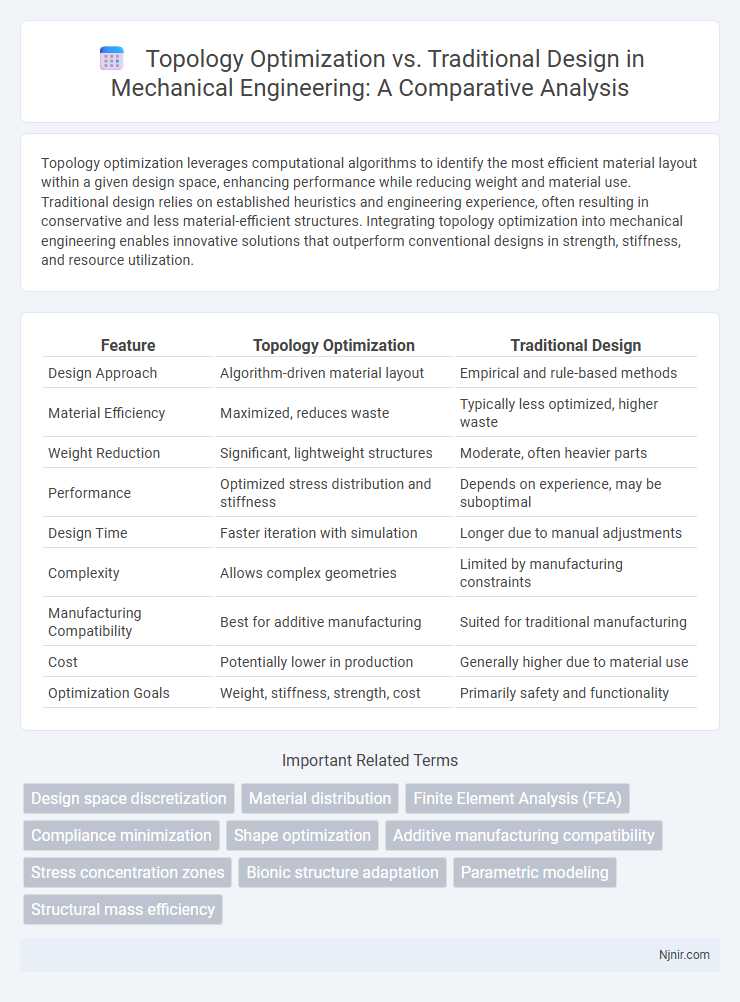
| Feature | Topology Optimization | Traditional Design |
|---|---|---|
| Design Approach | Algorithm-driven material layout | Empirical and rule-based methods |
| Material Efficiency | Maximized, reduces waste | Typically less optimized, higher waste |
| Weight Reduction | Significant, lightweight structures | Moderate, often heavier parts |
| Performance | Optimized stress distribution and stiffness | Depends on experience, may be suboptimal |
| Design Time | Faster iteration with simulation | Longer due to manual adjustments |
| Complexity | Allows complex geometries | Limited by manufacturing constraints |
| Manufacturing Compatibility | Best for additive manufacturing | Suited for traditional manufacturing |
| Cost | Potentially lower in production | Generally higher due to material use |
| Optimization Goals | Weight, stiffness, strength, cost | Primarily safety and functionality |
Introduction to Topology Optimization and Traditional Design
Topology optimization leverages advanced computational algorithms to identify the most efficient material distribution within a given design space, resulting in lightweight structures with enhanced performance. Traditional design relies on established engineering heuristics and iterative adjustments based on experience, often leading to conservative material use and less innovative forms. The integration of topology optimization in the design process significantly improves structural efficiency, reduces weight, and fosters innovation compared to conventional design methodologies.
Fundamental Principles of Topology Optimization
Topology optimization fundamentally relies on computational algorithms to distribute material within a given design space, maximizing structural performance based on predefined constraints and load conditions. Unlike traditional design methods that depend on designer intuition and iterative modifications, topology optimization uses mathematical models and finite element analysis to identify optimal material layouts for minimum weight and maximum stiffness. This approach enables the creation of innovative, efficient structures by exploring a vast design space beyond conventional geometries.
Core Concepts in Traditional Mechanical Design
Traditional mechanical design relies on well-established principles such as stress analysis, factor of safety, and material selection to create components that meet performance and durability requirements. It uses iterative methods and engineering experience to refine shapes and sizes, often prioritizing manufacturability and simplicity. Core concepts emphasize deterministic approaches, standard geometries, and conservative design margins to ensure reliability and ease of production.
Design Objectives and Performance Criteria
Topology optimization uses computational algorithms to distribute material within a given design space, aiming to maximize structural efficiency by minimizing weight while maintaining or enhancing stiffness and strength. Traditional design often relies on established heuristics and designer experience, focusing on achieving safety factors and regulatory compliance without fully exploiting material distribution. The key performance criteria for topology optimization include stress distribution, deformation limits, and natural frequency, while traditional design prioritizes manufacturability, cost constraints, and simplified validation through empirical methods.
Material Usage and Manufacturing Efficiency
Topology optimization significantly reduces material usage by strategically distributing material only where necessary to meet performance criteria, resulting in lightweight and highly efficient structures. Traditional design often relies on conservative safety factors and uniform material allocation, leading to increased waste and heavier components. The manufacturing efficiency of topology-optimized designs is enhanced through advanced methods like additive manufacturing, enabling complex geometries that traditional manufacturing processes struggle to produce efficiently.
Computational Tools and Simulation Techniques
Topology optimization leverages advanced computational tools such as finite element analysis (FEA) and gradient-based algorithms to iteratively refine material distribution for optimal structural performance, significantly reducing weight and enhancing strength. Traditional design relies on heuristic methods and predefined shapes, often requiring extensive manual adjustments and multiple physical prototypes, making the process less efficient and more time-consuming. Simulation techniques in topology optimization incorporate high-resolution models and parametric studies, enabling precise prediction of stress distribution and dynamic behavior that traditional design methods lack.
Design Flexibility and Innovation Potential
Topology optimization enables highly flexible design by systematically removing unnecessary material, resulting in innovative, lightweight structures unattainable through traditional design methods reliant on predefined shapes and iterative adjustments. The algorithm-driven process explores a vast design space, fostering creativity and efficiency in engineering solutions, whereas traditional design often limits innovation due to conventional constraints and designer intuition. As a result, topology optimization significantly enhances innovation potential by delivering optimal, performance-driven designs tailored to specific functional requirements.
Structural Integrity and Safety Considerations
Topology optimization enhances structural integrity by efficiently distributing material to withstand specific load conditions, reducing stress concentrations and potential failure points compared to traditional design methods that often rely on heuristic or uniform material distribution. This optimization leads to safer structures by maximizing load-bearing capacity while minimizing weight, which traditional designs may not achieve due to conservative safety factors and less precise material usage. Advanced finite element analysis integrated with topology optimization ensures rigorous safety validation beyond conventional design assumptions, improving performance under dynamic and unexpected loads.
Practical Applications in Mechanical Engineering
Topology optimization enables engineers to create lightweight, high-strength components by distributing material efficiently based on load conditions, which reduces weight and improves performance in aerospace, automotive, and civil engineering sectors. Traditional design methods rely on predefined shapes and empirical rules, often resulting in over-engineered components with excess material and suboptimal performance. Practical applications in mechanical engineering benefit from topology optimization through enhanced fuel efficiency, reduced manufacturing costs, and improved structural integrity.
Future Trends and Industry Adoption
Topology optimization leverages advanced algorithms and computational power to create lightweight, high-performance structures by optimizing material distribution, contrasting traditional design's reliance on heuristic and experience-based methods. Future trends indicate increasing integration of AI and machine learning to enhance design efficiency, enabling real-time iterative improvements and more complex geometries tailored for additive manufacturing. Industry adoption is accelerating in aerospace, automotive, and biomedical sectors due to benefits in cost reduction, sustainability, and performance, driving a paradigm shift towards data-driven design processes.
Design space discretization
Topology optimization uses fine-grained design space discretization for material distribution, enabling innovative lightweight structures compared to the coarser, predefined geometry constraints typical in traditional design methods.
Material distribution
Topology optimization maximizes structural efficiency by strategically distributing material within a design space, reducing weight compared to traditional design methods that rely on predetermined shapes and uniform material allocation.
Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
Topology optimization leverages Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to systematically remove inefficient material and improve structural performance, whereas traditional design relies on heuristic methods and FEA primarily for validation rather than iterative refinement.
Compliance minimization
Topology optimization minimizes compliance by optimally distributing material within a given design space, achieving higher structural stiffness and efficiency compared to traditional design methods that rely on predefined shapes and dimensions.
Shape optimization
Topology optimization enables more efficient shape optimization by systematically redistributing material within a design space, outperforming traditional design methods that rely on predefined geometries and heuristic adjustments.
Additive manufacturing compatibility
Topology optimization enhances additive manufacturing compatibility by enabling lightweight, complex geometries unachievable with traditional design methods that rely on simpler, subtractive processes.
Stress concentration zones
Topology optimization significantly reduces stress concentration zones compared to traditional design by strategically distributing material to enhance structural performance and durability.
Bionic structure adaptation
Topology optimization enables bionic structure adaptation by mimicking natural forms for superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional design methods that rely on fixed geometric constraints.
Parametric modeling
Topology optimization significantly enhances parametric modeling by automatically generating efficient material layouts based on performance criteria, whereas traditional design relies on designer intuition and predefined parameters to create initial geometries.
Structural mass efficiency
Topology optimization significantly improves structural mass efficiency by strategically distributing material only where necessary, unlike traditional design methods that often rely on uniform material distribution and conservative safety factors.
Topology optimization vs Traditional design Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com