Green solvents offer environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional solvents by reducing toxicity, volatility, and persistence in ecosystems. These solvents are typically derived from renewable resources and promote safer chemical processes with lower emissions and waste generation. Implementing green solvents enhances sustainability in chemical engineering while maintaining high performance in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
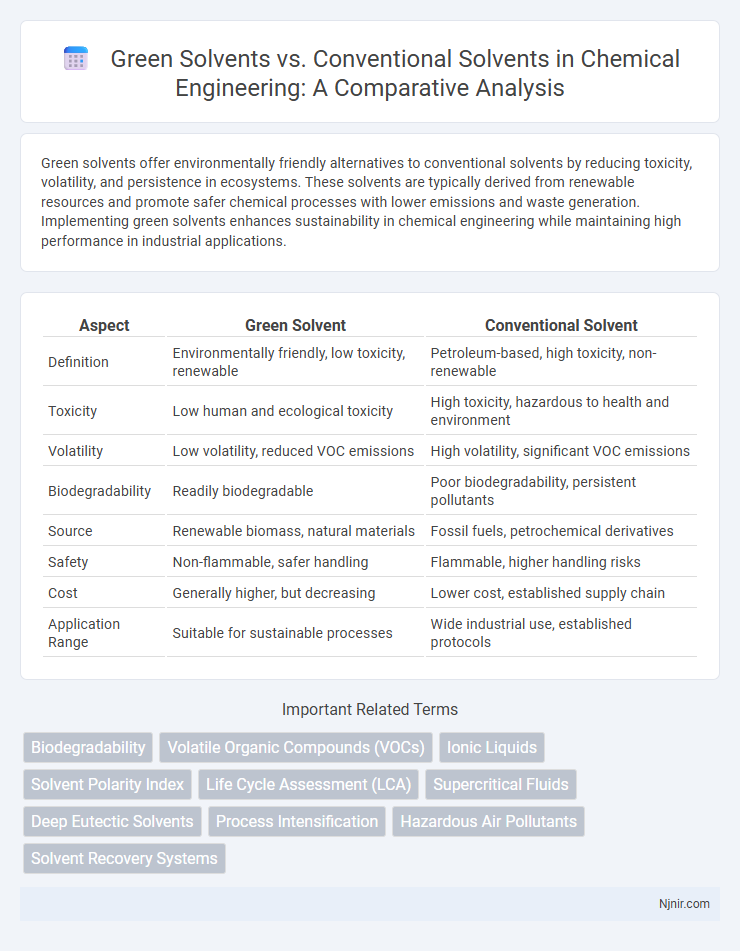
| Aspect | Green Solvent | Conventional Solvent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Environmentally friendly, low toxicity, renewable | Petroleum-based, high toxicity, non-renewable |
| Toxicity | Low human and ecological toxicity | High toxicity, hazardous to health and environment |
| Volatility | Low volatility, reduced VOC emissions | High volatility, significant VOC emissions |
| Biodegradability | Readily biodegradable | Poor biodegradability, persistent pollutants |
| Source | Renewable biomass, natural materials | Fossil fuels, petrochemical derivatives |
| Safety | Non-flammable, safer handling | Flammable, higher handling risks |
| Cost | Generally higher, but decreasing | Lower cost, established supply chain |
| Application Range | Suitable for sustainable processes | Wide industrial use, established protocols |
Introduction to Green and Conventional Solvents
Green solvents are derived from renewable resources and exhibit low toxicity, biodegradability, and minimal environmental impact compared to conventional solvents, which are predominantly petrochemical-based and often associated with high volatility and hazardous effects. Conventional solvents such as benzene, toluene, and acetone are widely used for their effectiveness but pose significant health risks and sustainability concerns. Advances in green chemistry promote solvents like water, supercritical CO2, and bio-based solvents to reduce ecological footprint and enhance safety in industrial and laboratory applications.
Environmental Impact of Solvent Choices
Green solvents significantly reduce environmental impact by minimizing toxic emissions, biodegrading rapidly, and lowering volatile organic compound (VOC) levels compared to conventional solvents. Conventional solvents often contribute to air and water pollution, persistence in ecosystems, and harmful health effects due to their non-biodegradable and hazardous chemical nature. Selecting green solvents supports sustainable manufacturing processes, reducing ecological footprint and promoting safer waste management practices.
Chemical Properties and Performance Comparison
Green solvents, often derived from bio-based or renewable sources, exhibit lower toxicity, reduced volatility, and enhanced biodegradability compared to conventional solvents like benzene or toluene. Their chemical properties, such as polarity and solvent power, are tailored to improve solubility and selectivity while minimizing environmental impact and health risks. Performance comparison reveals green solvents maintain comparable or superior efficiency in applications like extraction and cleaning, with the added advantage of decreased flammability and sustainable lifecycle profiles.
Economic Considerations in Solvent Selection
Green solvents often reduce overall costs by minimizing waste disposal fees and regulatory compliance expenses compared to conventional solvents, which typically incur higher environmental and health-related costs. Investment in green solvent technology can improve operational efficiency and long-term savings despite potentially higher upfront prices. Economic considerations increasingly favor green solvents due to evolving regulations, market demand for sustainable products, and potential tax incentives.
Safety and Health Aspects
Green solvents, derived from renewable resources and exhibiting low toxicity, significantly reduce health risks associated with chemical exposure compared to conventional solvents, which often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) linked to respiratory issues and long-term chronic effects. Their lower volatility minimizes inhalation hazards, while many green solvents are biodegradable and less flammable, enhancing workplace safety. Regulatory bodies increasingly favor green solvents for compliance with stringent health and environmental standards, promoting safer industrial practices and reducing occupational illness.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Green solvents offer significant advantages over conventional solvents in regulatory and compliance contexts due to their reduced toxicity, biodegradability, and lower environmental impact, which align with increasingly stringent global chemical safety regulations like REACH and TSCA. Conventional solvents often face regulatory restrictions, including limits on volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs), leading to higher compliance costs and potential liabilities. Industries transitioning to green solvents benefit from streamlined regulatory approval processes and improved adherence to workplace safety standards, facilitating sustainable manufacturing practices.
Applications in Chemical Processes
Green solvents, including bio-based solvents and supercritical fluids, are increasingly applied in chemical processes for sustainable extraction, catalysis, and reaction media, reducing environmental impact and toxicity compared to conventional solvents like hydrocarbons and chlorinated compounds. Their use enhances process efficiency in pharmaceuticals, polymer synthesis, and agrochemical production by minimizing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and facilitating safer waste disposal. Conventional solvents remain prevalent due to cost-effectiveness and established protocols but face regulatory pressures driving industries toward greener alternatives for cleaner production and compliance.
Advances in Green Solvent Technologies
Advances in green solvent technologies focus on replacing hazardous traditional solvents with environmentally friendly alternatives such as supercritical fluids, bio-based solvents, and ionic liquids that reduce toxicity and improve sustainability. These innovations enhance chemical processes by offering lower volatility, higher biodegradability, and reduced environmental impact while maintaining or improving solvent performance. Research efforts prioritize developing green solvents that enable energy-efficient reactions and waste minimization across various industries including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and manufacturing.
Challenges in Replacing Conventional Solvents
Green solvents face significant challenges in replacing conventional solvents due to differences in solvency power and process compatibility. Many green solvents lack the broad-spectrum effectiveness and established industrial infrastructure that conventional solvents possess. Scale-up difficulties and higher costs further limit the widespread adoption of green solvents in various chemical manufacturing processes.
Future Trends and Opportunities in Green Solvent Adoption
Green solvent adoption is rapidly advancing due to increasing environmental regulations and growing demand for sustainable industrial processes. Innovations in bio-based solvents and biodegradable formulations are creating new market opportunities while reducing toxic emissions and hazardous waste. Investment in green chemistry research and circular economy principles is expected to drive the future growth and scalability of eco-friendly solvent technologies.
Biodegradability
Green solvents exhibit significantly higher biodegradability rates than conventional solvents, reducing environmental toxicity and enhancing sustainability in industrial applications.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Green solvents significantly reduce Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) emissions compared to conventional solvents, enhancing air quality and minimizing environmental and health risks.
Ionic Liquids
Ionic liquids, as green solvents, offer non-volatile, recyclable, and tunable properties that significantly reduce environmental impact compared to conventional volatile organic solvents.
Solvent Polarity Index
Green solvents generally exhibit lower solvent polarity indexes compared to conventional solvents, enhancing environmental safety and reducing toxicity while maintaining effective solvation properties.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) reveals that green solvents significantly reduce environmental impact and resource consumption compared to conventional solvents throughout production, usage, and disposal stages.
Supercritical Fluids
Supercritical fluids, as green solvents, offer superior environmental benefits and enhanced solubility compared to conventional solvents, reducing toxicity and waste in chemical processes.
Deep Eutectic Solvents
Deep eutectic solvents (DES) offer a sustainable and non-toxic alternative to conventional solvents, exhibiting superior biodegradability, low volatility, and tunable physicochemical properties ideal for green chemistry applications.
Process Intensification
Green solvents enhance process intensification by reducing environmental impact and improving reaction efficiency compared to conventional solvents.
Hazardous Air Pollutants
Green solvents significantly reduce hazardous air pollutant emissions compared to conventional solvents, promoting safer air quality and environmental sustainability.
Solvent Recovery Systems
Green solvent recovery systems achieve higher efficiency and lower environmental impact than conventional solvent recovery systems by utilizing advanced membrane technology and energy-efficient distillation processes.
Green solvent vs Conventional solvent Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com