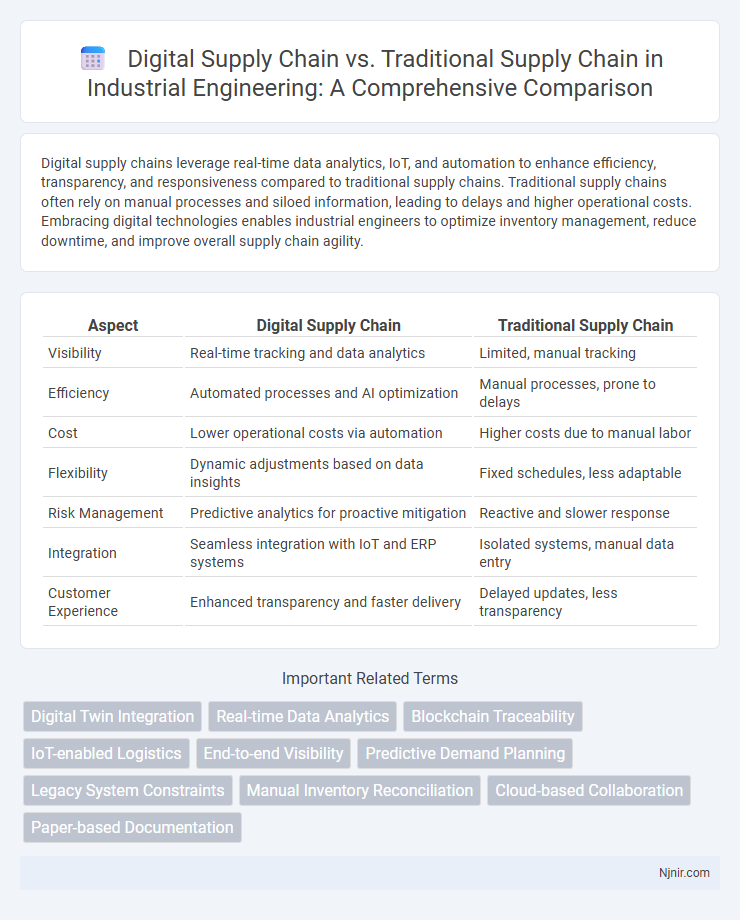
Digital supply chains leverage real-time data analytics, IoT, and automation to enhance efficiency, transparency, and responsiveness compared to traditional supply chains. Traditional supply chains often rely on manual processes and siloed information, leading to delays and higher operational costs. Embracing digital technologies enables industrial engineers to optimize inventory management, reduce downtime, and improve overall supply chain agility.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Digital Supply Chain | Traditional Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Real-time tracking and data analytics | Limited, manual tracking |
| Efficiency | Automated processes and AI optimization | Manual processes, prone to delays |
| Cost | Lower operational costs via automation | Higher costs due to manual labor |
| Flexibility | Dynamic adjustments based on data insights | Fixed schedules, less adaptable |
| Risk Management | Predictive analytics for proactive mitigation | Reactive and slower response |
| Integration | Seamless integration with IoT and ERP systems | Isolated systems, manual data entry |
| Customer Experience | Enhanced transparency and faster delivery | Delayed updates, less transparency |
Overview of Digital vs Traditional Supply Chains
Digital supply chains leverage advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain to enhance real-time data visibility, predictive analytics, and automation across procurement, production, and logistics. Traditional supply chains rely heavily on manual processes, paper-based documentation, and limited data integration, leading to slower response times and reduced flexibility. The digital model prioritizes agility, transparency, and efficiency, transforming how businesses manage inventory, demand forecasting, and supplier collaboration.
Key Technologies in Digital Supply Chains
Key technologies in digital supply chains include the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and advanced analytics, which enable real-time data tracking, predictive maintenance, and enhanced decision-making. Digital supply chains leverage cloud computing and automation tools such as robotic process automation (RPA) to streamline operations and increase responsiveness. These technologies dramatically improve visibility, efficiency, and agility compared to traditional supply chains, which rely heavily on manual processes and disconnected systems.
Process Flow: Digital vs Traditional Approaches
Digital supply chains utilize real-time data analytics, automation, and cloud computing to streamline process flow, enabling faster decision-making and enhanced responsiveness. Traditional supply chains rely on manual tracking, paper-based documentation, and sequential workflows, often resulting in longer lead times and reduced visibility. Integration of IoT sensors and AI in digital supply chains optimizes inventory management, demand forecasting, and supplier collaboration compared to the reactive nature of traditional approaches.
Data Management and Analytics in Supply Chains
Digital supply chains leverage advanced data management systems and real-time analytics to optimize inventory levels, forecast demand accurately, and enhance overall operational efficiency. In contrast, traditional supply chains rely on manual data entry and periodic reporting, which often leads to delays and less precise decision-making. The integration of AI-driven analytics and IoT sensors in digital supply chains enables continuous monitoring and predictive insights, transforming supply chain responsiveness and agility.
Cost Efficiency Comparison
Digital supply chains leverage advanced analytics, IoT sensors, and real-time data visibility, significantly reducing operational costs by minimizing inventory holding and streamlining logistics. In contrast, traditional supply chains often face higher expenses due to manual processes, delayed information flow, and inefficient resource allocation. Cost efficiency in digital supply chains improves through automated demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, and enhanced collaboration among stakeholders, resulting in overall lower total supply chain costs.
Impact on Supply Chain Visibility
Digital supply chains enhance supply chain visibility by leveraging real-time data analytics, IoT sensors, and cloud computing to provide end-to-end transparency across all stages of production and distribution. Traditional supply chains rely on manual processes and limited historical data, resulting in slower response times and less accurate insights into inventory levels, shipment status, and demand fluctuations. Advanced digital platforms enable proactive decision-making and risk management by offering dynamic, data-driven insights that transform supply chain operations.
Flexibility and Responsiveness Analysis
Digital supply chains leverage advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and real-time analytics to enhance flexibility by enabling dynamic resource allocation and rapid adaptation to demand fluctuations. Traditional supply chains often struggle with slower response times due to manual processes and limited data visibility, resulting in reduced responsiveness to market changes. Enhanced digital integration improves decision-making speed and accuracy, allowing businesses to better anticipate disruptions and meet customer demands efficiently.
Integration with Industry 4.0
Digital supply chains leverage Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain to achieve real-time data integration, enhancing visibility and predictive analytics across the entire value network. Traditional supply chains rely on manual processes and fragmented systems, resulting in slower response times and limited end-to-end integration. The shift to digital supply chains enables seamless connectivity between manufacturing, logistics, and customer demand, driving efficiency and agility in dynamic market environments.
Risk Management and Security Challenges
Digital supply chains leverage real-time data analytics and IoT integration to identify and mitigate risks faster than traditional supply chains, enhancing predictive risk management and resilience against disruptions. Traditional supply chains often rely on manual processes and fragmented information, increasing vulnerability to security breaches and delayed responses to potential threats. Cybersecurity challenges in digital supply chains include data privacy concerns and system hacking, requiring robust encryption and continuous monitoring to safeguard against cyber-attacks.
Future Trends in Supply Chain Evolution
Digital supply chains leverage AI, IoT, and blockchain to enhance transparency, agility, and real-time decision-making, outperforming traditional supply chains reliant on manual processes and static data. Future trends include increased automation through robotics, predictive analytics for demand forecasting, and integration of edge computing to optimize supply chain responsiveness. The shift towards sustainability and resilient networks driven by digital technologies will define the next era of supply chain evolution.
Digital Twin Integration
Digital supply chains leverage digital twin integration to enhance real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and operational efficiency, unlike traditional supply chains that rely on static, manual processes.
Real-time Data Analytics
Digital supply chains leverage real-time data analytics to enhance visibility, optimize inventory management, and accelerate decision-making, unlike traditional supply chains that rely on delayed, manual data processing.
Blockchain Traceability
Blockchain traceability in digital supply chains enhances transparency, reduces fraud, and improves efficiency compared to traditional supply chains lacking real-time, immutable data records.
IoT-enabled Logistics
IoT-enabled logistics in digital supply chains enhances real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, and automated inventory management, significantly outperforming traditional supply chains in efficiency and transparency.
End-to-end Visibility
Digital supply chains provide enhanced end-to-end visibility through real-time data integration and advanced analytics, unlike traditional supply chains that rely on limited, fragmented information flows.
Predictive Demand Planning
Digital supply chains leverage advanced predictive demand planning using AI and big data analytics to enhance accuracy and responsiveness compared to traditional supply chains relying on historical data and manual forecasting.
Legacy System Constraints
Legacy system constraints in traditional supply chains limit data integration and real-time visibility, whereas digital supply chains leverage advanced technologies for seamless connectivity and enhanced operational efficiency.
Manual Inventory Reconciliation
Digital supply chains automate inventory reconciliation using real-time data integration, significantly reducing errors and time compared to the manual, error-prone processes of traditional supply chains.
Cloud-based Collaboration
Cloud-based collaboration in digital supply chains enhances real-time data sharing, improves transparency, and accelerates decision-making compared to traditional supply chains reliant on manual processes and siloed information.
Paper-based Documentation
Digital supply chains eliminate inefficiencies of paper-based documentation found in traditional supply chains by automating data capture, enhancing real-time tracking, and improving accuracy.
Digital supply chain vs Traditional supply chain Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com