Ergonomics in industrial engineering focuses on designing workplaces and systems to optimize human well-being and overall system performance, emphasizing interaction between workers and their environment. Anthropometrics provides the crucial data on human body measurements and physical variations, enabling ergonomic designs tailored to diverse user populations. Combining ergonomics with anthropometric data ensures workplaces reduce injury risks while enhancing comfort, efficiency, and productivity.
Table of Comparison
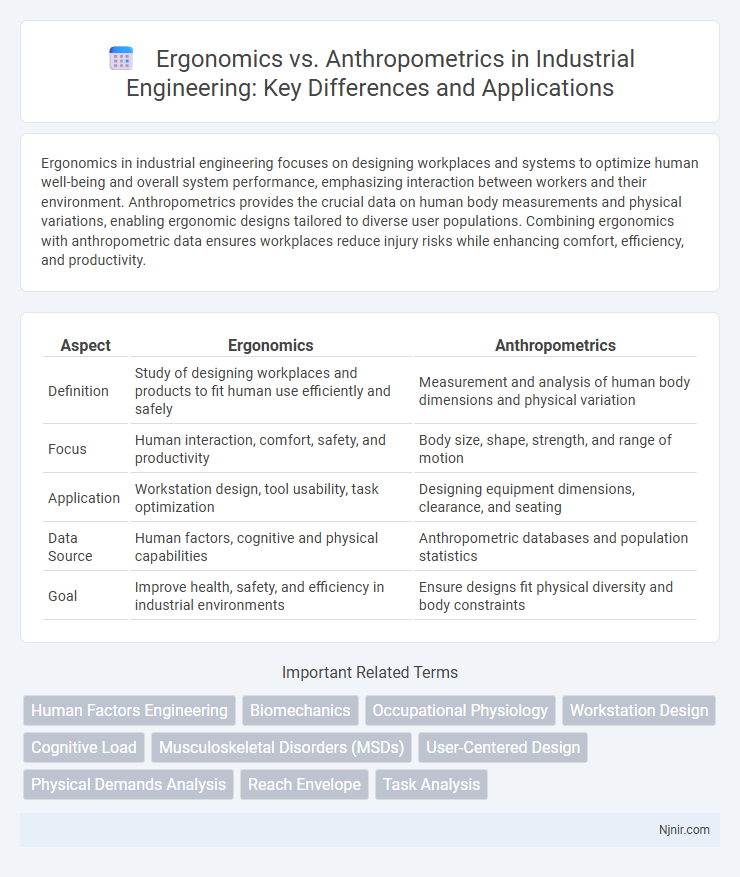
| Aspect | Ergonomics | Anthropometrics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of designing workplaces and products to fit human use efficiently and safely | Measurement and analysis of human body dimensions and physical variation |
| Focus | Human interaction, comfort, safety, and productivity | Body size, shape, strength, and range of motion |
| Application | Workstation design, tool usability, task optimization | Designing equipment dimensions, clearance, and seating |
| Data Source | Human factors, cognitive and physical capabilities | Anthropometric databases and population statistics |
| Goal | Improve health, safety, and efficiency in industrial environments | Ensure designs fit physical diversity and body constraints |
Introduction to Ergonomics and Anthropometrics
Ergonomics studies designing tools and environments to optimize human well-being and overall system performance, focusing on cognitive, physical, and organizational factors. Anthropometrics specifically deals with measuring human body dimensions to tailor products, workspaces, and equipment for various populations. These disciplines overlap in creating user-centered solutions that enhance comfort, efficiency, and safety by addressing human variability.
Defining Ergonomics in Industrial Engineering
Ergonomics in industrial engineering focuses on designing work environments and systems that optimize human well-being and overall system performance. It integrates principles from anatomy, physiology, and psychology to enhance safety, comfort, and productivity. Anthropometrics specifically provides the quantitative measurements of human body dimensions used to tailor tools, workstations, and equipment in ergonomic design.
Understanding Anthropometrics and Its Importance
Anthropometrics involves the systematic measurement of the human body's physical dimensions, essential for designing tools, workspaces, and products that fit diverse user populations. Understanding anthropometric data ensures safety, comfort, and efficiency by accommodating variations in size, strength, and reach among individuals. This data-driven approach minimizes physical strain and enhances overall functionality in ergonomic design.
Key Differences Between Ergonomics and Anthropometrics
Ergonomics focuses on designing tools, systems, and environments to optimize human well-being and overall system performance, while anthropometrics deals with the measurement and analysis of human body dimensions and physical variations. Key differences include ergonomics encompassing cognitive and organizational factors beyond physical dimensions, whereas anthropometrics strictly quantifies body size and shape for design specifications. Ergonomics applies these measurements to improve usability and reduce strain, whereas anthropometrics provides the raw data essential for ergonomic design processes.
Applications of Ergonomics in the Workplace
Ergonomics in the workplace enhances employee productivity and safety by designing tools, workstations, and tasks that align with human capabilities and limitations. It applies principles of biomechanics, psychology, and environmental design to reduce strain, prevent injuries, and improve comfort. Integrating ergonomic solutions lowers absenteeism, increases job satisfaction, and optimizes overall organizational performance.
Role of Anthropometrics in Product and Workplace Design
Anthropometrics plays a crucial role in product and workplace design by providing precise measurements of human body dimensions, which ensure that designs accommodate a wide range of users comfortably and safely. Incorporating anthropometric data helps optimize the fit, reach, and interaction between users and products or work environments, reducing strain and enhancing usability. This data-driven approach leads to improved ergonomics, minimizing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and boosting overall productivity.
Integrating Ergonomics and Anthropometrics for Optimal Design
Integrating ergonomics and anthropometrics in design ensures products and workspaces accommodate human physical variations, enhancing comfort and efficiency. Ergonomics focuses on optimizing interactions between people and systems, while anthropometrics provides quantitative data on human body dimensions to inform design parameters. Combining these disciplines leads to user-centered solutions that reduce injury risk and improve overall performance.
Benefits of Ergonomics for Worker Health and Productivity
Ergonomics enhances worker health and productivity by designing work environments that reduce physical strain and prevent musculoskeletal disorders, leading to fewer injuries and absenteeism. Applying ergonomic principles optimizes workstation layout, tool design, and workflow, which increases comfort, efficiency, and precision during tasks. Improved ergonomics also supports cognitive function and reduces fatigue, enabling sustained focus and higher overall job performance.
Anthropometric Data Collection and Analysis Techniques
Anthropometric data collection involves precise measurement of human body dimensions, using tools such as calipers, 3D body scanners, and photogrammetry to capture static and dynamic body information. Analysis techniques include statistical methods to create percentile ranges and ergonomic models that accommodate diverse populations in product design and workspace layout. Accurate anthropometric data supports ergonomic solutions by ensuring designs meet physical requirements and improve comfort, safety, and efficiency.
Future Trends in Ergonomics and Anthropometrics in Industry
Future trends in ergonomics and anthropometrics in industry emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as AI-driven ergonomic assessments and real-time data collection through wearable sensors. Innovations in 3D body scanning and digital twin modeling enable personalized workplace designs that enhance comfort, safety, and productivity. The adoption of machine learning algorithms for predictive analysis supports dynamic adjustments tailored to individual workers' ergonomic needs, driving a shift toward more adaptive and inclusive industrial environments.
Human Factors Engineering
Human Factors Engineering integrates ergonomics and anthropometrics to optimize workplace design by aligning equipment and environments with human physical dimensions and cognitive capabilities.
Biomechanics
Biomechanics integrates ergonomic principles with anthropometric data to optimize human movement efficiency and reduce injury risk in workplace design.
Occupational Physiology
Occupational physiology integrates ergonomics and anthropometrics to optimize workplace design by analyzing human body measurements and physiological responses for improved safety and productivity.
Workstation Design
Ergonomics optimizes workstation design by enhancing human comfort and efficiency, while anthropometrics provides precise body measurements to tailor workspaces for diverse user dimensions.
Cognitive Load
Ergonomics addresses cognitive load by optimizing human-system interactions to reduce mental effort, while anthropometrics provides physical data that indirectly influences cognitive load through ergonomic design adjustments.
Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)
Ergonomics integrates anthropometric data to design workplaces that minimize Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) by optimizing human-machine interactions and reducing physical strain.
User-Centered Design
User-centered design integrates ergonomics to optimize comfort and efficiency by considering anthropometric data to tailor products to users' physical dimensions.
Physical Demands Analysis
Physical Demands Analysis utilizes ergonomic principles to assess task requirements while incorporating anthropometric data to tailor evaluations based on human body dimensions and capabilities.
Reach Envelope
Ergonomics focuses on designing workspaces for user comfort and efficiency, while anthropometrics provides precise body measurements used to define the reach envelope for optimized human-machine interaction.
Task Analysis
Task analysis in ergonomics emphasizes optimizing human interaction with work environments, while anthropometrics focuses on measuring physical body dimensions to design equipment that fits user capabilities.
Ergonomics vs Anthropometrics Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com