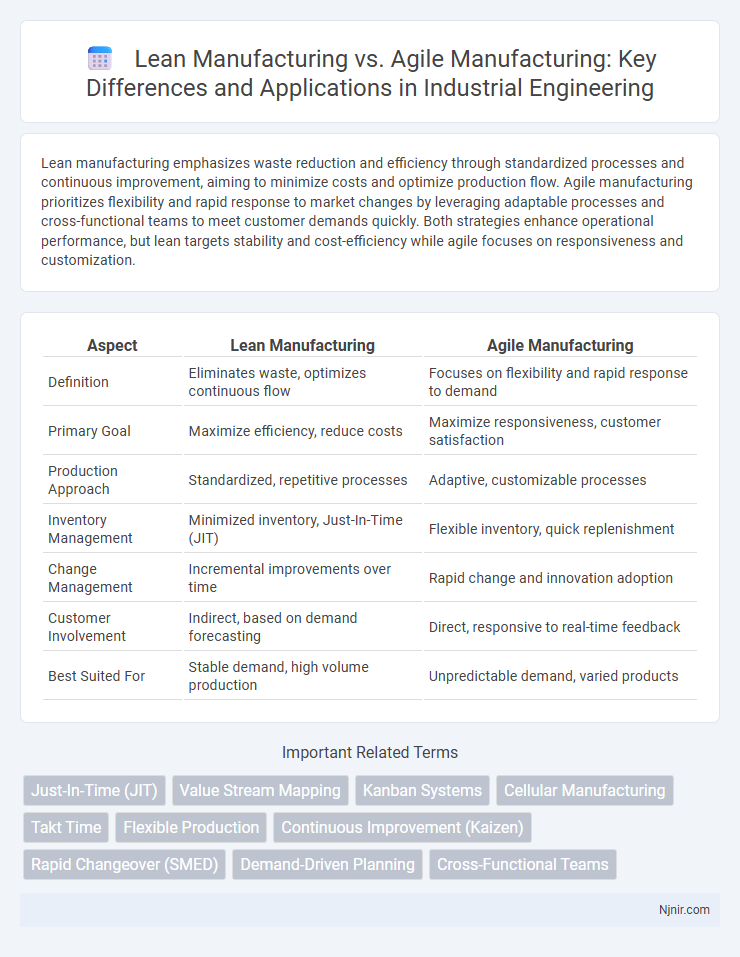
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and efficiency through standardized processes and continuous improvement, aiming to minimize costs and optimize production flow. Agile manufacturing prioritizes flexibility and rapid response to market changes by leveraging adaptable processes and cross-functional teams to meet customer demands quickly. Both strategies enhance operational performance, but lean targets stability and cost-efficiency while agile focuses on responsiveness and customization.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lean Manufacturing | Agile Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Eliminates waste, optimizes continuous flow | Focuses on flexibility and rapid response to demand |
| Primary Goal | Maximize efficiency, reduce costs | Maximize responsiveness, customer satisfaction |
| Production Approach | Standardized, repetitive processes | Adaptive, customizable processes |
| Inventory Management | Minimized inventory, Just-In-Time (JIT) | Flexible inventory, quick replenishment |
| Change Management | Incremental improvements over time | Rapid change and innovation adoption |
| Customer Involvement | Indirect, based on demand forecasting | Direct, responsive to real-time feedback |
| Best Suited For | Stable demand, high volume production | Unpredictable demand, varied products |
Introduction to Lean and Agile Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and continuous improvement by streamlining processes to maximize value and minimize resources. Agile manufacturing prioritizes flexibility and responsiveness, enabling rapid adaptation to market changes and customer demands through modular production and cross-functional teams. Both methodologies seek efficiency but differ in their strategic focus--Lean on stability and cost-efficiency, Agile on speed and customization.
Core Principles of Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing centers on eliminating waste, enhancing flow, and delivering value through continuous improvement and respect for people. Its core principles include defining value from the customer's perspective, mapping the value stream to identify and remove non-value-added activities, creating smooth workflow by leveling production, establishing pull systems to produce only what is needed, and pursuing perfection through relentless refinement. In contrast, Agile manufacturing emphasizes flexibility, rapid response to market changes, and cross-functional collaboration to quickly adapt to customer demands.
Core Principles of Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing centers on flexibility, rapid response to market changes, and customer-driven customization, emphasizing modular product designs and cross-functional teams. Core principles include adaptive planning, continuous improvement, and integration of innovative technologies to accelerate product development cycles. Unlike lean manufacturing's focus on waste reduction and efficiency, agile manufacturing prioritizes responsiveness and collaboration to meet evolving customer demands.
Key Differences: Lean vs Agile Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste elimination and process efficiency by streamlining operations and reducing non-value-added activities. Agile manufacturing focuses on flexibility and rapid responsiveness to market changes, enabling quick adaptation to customer demands and product variations. Key differences include Lean's priority on cost reduction and standardized workflows, while Agile prioritizes adaptability and speed in production.
Process Flow in Lean and Agile Approaches
Lean manufacturing emphasizes a streamlined process flow by eliminating waste and optimizing each step for efficiency, ensuring smooth and consistent production with minimal delays. Agile manufacturing focuses on flexible process flow, adapting quickly to changes in customer demand and market conditions through iterative cycles and rapid response mechanisms. Both approaches prioritize continuous improvement, but Lean targets stability and cost reduction, while Agile prioritizes responsiveness and adaptability.
Benefits and Limitations of Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing enhances operational efficiency by minimizing waste, improving product quality, and reducing production costs through continuous process improvement. Its limitations include inflexibility to sudden market changes and the potential for employee burnout due to high levels of standardization and demand for continuous performance. Agile manufacturing offers greater adaptability and responsiveness but may incur higher operational complexity and costs compared to lean methodologies.
Advantages and Challenges of Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing offers advantages such as rapid responsiveness to market changes, increased flexibility in production processes, and enhanced customer customization capabilities, allowing companies to quickly adapt to evolving demands. However, challenges include the need for significant investment in technology and skilled personnel, complexity in coordinating cross-functional teams, and potential difficulties in maintaining consistent quality due to frequent process adjustments. Despite these obstacles, agile manufacturing helps firms stay competitive by embracing innovation and minimizing lead times.
Industry Applications: When to Use Lean or Agile
Lean manufacturing excels in industries with predictable demand and repetitive processes, such as automotive or electronics production, where minimizing waste and optimizing efficiency are crucial. Agile manufacturing is better suited for dynamic markets like consumer electronics or fashion, where rapid responsiveness and flexibility to changing customer requirements drive success. Choosing between Lean and Agile depends on the industry's volatility, product customization needs, and supply chain complexity.
Integrating Lean and Agile Methodologies
Integrating Lean and Agile methodologies combines Lean manufacturing's emphasis on waste reduction, process efficiency, and continuous improvement with Agile manufacturing's flexibility, rapid response to market changes, and customer-focused adaptability. This integration allows companies to optimize production processes while maintaining the ability to pivot quickly in response to volatile demand or customization requirements. By leveraging Lean's value stream mapping alongside Agile's iterative planning cycles, manufacturers can achieve both operational excellence and enhanced responsiveness.
Future Trends in Manufacturing: Lean, Agile, or Hybrid?
Future trends in manufacturing indicate a growing convergence of Lean and Agile methodologies, with hybrid models gaining traction to balance efficiency and flexibility. Lean manufacturing continues to optimize processes by minimizing waste and improving quality, while Agile manufacturing emphasizes rapid adaptation to market changes and customization. Emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and advanced automation are enabling manufacturers to integrate Lean's process stability with Agile's responsiveness, fostering a more resilient and dynamic production environment.
Just-In-Time (JIT)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes Just-In-Time (JIT) to eliminate waste and streamline production flow, while Agile manufacturing uses JIT to enhance flexibility and rapidly respond to market changes.
Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping enhances Lean manufacturing by identifying waste and streamlining processes, while in Agile manufacturing it supports rapid adaptation and continuous value delivery through iterative workflow visualization.
Kanban Systems
Kanban systems in Lean manufacturing emphasize continuous flow and waste reduction, whereas in Agile manufacturing they prioritize flexibility and rapid response to customer demands.
Cellular Manufacturing
Cellular manufacturing enhances both lean and agile manufacturing by organizing workstations into dedicated cells that minimize waste, reduce lead times, and increase responsiveness to customer demand.
Takt Time
Lean manufacturing optimizes Takt Time to synchronize production pace with customer demand, while Agile manufacturing adapts Takt Time flexibly to rapidly respond to market changes and variability.
Flexible Production
Agile manufacturing emphasizes flexible production systems that quickly adapt to changing customer demands, whereas Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and improving efficiency within stable production processes.
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes Continuous Improvement (Kaizen) through waste reduction and process standardization, while Agile manufacturing applies Kaizen to enhance flexibility and rapid response to market changes.
Rapid Changeover (SMED)
Lean manufacturing's Rapid Changeover (SMED) reduces setup times through standardized steps, while Agile manufacturing prioritizes SMED for flexibility and swift adaptation to customer demands.
Demand-Driven Planning
Demand-driven planning in Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and efficiency through pull-based workflows, while Agile manufacturing prioritizes rapid responsiveness and flexibility to fluctuating customer demands.
Cross-Functional Teams
Cross-functional teams in Agile manufacturing enhance flexibility and rapid problem-solving by integrating diverse skills, whereas Lean manufacturing uses them primarily to streamline workflows and eliminate waste for continuous improvement.
Lean manufacturing vs Agile manufacturing Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com