Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) provide comprehensive production management by tracking and documenting the transformation of raw materials to finished goods, optimizing workflow, and ensuring quality control in real time. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) focuses on monitoring and controlling industrial processes through data acquisition from sensors and machinery, ensuring operational continuity and system safety. Integrating MES with SCADA enhances manufacturing efficiency by combining production execution with real-time process visualization and control.
Table of Comparison
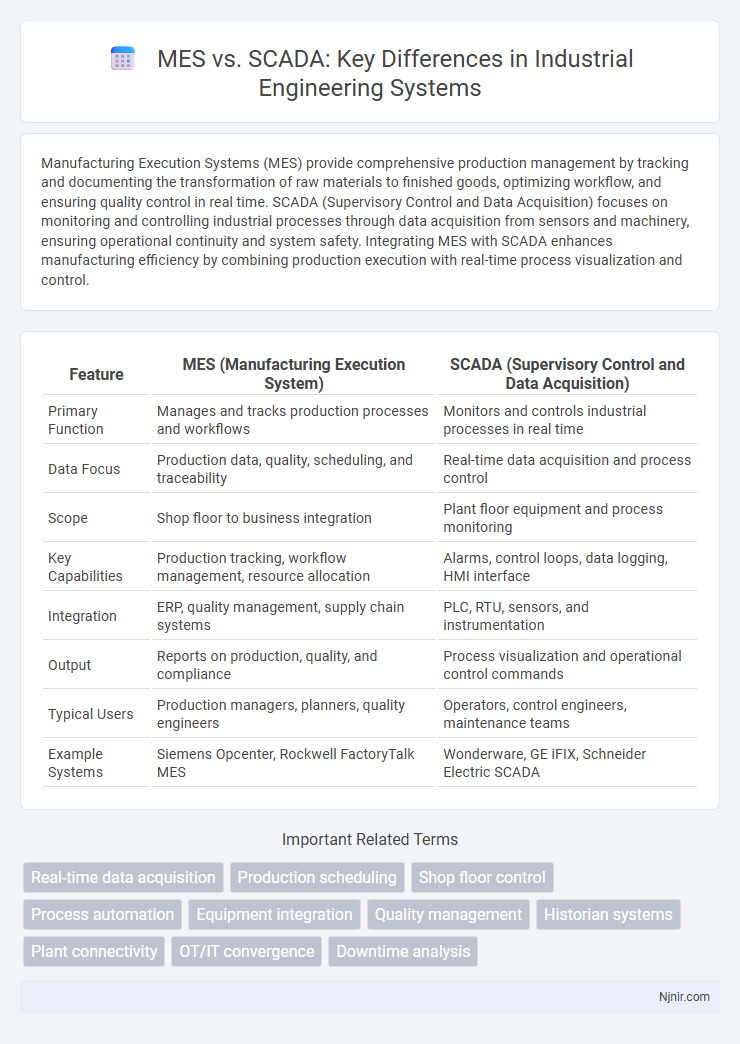
| Feature | MES (Manufacturing Execution System) | SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages and tracks production processes and workflows | Monitors and controls industrial processes in real time |
| Data Focus | Production data, quality, scheduling, and traceability | Real-time data acquisition and process control |
| Scope | Shop floor to business integration | Plant floor equipment and process monitoring |
| Key Capabilities | Production tracking, workflow management, resource allocation | Alarms, control loops, data logging, HMI interface |
| Integration | ERP, quality management, supply chain systems | PLC, RTU, sensors, and instrumentation |
| Output | Reports on production, quality, and compliance | Process visualization and operational control commands |
| Typical Users | Production managers, planners, quality engineers | Operators, control engineers, maintenance teams |
| Example Systems | Siemens Opcenter, Rockwell FactoryTalk MES | Wonderware, GE iFIX, Schneider Electric SCADA |
Introduction to MES and SCADA in Industrial Engineering
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) streamlines production processes by providing real-time monitoring, scheduling, and quality management across the shop floor, enhancing operational efficiency in industrial engineering. Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) primarily focuses on data acquisition and automated control of industrial equipment, enabling centralized monitoring and control of various physical processes. Integrating MES with SCADA bridges the gap between high-level production management and low-level process control, optimizing manufacturing operations through comprehensive data flow and decision support.
Core Functions of MES
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) core functions include real-time production monitoring, workflow and process management, and data collection for performance analysis. MES provides detailed tracking of work orders, resource allocation, and quality control, enabling optimized production scheduling and traceability from raw materials to finished goods. Unlike SCADA, which primarily focuses on real-time process control and equipment monitoring, MES integrates shop floor operations with enterprise systems for comprehensive manufacturing execution and decision support.
Core Functions of SCADA
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems primarily focus on real-time monitoring, data collection, and control of industrial processes through centralized interfaces that visualize sensor data and alarms. Core functions include acquiring precise field data, remote equipment control, system diagnostics, and trend analysis to ensure operational efficiency and fault detection. Unlike MES, which manages production workflows and scheduling, SCADA emphasizes process automation and immediate response to system conditions.
Key Differences Between MES and SCADA
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) primarily manages and monitors work-in-progress on the factory floor, focusing on production scheduling, quality control, and traceability, while SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) concentrates on real-time process monitoring and control of industrial equipment and infrastructure. MES integrates with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to optimize manufacturing operations, whereas SCADA interfaces with sensors and PLCs to gather data and provide immediate control feedback. The key difference lies in MES optimizing production workflows and business processes, while SCADA ensures operational reliability and real-time equipment supervision.
Integration of MES and SCADA Systems
Integration of MES and SCADA systems enhances real-time data exchange and process visibility, enabling seamless synchronization of production operations with plant control functions. MES captures detailed manufacturing data, while SCADA monitors and controls equipment status, together providing a comprehensive view of production performance and facilitating proactive decision-making. This integration supports improved scalability, reduced downtime, and optimized resource utilization across manufacturing workflows.
Advantages of MES for Manufacturing Operations
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) offers real-time production tracking and detailed process control that SCADA lacks, enabling manufacturers to optimize workflow and reduce downtime. MES integrates with enterprise systems for seamless data flow, improving traceability, quality management, and regulatory compliance across manufacturing operations. Its ability to provide granular insights into labor, equipment, and material usage significantly enhances decision-making and operational efficiency compared to SCADA's primary focus on supervisory control.
Benefits of SCADA in Industrial Automation
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) enhances industrial automation by providing real-time data monitoring, enabling quick detection and response to process anomalies. Its centralized control capabilities improve operational efficiency and reduce downtime through continuous data acquisition and system visualization. SCADA's scalability and integration with various hardware devices make it essential for large-scale, complex manufacturing environments seeking improved process control and asset management.
Challenges in Implementing MES and SCADA
Implementing MES (Manufacturing Execution System) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) faces challenges such as system integration with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) and operational technology (OT) infrastructures. Data synchronization between MES's production-centric processes and SCADA's real-time monitoring can cause complexities. Ensuring cybersecurity, managing large volumes of data, and achieving user training and adoption further complicate deployment in manufacturing environments.
MES vs. SCADA: Use Cases and Industry Applications
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) excels in real-time production management, quality control, and detailed scheduling across industries like automotive, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) specializes in real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, commonly applied in utilities, oil and gas, and water treatment plants. MES integrates deeper with production workflows to optimize manufacturing execution, while SCADA focuses on data acquisition and supervisory-level control for operational system stability.
Future Trends in MES and SCADA Technologies
Future trends in MES and SCADA technologies emphasize increased integration with Industrial IoT (IIoT) and advanced data analytics, enabling real-time decision-making and predictive maintenance. MES platforms are evolving to incorporate AI-driven process optimization and cloud-based scalability, enhancing production flexibility and responsiveness. SCADA systems are advancing with edge computing and cybersecurity improvements to support decentralized control and secure data transmission in complex industrial environments.
Real-time data acquisition
MES integrates real-time data acquisition with production scheduling and quality management, while SCADA primarily focuses on real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes.
Production scheduling
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) provides real-time production scheduling and detailed shop floor control, while SCADA primarily monitors and controls equipment without advanced scheduling capabilities.
Shop floor control
MES provides comprehensive real-time shop floor control by managing production workflows and quality data, while SCADA primarily monitors and controls equipment and processes at the operational level.
Process automation
MES enhances process automation by managing and optimizing production workflows and real-time manufacturing data, while SCADA primarily focuses on monitoring and controlling industrial equipment and processes at the supervisory level.
Equipment integration
MES integrates with equipment by providing real-time production scheduling and quality management, while SCADA focuses on direct control and monitoring of equipment status and process variables.
Quality management
MES enhances quality management by providing real-time production tracking, defect detection, and corrective action documentation, whereas SCADA focuses primarily on monitoring and controlling industrial processes without detailed quality oversight.
Historian systems
MES systems provide detailed production tracking and process optimization, while SCADA focuses on real-time control and data acquisition, with Historian systems in SCADA offering time-series data storage critical for operational analytics and MES integration.
Plant connectivity
MES provides comprehensive plant connectivity by integrating real-time production data and enterprise systems, while SCADA primarily focuses on monitoring and controlling equipment within the plant.
OT/IT convergence
MES integrates real-time production data and operational workflows at the OT/IT convergence to optimize manufacturing processes, while SCADA primarily monitors and controls industrial equipment and infrastructure.
Downtime analysis
MES provides detailed downtime analysis by tracking production workflows and machine statuses in real-time, whereas SCADA primarily monitors equipment performance and process control without in-depth downtime root cause analysis.
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) vs SCADA Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com