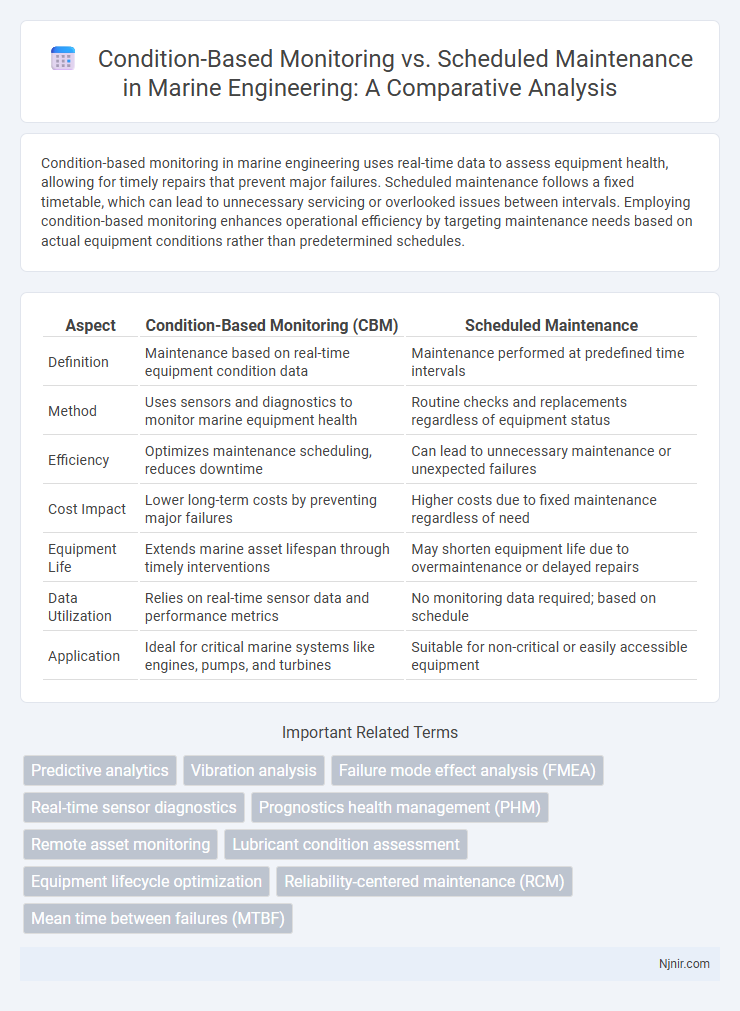
Condition-based monitoring in marine engineering uses real-time data to assess equipment health, allowing for timely repairs that prevent major failures. Scheduled maintenance follows a fixed timetable, which can lead to unnecessary servicing or overlooked issues between intervals. Employing condition-based monitoring enhances operational efficiency by targeting maintenance needs based on actual equipment conditions rather than predetermined schedules.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM) | Scheduled Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance based on real-time equipment condition data | Maintenance performed at predefined time intervals |
| Method | Uses sensors and diagnostics to monitor marine equipment health | Routine checks and replacements regardless of equipment status |
| Efficiency | Optimizes maintenance scheduling, reduces downtime | Can lead to unnecessary maintenance or unexpected failures |
| Cost Impact | Lower long-term costs by preventing major failures | Higher costs due to fixed maintenance regardless of need |
| Equipment Life | Extends marine asset lifespan through timely interventions | May shorten equipment life due to overmaintenance or delayed repairs |
| Data Utilization | Relies on real-time sensor data and performance metrics | No monitoring data required; based on schedule |
| Application | Ideal for critical marine systems like engines, pumps, and turbines | Suitable for non-critical or easily accessible equipment |
Introduction to Marine Maintenance Strategies
Condition-based monitoring leverages real-time data from sensors to assess the actual health of marine equipment, enabling timely interventions only when necessary. Scheduled maintenance relies on predetermined intervals, regardless of equipment condition, which can lead to unnecessary downtime or unexpected failures. Implementing condition-based monitoring in marine maintenance strategies enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and extends the lifespan of critical ship components.
Defining Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM)
Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM) leverages real-time data from sensors and advanced analytics to assess the actual state of equipment, enabling maintenance only when specific indicators reveal potential failures. This approach contrasts with scheduled maintenance, which relies on fixed time intervals regardless of equipment condition, often leading to unnecessary repairs or overlooked issues. By utilizing vibration analysis, temperature monitoring, and oil analysis, CBM enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime through predictive insights.
Overview of Scheduled Maintenance in Marine Engineering
Scheduled maintenance in marine engineering involves performing routine inspections, servicing, and repairs at predetermined intervals to ensure vessel safety and operational efficiency. This preventive approach relies on manufacturer recommendations and regulatory requirements to minimize unexpected failures and extend equipment lifespan. Regularly planned tasks include engine overhauls, lubrication, and hull inspections to maintain compliance with maritime standards.
Key Differences: CBM vs Scheduled Maintenance
Condition-based monitoring (CBM) uses real-time data from sensors to predict equipment failures and perform maintenance only when necessary, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. Scheduled maintenance relies on predetermined time intervals regardless of equipment condition, often leading to unnecessary maintenance or unexpected failures. CBM offers a proactive approach with improved asset utilization and cost savings compared to the reactive nature of scheduled maintenance.
Advantages of Condition-Based Monitoring for Marine Systems
Condition-based monitoring enhances marine system reliability by using real-time sensor data to detect early signs of wear and potential failures, reducing unplanned downtime. This predictive approach optimizes maintenance intervals, resulting in lower operational costs and extended equipment lifespan compared to traditional scheduled maintenance. Continuous monitoring also improves safety by allowing timely interventions based on actual system conditions rather than fixed schedules.
Limitations of Scheduled Maintenance Approaches
Scheduled maintenance relies on fixed intervals that may lead to unnecessary equipment downtime or unexpected failures due to its inability to account for real-time machine conditions. This approach often results in increased operational costs and inefficient resource allocation as maintenance tasks may be performed too early or too late. In contrast, condition-based monitoring uses sensor data and predictive analytics to optimize maintenance timing, reducing both risks and expenses.
Technological Requirements for Implementing CBM
Implementing condition-based monitoring (CBM) requires advanced sensor technology, real-time data acquisition systems, and robust analytics software to predict equipment failures accurately. Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) platforms and machine learning algorithms enhances CBM's efficiency by enabling continuous monitoring and automated decision-making. These technological elements contrast with scheduled maintenance, which relies on time-based intervals without real-time operational data or predictive insights.
Impact on Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Condition-based monitoring significantly enhances operational efficiency by providing real-time data that allows for targeted maintenance only when equipment shows signs of wear or failure. Scheduled maintenance often leads to unnecessary downtime and higher costs due to routine inspections and part replacements regardless of actual equipment condition. By minimizing unplanned outages and optimizing maintenance intervals, condition-based monitoring reduces labor, materials, and operational costs, driving substantial savings and maximizing asset utilization.
Case Studies: CBM and Scheduled Maintenance in Marine Vessels
Case studies in marine vessels highlight that condition-based monitoring (CBM) significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs by enabling real-time detection of equipment anomalies, unlike scheduled maintenance which often leads to unnecessary part replacements. CBM leverages sensors and data analytics to predict failures, enhancing vessel reliability and operational efficiency across navigation, propulsion, and auxiliary systems. Comparative analyses reveal that vessels employing CBM experience longer intervals between repairs and improved fuel consumption, demonstrating its superiority over traditional time-based maintenance strategies.
Future Trends in Marine Maintenance Practices
Condition-based monitoring leverages real-time sensor data and advanced analytics to predict equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance that minimizes downtime and extends asset life. Scheduled maintenance relies on fixed intervals, often leading to unnecessary servicing or unexpected breakdowns, making it a less efficient approach for modern marine vessels. Future trends in marine maintenance increasingly emphasize AI-driven condition monitoring, integrated IoT platforms, and digital twins to optimize reliability and operational efficiency in complex maritime environments.
Predictive analytics
Condition-based monitoring leverages predictive analytics to forecast equipment failures by analyzing real-time sensor data, enabling maintenance only when necessary compared to the fixed intervals of scheduled maintenance.
Vibration analysis
Vibration analysis in condition-based monitoring detects equipment faults early by continuously measuring vibrations, reducing unplanned downtime compared to time-based scheduled maintenance.
Failure mode effect analysis (FMEA)
Condition-based monitoring enhances Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) by providing real-time data to predict failures accurately, reducing unnecessary maintenance compared to scheduled maintenance.
Real-time sensor diagnostics
Condition-based monitoring leverages real-time sensor diagnostics to detect equipment anomalies instantly, optimizing maintenance schedules and reducing downtime compared to fixed scheduled maintenance.
Prognostics health management (PHM)
Prognostics Health Management (PHM) enhances Condition-based Monitoring by predicting equipment failures through real-time data analysis, offering a more precise and cost-effective alternative to traditional Scheduled Maintenance.
Remote asset monitoring
Remote asset monitoring enhances condition-based monitoring by providing real-time data and predictive insights, reducing downtime and costs compared to traditional scheduled maintenance.
Lubricant condition assessment
Condition-based monitoring of lubricant condition detects degradation and contamination in real-time, extending equipment life and reducing costs compared to scheduled maintenance intervals.
Equipment lifecycle optimization
Condition-based monitoring extends equipment lifecycle by enabling real-time performance analysis and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime compared to traditional scheduled maintenance.
Reliability-centered maintenance (RCM)
Condition-based monitoring enhances Reliability-centered Maintenance (RCM) by using real-time data to predict equipment failures, reducing unscheduled downtime compared to traditional scheduled maintenance.
Mean time between failures (MTBF)
Condition-based monitoring significantly extends Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) by detecting faults early, whereas scheduled maintenance follows fixed intervals that may not optimize MTBF.
Condition-based monitoring vs scheduled maintenance Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com