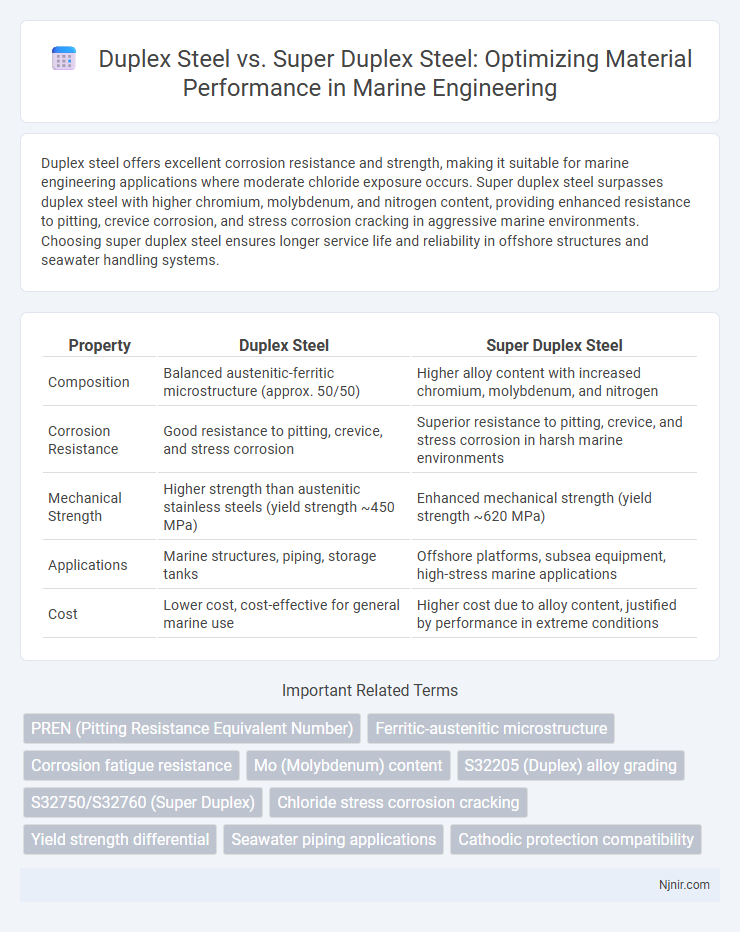
Duplex steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for marine engineering applications where moderate chloride exposure occurs. Super duplex steel surpasses duplex steel with higher chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen content, providing enhanced resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking in aggressive marine environments. Choosing super duplex steel ensures longer service life and reliability in offshore structures and seawater handling systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Duplex Steel | Super Duplex Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Balanced austenitic-ferritic microstructure (approx. 50/50) | Higher alloy content with increased chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good resistance to pitting, crevice, and stress corrosion | Superior resistance to pitting, crevice, and stress corrosion in harsh marine environments |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher strength than austenitic stainless steels (yield strength ~450 MPa) | Enhanced mechanical strength (yield strength ~620 MPa) |
| Applications | Marine structures, piping, storage tanks | Offshore platforms, subsea equipment, high-stress marine applications |
| Cost | Lower cost, cost-effective for general marine use | Higher cost due to alloy content, justified by performance in extreme conditions |
Introduction to Duplex and Super Duplex Steels
Duplex Steel is a stainless steel alloy known for its balanced microstructure of approximately 50% ferrite and 50% austenite, offering enhanced strength and corrosion resistance compared to standard austenitic stainless steels. Super Duplex Steel contains higher alloying elements, especially chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen, resulting in superior resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, making it ideal for aggressive environments. Both materials are widely used in the oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine industries due to their durability and performance under harsh conditions.
Chemical Composition Differences
Duplex steel typically contains 18-22% chromium, 4-6% nickel, and up to 3% molybdenum, whereas super duplex steel increases these levels, featuring 24-26% chromium, 6-8% nickel, and 3-5% molybdenum to enhance corrosion resistance. The higher molybdenum and chromium content in super duplex steel significantly improve its ability to withstand chloride-induced pitting and crevice corrosion compared to standard duplex grades. Nitrogen content is also elevated in super duplex steels, generally around 0.14-0.20%, which stabilizes the microstructure and contributes to higher strength and corrosion performance.
Microstructure Comparison
Duplex steel features a balanced microstructure of approximately 50% ferrite and 50% austenite, providing high strength and good corrosion resistance. Super duplex steel enhances this with a higher ferrite content (around 60-70%) and increased alloying elements such as chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen, resulting in superior resistance to pitting, stress corrosion cracking, and crevice corrosion. The refined microstructure of super duplex steel offers improved mechanical properties and enhanced durability in aggressive environments compared to standard duplex steel.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Ductility
Duplex steel exhibits a balanced combination of strength and ductility, with tensile strength typically ranging from 700 to 900 MPa and elongation around 25-30%. Super duplex steel offers significantly higher tensile strength, often exceeding 900 MPa, while maintaining comparable or slightly reduced ductility, generally around 20-25%. This enhanced mechanical performance in super duplex steel results from increased alloying elements such as chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen, providing superior resistance to stress corrosion cracking and improved overall toughness.
Corrosion Resistance in Marine Environments
Super Duplex Steel exhibits superior corrosion resistance in marine environments compared to Duplex Steel due to its higher chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen content, which enhances pitting and crevice corrosion resistance. The enhanced microstructure of Super Duplex Steel provides better resistance to stress corrosion cracking in aggressive chloride-containing seawater. This makes Super Duplex Steel the preferred material for offshore oil and gas applications requiring long-term durability against saltwater-induced corrosion.
Weldability and Fabrication Considerations
Duplex steel offers good weldability with lower heat input requirements, making it suitable for various fabrication processes, while super duplex steel demands more precise control during welding to maintain its enhanced corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Super duplex requires preheating and post-weld heat treatment to prevent cracking and phase imbalance, whereas duplex steel is more forgiving in standard fabrication environments. Selecting the appropriate welding technique and parameters is critical to preserving the integrity and performance of both duplex and super duplex steel in industrial applications.
Applications in Marine Engineering
Duplex steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for moderate marine environments such as ship hulls and offshore platforms. Super duplex steel provides enhanced resistance to chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking, ideal for more aggressive conditions like subsea pipelines and chemical tankers. Both materials improve durability and reduce maintenance costs in marine engineering applications, with super duplex preferred for high-pressure and highly corrosive seawater exposure.
Cost Implications and Availability
Duplex steel offers a cost-effective solution with moderate resistance to corrosion and high strength, making it widely available and suitable for various industrial applications. Super duplex steel provides superior corrosion resistance and strength, particularly in harsh environments such as offshore oil and gas, but this enhanced performance comes at a significantly higher material and processing cost. Availability of super duplex steel can be limited due to its specialized production requirements and demand in niche markets, impacting lead times and overall project budgets.
Lifecycle and Maintenance Requirements
Duplex steel offers a balanced combination of strength and corrosion resistance with moderate lifecycle costs, making it suitable for less aggressive environments. Super duplex steel provides enhanced durability and superior resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, leading to extended lifecycle performance and reduced maintenance frequency in highly corrosive settings. The higher alloy content in super duplex results in increased upfront costs but significantly lowers long-term maintenance requirements and lifecycle expenses.
Choosing the Right Material for Marine Projects
Super Duplex Steel offers superior corrosion resistance and higher strength compared to Duplex Steel, making it ideal for harsh marine environments with exposure to chlorides and seawater. Duplex Steel may be suitable for less aggressive conditions, offering cost-effective performance while still providing good durability and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Selecting the right material depends on factors like water chemistry, temperature, and the specific structural demands of the marine project to ensure longevity and safety.
PREN (Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number)
Super Duplex Steel typically has a higher PREN (40-48) compared to Duplex Steel (28-38), indicating superior resistance to pitting corrosion in aggressive chloride environments.
Ferritic-austenitic microstructure
Duplex Steel features a balanced ferritic-austenitic microstructure with approximately 50% ferrite and 50% austenite for optimal strength and corrosion resistance, while Super Duplex Steel contains a higher ferrite content, typically 55-65%, enhancing its strength and resistance against chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking.
Corrosion fatigue resistance
Super Duplex Steel exhibits significantly higher corrosion fatigue resistance than Duplex Steel due to its enhanced microstructure and greater alloying elements like chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen.
Mo (Molybdenum) content
Super Duplex Steel contains approximately 3-5% Molybdenum, providing superior corrosion resistance compared to Duplex Steel, which typically contains about 2-3% Molybdenum.
S32205 (Duplex) alloy grading
S32205 Duplex Steel offers corrosion resistance and strength for moderate environments, while Super Duplex Steel grades provide enhanced performance with higher alloy content for superior resistance in aggressive conditions.
S32750/S32760 (Super Duplex)
Super Duplex Steel grades S32750 and S32760 offer superior corrosion resistance and higher tensile strength compared to Duplex Steel, making them ideal for aggressive environments in oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine applications.
Chloride stress corrosion cracking
Super Duplex Steel exhibits significantly higher resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking compared to Duplex Steel due to its enhanced microstructure and increased molybdenum and chromium content.
Yield strength differential
Super Duplex steel typically exhibits a yield strength approximately 20-30% higher than Duplex steel, making it more suitable for high-stress industrial applications.
Seawater piping applications
Super Duplex Steel offers superior corrosion resistance and strength compared to Duplex Steel, making it more suitable for seawater piping applications exposed to harsh marine environments.
Cathodic protection compatibility
Super Duplex Steel exhibits superior cathodic protection compatibility compared to Duplex Steel due to its higher corrosion resistance and enhanced resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in aggressive environments.
Duplex Steel vs Super Duplex Steel Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com