SolidWorks offers advanced simulation capabilities and extensive parametric modeling tools ideal for complex mechanical engineering projects, while Fusion 360 excels in cloud-based collaboration and integrated CAM features for streamlined manufacturing processes. SolidWorks' robust assembly management and detailed part design make it preferred for large-scale industrial applications, whereas Fusion 360 provides a more user-friendly interface and faster iteration cycles suited for startups and smaller teams. Choosing between the two depends on the project requirements, budget constraints, and whether seamless cloud integration or high-level mechanical fidelity is prioritized.
Table of Comparison
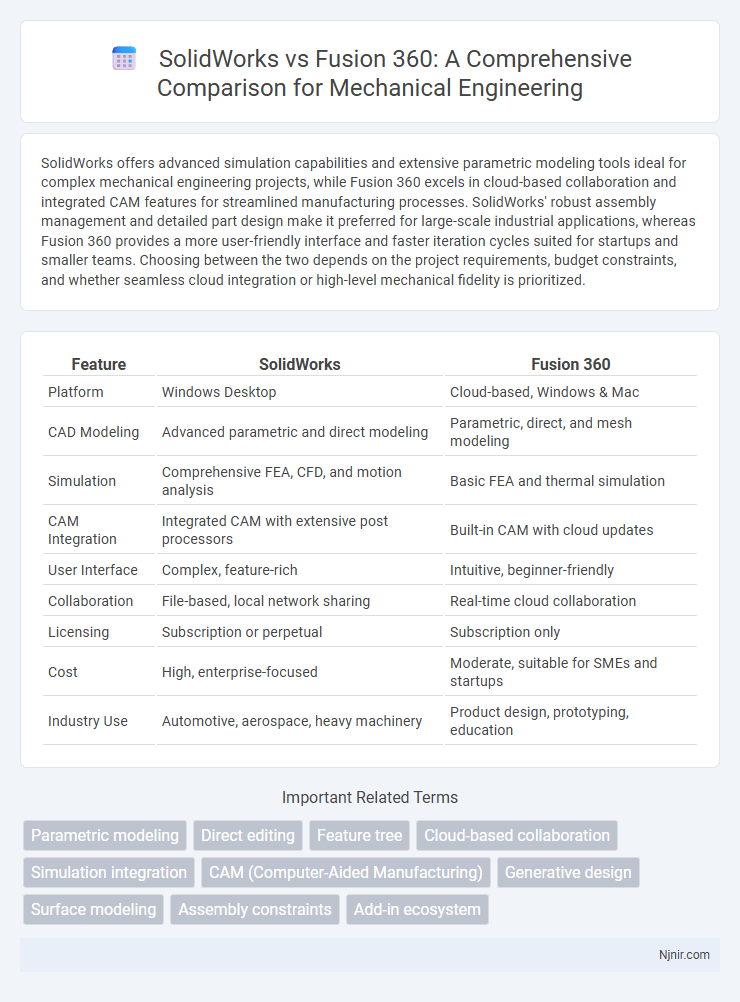
| Feature | SolidWorks | Fusion 360 |
|---|---|---|
| Platform | Windows Desktop | Cloud-based, Windows & Mac |
| CAD Modeling | Advanced parametric and direct modeling | Parametric, direct, and mesh modeling |
| Simulation | Comprehensive FEA, CFD, and motion analysis | Basic FEA and thermal simulation |
| CAM Integration | Integrated CAM with extensive post processors | Built-in CAM with cloud updates |
| User Interface | Complex, feature-rich | Intuitive, beginner-friendly |
| Collaboration | File-based, local network sharing | Real-time cloud collaboration |
| Licensing | Subscription or perpetual | Subscription only |
| Cost | High, enterprise-focused | Moderate, suitable for SMEs and startups |
| Industry Use | Automotive, aerospace, heavy machinery | Product design, prototyping, education |
Overview of SolidWorks and Fusion 360
SolidWorks is a comprehensive CAD software widely used for parametric 3D modeling, mechanical design, and engineering simulations, favored by professionals for its robustness in product design and manufacturing workflows. Fusion 360 combines CAD, CAM, and CAE capabilities in a cloud-based platform, offering integrated version control and real-time collaboration, making it ideal for iterative design and cross-functional teams. Both tools support advanced modeling and prototyping but differ in deployment: SolidWorks is primarily desktop-based, while Fusion 360 leverages cloud computing for accessibility and scalability.
User Interface and Ease of Use
SolidWorks offers a robust, feature-rich user interface tailored for professional engineers with extensive customization options, but it can have a steeper learning curve for beginners. Fusion 360 provides a more intuitive and streamlined UI that integrates CAD, CAM, and CAE tools, making it easier for new users and hobbyists to navigate and learn quickly. Both platforms support parametric modeling, but Fusion 360's cloud-based interface enhances collaboration and accessibility across devices.
Core Modeling Capabilities
SolidWorks offers advanced parametric modeling with robust feature-based design tools ideal for complex assemblies and detailed parts, supporting extensive customization and simulation integration. Fusion 360 emphasizes cloud-based collaborative modeling with direct and parametric workflows, combining CAD, CAM, and CAE in a single platform for streamlined product development. Both support 3D solid modeling and surface modeling, but Fusion 360 excels in real-time collaboration and version control, while SolidWorks provides deeper industry-specific toolsets.
Simulation and Analysis Tools
SolidWorks offers a comprehensive suite of advanced simulation and analysis tools, including structural, thermal, fluid flow, and motion analysis, leveraging its powerful FEA solver for detailed validation of complex designs. Fusion 360 integrates cloud-based simulation capabilities such as static stress, modal frequencies, thermal, and generative design analysis, allowing seamless collaboration and rapid iteration during product development. SolidWorks is preferred for high-fidelity, in-depth simulation workflows, while Fusion 360 excels in accessibility and real-time cloud-driven analysis for iterative design processes.
Collaboration and Cloud Features
SolidWorks primarily operates as a desktop application with limited cloud collaboration features, relying on local file management and traditional PDM (Product Data Management) systems for team workflows. Fusion 360, developed by Autodesk, is fundamentally cloud-based, enabling real-time collaboration, version control, and seamless access to design data across devices and locations. Its integrated cloud platform supports simultaneous multi-user editing, automatic updates, and cloud rendering, making it ideal for distributed engineering teams.
Supported File Formats and Interoperability
SolidWorks supports a wide range of file formats including native SLDPRT, SLDASM, and SLDDRW, as well as common industry standards like STEP, IGES, DXF, and DWG, enabling seamless integration with various CAD systems. Fusion 360 offers extensive interoperability by supporting formats such as F3D, STEP, IGES, STL, OBJ, and DWG, alongside cloud-based collaboration features that enhance multi-platform access and version control. Both platforms facilitate efficient data exchange, but Fusion 360's cloud-native environment provides superior real-time collaboration and cross-device flexibility compared to SolidWorks' traditionally desktop-centered approach.
Add-ons and Customization
SolidWorks offers an extensive range of add-ons like Simulation, CAM, and PDM, providing deep customization tailored for complex engineering workflows, while Fusion 360 integrates cloud-based extensions including generative design and advanced manufacturing tools, enabling seamless collaboration and real-time updates. SolidWorks' API supports robust custom scripting and third-party applications, making it ideal for specialized automation and bespoke tool creation. Fusion 360's modular architecture allows users to activate or deactivate features as needed, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency in versatile design environments.
Pricing and Licensing Models
SolidWorks offers a subscription-based licensing model with prices starting around $3,995 for a perpetual license plus annual maintenance fees, making it a significant upfront investment suited for long-term use in professional settings. Fusion 360 utilizes a flexible subscription model with affordable monthly, annual, and multi-year plans starting at approximately $495 per year, including cloud-based collaboration and regular updates. Fusion 360 also provides free licenses for students, educators, startups, and hobbyists, making it a cost-effective option for individuals and small businesses.
Industry Adoption and Community Support
SolidWorks boasts widespread adoption in traditional manufacturing sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial design, supported by a vast global user community and extensive third-party integrations. Fusion 360 is increasingly favored in startups, education, and small-to-medium enterprises for its cloud-based collaboration features and continuous updates, backed by an active online forum and Autodesk's broad ecosystem. Both platforms offer robust community resources, but SolidWorks' established presence lends it a stronger foothold in large-scale, legacy industries.
Best Use Cases for Mechanical Engineering
SolidWorks excels in complex mechanical engineering projects requiring advanced parametric modeling, detailed assemblies, and robust simulation capabilities, making it ideal for large-scale product design and manufacturing workflows. Fusion 360 offers cloud-based collaboration, integrated CAD/CAM workflows, and flexible modeling tools suited for rapid prototyping, iterative design, and small to mid-sized mechanical components development. Mechanical engineers select SolidWorks for detailed mechanical part design and extensive analysis, while Fusion 360 is preferred for innovation-driven projects needing seamless multi-user access and combined design-to-manufacturing solutions.
Parametric modeling
SolidWorks offers advanced parametric modeling with robust feature-based design and extensive control over constraints, while Fusion 360 provides cloud-based parametric modeling with integrated CAD, CAM, and CAE tools ideal for collaborative and iterative product development.
Direct editing
Fusion 360 excels in direct editing with its flexible history-free modeling, while SolidWorks offers powerful direct editing tools but primarily relies on history-based parametric modeling.
Feature tree
SolidWorks offers a robust and detailed feature tree ideal for complex assemblies, while Fusion 360 provides a streamlined, cloud-based feature tree designed for collaborative and iterative design workflows.
Cloud-based collaboration
Fusion 360 offers superior cloud-based collaboration with real-time multi-user access, version control, and seamless cross-platform integration compared to SolidWorks' primarily desktop-focused environment with limited cloud features.
Simulation integration
SolidWorks offers advanced, industry-standard simulation tools fully integrated for complex engineering analyses, while Fusion 360 provides cloud-based simulation features suitable for collaborative and iterative design workflows.
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
Fusion 360 offers more advanced and integrated CAM capabilities with cloud-based machining simulations, while SolidWorks CAM is best suited for users needing seamless CAD-CAM workflow within the SolidWorks environment.
Generative design
Fusion 360 offers advanced generative design capabilities with cloud-based AI optimization, while SolidWorks provides robust CAD tools but has limited native generative design features.
Surface modeling
Solidworks offers robust parametric surface modeling suitable for complex mechanical parts, while Fusion 360 provides versatile T-spline-based surface modeling optimized for organic and freeform designs.
Assembly constraints
SolidWorks offers advanced assembly constraints with extensive mate types and real-time collision detection, while Fusion 360 provides cloud-based collaboration and dynamic joint connections for flexible assembly modeling.
Add-in ecosystem
SolidWorks offers a robust and extensive add-in ecosystem with thousands of specialized plugins for advanced simulation, manufacturing, and design automation, while Fusion 360 provides a growing but more integrated cloud-based add-in ecosystem focused on collaborative CAD, CAM, and CAE tools.
Solidworks vs Fusion 360 Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com